Two-Port Networks: Analysis & Parameters
advertisement

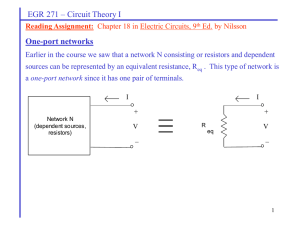
Two-port networks Review of one ports Various two-port descriptions Terminated nonlinear two-ports Impedance and admittance matrices of two-ports Other two-port parameter matrices The hybrid matrices The transmission matrices 1-port 2-port 2-port 2-port 1-port Thevenin’s Equivalent Circuit Norton’s Equivalent Circuit i N v i NO v eO C v ( t ) eO C ( t ) t h ( t , ) i ( ) d t0 0 For LTI network v ( t ) eO C ( t ) t h ( t ) i ( ) d 0 In frequency domain V ( s ) EOC ( s ) Z ( s ) I ( s ) 0 No independent sources t0 iD(t) + vd(t) vD(t) + VD Nonlinear one port - - vA=VA+va VA |va|p 0 va t 0 t iD(mA) 3.5 3 2.5 id 2 ID 1.5 Bias point t Q 1 0.5 VD 0 0.5 0.55 0.6 0.65 0.75 0.7 vd t vD(V) iD (mA) 1.52 1.50 1.48 1.46 id ID t 1.44 1.42 1.40 VD 1.38 0.699 0.6995 0.7005 0.7 0.701 vD (V) For small v d vd t ID ISe For DC bias V D / nV T For DC bias + small signal iD I S e ISe v D / nV T IS e (V D v d ) / nV T V D / nV T v d / nV T e IDe v d / nV T From Taylor’s series expansion e x 1 x x 2 2! x 3 3! ... 2 3 x x iD I D 1 x ... 2! 3! Where x v d / nVT For x 1 or v d nVT i D I D 1 x I D ID id nV T ID nV T vd vd rd vd id n VT I D + iD = ID+ id vD = VD+ vd vd - nV T rd ID id + rd iD(mA) 3.5 3 2.5 Slope at Q point = g d 2 Bias point ID 1.5 t Q 1 0.5 VD 0 0.5 0.55 0.6 0.65 0.75 0.7 t vD(V) 1 rd Example If V 10 V 10 m V sin(100 t ) find v D V V D 0 .7 V ID 10 kW iD rd vD vd 10 V 0 . 7 V 10 k W nV T ID rd rd 10 k W 0 . 93 mA 2 25 mV 53 . 8 W 0 . 93 mA 1 0 mV sin( 100 t ) 53 . 5 μV sin( 100 t ) v D 0 . 7 V 53 . 5 μ V sin( 100 t ) Two-port networks LTI one ports I1 + V1 - One port network Fig. 1 Zin Yin Input impedance Z in Input admittance V1 I1 Yin I1 V1 Two-port networks Example 1 Determine the input impedance of the circuit in Fig. 2 I1 I1 Z2 Fig. 2 Z3 Zin I in I 1 I 1 V in Z2 Vin (1 ) Z 2 I in Z in (1 ) Z 2 Example 2 Determine the output impedance of the circuit in Fig. 3 I1 I out + Z1 I1 Vout Fig. 3 Z3 Z out - I out I 1 I 1 (1 ) V out Z1 Z out V out I out Z1 1 Two-port networks Circuits can be considered by theirs terminal variables Voltages and currents are terminal’s variables Complex circuit can be analyzed more easily. There are many kinds of two port parameters. I1 + V1 - I2 Two port network Fig. 4 A two port network + V2 - Common-Emitter (CE) Fixed-Bias Configuration Removing DC effects of VCC and Capacitors Small signal equivalent circuit Hybrid equivalent model re equivalent model Various two-port descriptions i g (v) or i1 g 1 ( v1 , v 2 ) i2 g 2 ( v1 , v 2 ) Port current Port voltage v r (i) or v1 r1 ( i1 , i2 ) v 2 r2 ( i1 , i2 ) Or hybrid v1 h1 ( i1 , v 2 ) i2 h2 ( i1 , v 2 ) Two-port networks The Y parameter The admittance or Y parameter of a two port network is defined by I 1 y11 I 2 y 21 y12 V1 y 22 V 2 or in scalar form I 1 y11V1 y12V 2 I 2 y 21V1 y 22V 2 The Y parameter The Y parameters can found from y11 y 21 I1 V1 y12 V2 0 I2 V1 y 22 V2 0 I1 V2 V1 0 I2 V2 V1 0 These parameters are call short-circuited admittance parameters The Y parameter Example 3 Determine the admittance parameters from the circuit in Fig 5. I1 Y2 + V1 I2 Y1 Y3 0.5V1 - + V2 Fig 5. - I1 Y1V1 Y2 (V1 V 2 ) (Y1 Y2 )V1 Y2V 2 I 2 0.5V1 Y3V 2 Y2 (V 2 V1 ) (0.5 Y2 )V1 (Y2 Y3 )V 2 I 1 Y1 Y2 I 2 0.5 Y2 Y2 V1 Y2 Y3 V 2 y11 Y1 Y 2 , y12 Y 2 y 21 0.5 Y 2 , y 22 Y 2 Y3 The Y parameter Example 4 Compute the y-parameter of the circuit in Fig.6 1W I1 I2 Iˆ1 1:a + V1 - 1W + ˆ 1W V1 - + V2 - Fig.6 1 ˆ ˆ I 1 V1 (V1 V1 ) 2V1 V1 2V1 V 2 a 1 ˆ 1 1 2 I 2 I 1 Vˆ1 (V1 Vˆ1 ) V1 V2 2 a a a a 2 I1 I2 1 a 1 a V1 2 V 2 2 a y11 2 , y12 1 y 21 1 a a , y 22 2 a 2 Y parameter analysis of terminated two-port I1 + V1 - I2 + Two port network V2 YL - Fig. 9 Terminated two-port Y-parameter equations I 1 y11 I 2 y 21 I 1 y11 0 y 21 y12 V1 y 22 V 2 V1 Y L V 2 y12 y 22 I 2 Y LV 2 Y parameter analysis of terminated two-port From Crammer’s rules V1 The input admittance Yin I1 y 12 0 y 22 Y L y 11 y 12 y 21 y 22 Y L Yin y11 and y 21 y 22 YL y 11 ( y 22 Y L ) y 12 y 21 y12 y 21 y11 ( y 22 Y L ) y 2 1V1 ( y 2 2 Y L )V 2 V2 ( y 22 Y L ) I 1 V1 Y parameter analysis of terminated two-port y y I1 y11V1 y12V 2 y11 12 21 y 22 Y L V2 Gain: V1 Rs + y 21 y 22 Y L I1 + vs V1 V1 y11 I2 y 12V2 y 21V1 + y22 V2 - - - Yin Fig 10 Terminated two-port Y-parameter model YL Two-port networks The Z parameter The impedance or Z parameter of a two port network is defined by V1 z11 V 2 z 21 z12 I 1 z 22 I 2 or in scalar form V1 z11 I 1 z12 I 2 V 2 z 21 I 1 z 22 I 2 The Z parameter The Z parameters can be found from z11 z 21 V1 I1 z12 I2 0 V2 I1 z 22 I2 0 V1 I2 I1 0 V2 I2 I1 0 These parameters are call open circuit impedance parameters The Z parameter Example 6 Determine the impedance parameters from the circuit in Fig 11 3W I1 I2 + 4I 2 + + V1 0.1F V2 - - Fig 11. In frequency domain V1 4 I 2 V2 3 I 2 z1 1 Z z 21 10 s ( I1 I 2 ) 10 s 10 ( I1 I 2 ) 10 z1 2 s z 22 1 0 s s I 1 (4 10 10 s I 1 (3 s 4 s 10 s 3s 10 s )I2 10 s )I2 The Y parameter Example 7 Compute the z-parameter of the circuit in Fig.12 I1 R2 I2 + V1 R1 - R3 I3 + V2 Fig.12 - V1 R1 I1 R1 I 3 V 2 R3 I 2 R3 I 3 0 R1 I1 R3 I 2 ( R1 R 2 R3 ) I 3 I3 R1 R1 R 2 R 3 I1 R3 R1 R 2 R 3 I2 The Z parameter 2 V1 ( R1 V2 z 11 z 21 R1 R1 R 2 R 3 R1 ( R 2 R 3 ) R1 R 2 R 3 R1 R 3 R1 R 2 R 3 R1 R 3 R1 R 2 R 3 I1 ) I1 R1 R 3 R1 R 2 R 3 R1 R 3 I2 I2 R1 R 2 R 3 2 I1 ( R3 I1 R3 R1 R 2 R 3 R 3 ( R1 R 2 ) R1 R 2 R 3 R1 ( R 2 R 3 ) z 12 R1 R 2 R 3 R1 R 3 ) z 21 R R R 2 3 1 )I2 I2 R1 R 2 R 3 R 3 ( R1 R 2 ) R 1 R 2 R 3 R1 R 3 ) Z parameter analysis of terminated two-port I1 + V1 - I2 + Two port network V2 Z L - Fig. 14 Terminated two-port Z-parameter equations V1 z11 V 2 z 21 V1 z11 0 z 21 z12 I 1 z 22 I 2 I1 Z L I2 z12 z 22 V2 Z L I 2 Z parameter analysis of terminated two-port From Crammer’s rules I1 The input impedance Zin V1 z12 0 z 22 Z L z11 z12 z 21 z 22 Z L Z in z11 z12 z 21 z 22 Z L and z 21 I1 ( z 22 Z L ) I 2 I2 z 21 z 22 Z L I1 ( z 22 Z L )V1 z11 ( z 22 Z L ) z12 z 21 Z parameter analysis of terminated two-port z z V1 z11 I 1 z12 I 2 z11 12 21 z 22 Z L Z in V2 V V ZL z 21 1 2 Vs V s V1 Z in Z s z 22 Z L Z in Gain: Rs + ZL V1 - z 21 z 22 Z L Z in Z s I1 + vs I1 I2 z11 z 12 I 2 + + - - z22 z 21 I1 - Z in Fig 15 Terminated two-port Z-parameter model + V2 - ZL Z parameter analysis of terminated two-port Example 9 The circuit in Fig 16 is a two-stage transistor amplifier. The Z-parameters for each stage are I1 Vs + V1 - Z in Z1 1.0262 10 6 Z2 6 1.0258 10 I2 k 0.5W + - 2.667 6, 667 2 W 350 Z1 6 10 Stage 1 + V2 - Z in 2 Determine a) The input impedance Z in 2 and Z in b) The overall voltage gain 6, 790.8 6, 793.5 Z2 Stage 2 I out + Vout 16W - Fig 16 c) Check the matching of the load and output impedance Z parameter analysis of terminated two-port Solution Z in 2 z11 z12 z 21 z 22 Z L 6 1.0262 10 6790.8 1.0258 10 6793.5 16 3,159 W V out V2 ZL z 21 z 22 Z L Z in 2 6 16(1.0258 10 ) (16 6793.5)3,159 0.7629 6 Z parameter analysis of terminated two-port Z L1 2 k // Z in 2 2000 // 3159 1224 . 7 W Z in z11 z12 z 21 z 22 Z L 1 350 2.667 10 6 6667 1224.7 687.9 W V2 Vs Z L1 z 21 Z L 1 z 22 Z s Z in 1224.7 1224.7 6667 10 75 687.9 6 203.4 0.902 V2 Vs V1 V 2 V s V1 Z in 225.6 ZL z 21 Z in Z s z 22 Z L Z in ZL z 21 z 22 Z L Z in Z s Z parameter analysis of terminated two-port The overall voltage gain AVS V out Vs V out V 2 V2 Vs 0 . 7629 ( 203 . 4 ) 155 . 2 V / V Out put impedance Z out V2 I2 Vs 0 The detail is left to the student to show that Z out z 22 z12 z 21 R s z11 Z parameter analysis of terminated two-port Z out 1 z 22 z12 z 21 R s z11 6667 2.667 10 6 0.5 350 14.276 k W R s 2 Z out 1 // 2 k 1.7542 k W Z out 6793.5 6790.8 1.0258 10 6 1754.24 1.0262 10 6 16.93 W Therefore the load is closely matched to the output impedance The h-parameter (Hybrid parameter) H-parameter is the combination of Z and Y parameter defined by V1 h11 I 2 h21 h12 I 1 h22 V 2 or in scalar form V1 h11 I 1 h12V 2 I 2 h 21 I 1 h 22V 2 H-parameter is commonly used in transistor modeling. The h-parameter The h parameters can found from h1 1 h2 1 h2 2 h1 2 V1 I1 y 21 y 22 I1 0 y1 2 y1 1 z1 2 z 2 1 z 22 z 21 z 22 y1 2 y 2 1 y1 1 I1 0 V1 V2 z1 1 y1 1 V2 0 I2 V2 y1 1 V2 0 I2 I1 1 z1 2 z 22 1 z 22 The h-parameter Rs I1 h11 I2 + vs + V1 - - h 12V2 + h 21 I1 + - V2 h22 Z in Fig 17 Hybrid parameter model - ZL The h-parameter Example 10 Determine the h-parameter of the two-port circuit shown in Fig. 18 + + Fig. 18 R 1:a I1 V1 V1 2 I1 1 V2 - - V2 a a V 2 Vˆ2 Vˆ2 V 2 I2 R R R 1 a I 1 0V 2 + Vˆ2 - R I2 1 ˆ V1 V 2 a I1 aI 2 R ˆ V2 V2 R I 2 I1 V 2 a R V1 a 2 1 I 2 a 1 a I1 V 0 2 The h-parameter Example 10 Find the h-parameter of the circuit in Fig. 19 assuming L1=L2=M=1H I1 Iˆ1 V1 - 1W I2 + + Fig. 19 M 1W L1 Vˆ2 L2 - In frequency domain V1 sL 1 Iˆ1 sMI + V2 2 Iˆ1 I 1 V 1 (1 sL1 )V1 sM I 2 sL1 I 1 - The h-parameter V 2 Vˆ2 I 2 Vˆ2 sL 2 I 2 sM Iˆ1 sL 2 I 2 sM ( I 1 V1 ) V 2 (1 sL2 ) I 2 sM ( I1 V1 ) sM V1 (1 sL 2 ) I 2 sM I 1 V 2 In matrix form 1 sL 1 sM sM V1 sL 1 (1 sL 2 ) I 2 sM V1 1 sL1 I 2 sM sM (1 sL 2 ) 1 sL1 sM 0 I1 1 V 2 0 I1 1 V 2 The h-parameter With L1=L2=M=1 H V1 1 s I2 s s (1 s ) s 2 s 1 s 1 1 s s 0 I1 1 V 2 s I1 s 1 V 2 The inverse hybrid parameter (g- parameter) g-parameter is defined by I 1 g 11 V 2 g 21 g 12 V1 g 22 I 2 or in scalar form I 1 g 11V1 g 12 I 2 V 2 g 21V1 g 22 I 2 g-parameter is an alternative form of hybrid representation. The g parameters can found from g11 g 21 g 22 g12 I1 V1 V1 I2 0 V2 I2 z 21 z1 1 y 21 z 22 z1 2 z 2 1 z1 2 y1 2 V1 0 y1 2 y 2 1 z1 1 z1 1 y 22 w h ere h h1 1 h 2 2 h1 2 h 2 1 y 22 y 22 h h 1 h2 2 h2 1 y 22 V1 0 I1 I2 y1 1 z1 1 I2 0 V2 1 h1 2 h h1 1 h Inverse hybrid parameter model Conversion of Two-port parameters Two port parameters can be converted to any form as follows From And I 1 y11 I 2 y 21 y12 V1 y 22 V 2 I YV V1 z11 V 2 z 21 z12 I 1 z 22 I 2 V ZI V ZYV ZY 1 and Y Z 1 y11 y 21 z 22 y12 Z y 22 z 21 Z z12 Z z11 Z z11 z 21 y 22 z12 Y z 22 y 21 Y y12 Y y11 Y where Z z11 z 22 z12 z 21 Y y11 y 22 y12 y 21 Conversion of Two-port parameters From y to h I 1 y11 I 2 y 21 y12 V1 y 22 V 2 y11V1 I 1 y12V 2 y 21V 1 I 2 y 22V 2 y11 y 21 0 V1 1 1 I2 0 V1 y11 I 2 y 21 y12 I1 y 22 V 2 0 1 1 1 0 y12 I 1 y 22 V 2 Conversion of Two-port parameters y12 V1 1 1 y11 y 21 I2 Hence h11 h 21 h12 h22 y11 y 22 1 I1 y12 y 21 V 2 y12 y11 y11 y 21 y12 y 21 y11 y 22 y11 Conversion of Two-port parameters It can be shown that for the terminated two-port with h-parameter the following equations can be derived V2 Z in I1 V1 and AVS V2 Vs I1 h 22 Y L V1 Z out V2 h 21 V2 I2 h11 h12 h 21 h 22 Y L h22 h12 h21 h11 Z s h21 ( h22 Y L ) Z in V1 V 2 V s V1 h21 1 ( h22 Y L ) Z in Z s Transmission parameter The t-parameter or transmission parameters are used in power system and it is called ABCD parameter. The transmission parameter is defined by V1 t11 I 1 t 21 t12 V 2 t 22 I 2 or V1 A I1 C B V2 D I2 This means that the power flows into the input port and flow out to the load from the output port. t-parameter can be calculated from t11 t 21 V1 V2 t12 I2 0 I1 V2 t 22 I2 0 V1 I2 V2 0 I1 I2 V2 0 Open or short circuit at the output port Transmission parameter Example 11 Determine the t-parameter of the circuit shown in Fig 20. I1 + V1 - 1 ˆ 1 V1 V 2 (V 2 RI 2 ) a a I 1 aI 2 R 1:a + I2 + Vˆ2 V2 - - V1 1 a I1 0 Fig 20 V2 I a 2 R a Transmission parameter One of the most importance characteristics of the two-port circuit with t-parameter is to determine the overall cascade parameter. I2 + I1 + V1 - V1 V2 T1 I I 2 1 Therefore T1 V2 - + V3 - V 3 V4 T2 I I 4 3 V1 T1 T2 I1 I4 I3 V4 I 4 + T2 V4 - V 2 V3 , I2 I3 Inverse Transmission parameter V 2 A I 2 C A V2 V1 C B D I1 0 V2 I1 I1 0 I2 V1 B V1 D I1 V1 0 I2 I1 V1 0 Interconnection of two-port network Two port networks can be connected in series parallel or cascaded Series and parallel of two-port have 4 configurations Series input-series output (Z-parameter) Series input-parallel output (h-parameter) Parallel in put-series output (g or h-1-parameter) Parallel input-parallel output (Y-parameter) With proper choice of parameters the combined parameters can be added together. Interconnection of two-port network + + + V11 Z1 - + V21 + V11 H1 - - + V2 V1 V1 + V12 - - + + Z2 V22 - - + G1 - H2 - H=H1+H2 Z=Z1+Z2 + V12 + V21 + V2 + Y1 V2 V1 + G2 G=G1+G2 V21 - - - Y2 Y=Y1+Y2 - Example Bridge-T network N1 // N2 For network N2 For network N1 1 T 0 Z4 1 Y-parameters of the bridge-t network are