The Menstrual Cycle
advertisement

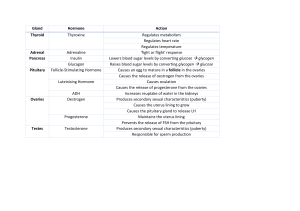
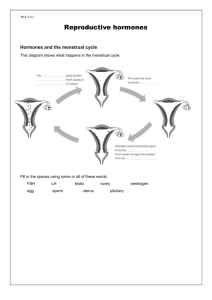
The Menstrual Cycle L.O: To know how hormones are used to control the menstrual cycle Complete this table Process Adrenalin increasing heart rate and sugar in the blood Type of response (nerve/hormone) Target organ Heart and liver Insulin controlling sugar Touching a hot tripod Testosterone in men Male reproductive organs Airzooka and blinking ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) kidneys Oestrogen Ovaries, uterus, pituitary gland What are hormones? The Endocrine System Hormones • Hormones are used to send information around the body • They work more slowly than nerves • They are secreted by glands (e.g. the pituitary gland • They travel in the blood • They go to all organs but usually only affect target organs e.g. ovaries and pancreas Why is the menstrual cycle important? • Matures the ovum for ovulation • Controls the release of the ovum (ovulation) • Thickens the uterus to receive an ovum • Maintains the lining of the uterus in pregnancy • Induces menstruation ‘a period’ if the ovum is not fertilized Endocrine glands pituitary gland The pituitary gland produces several specific hormones in females: follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) luteinizing hormone (LH) The ovaries produce oestrogen and progesterone The menstrual cycle – can we model this? Step 1: FSH produced by the pituitary gland causes both an egg to mature and the ovaries to start producing oestrogen Step 2: The rising levels of oestrogen cause the pituitary gland to stop producing FSH and produce LH instead Step 3: LH stimulates the release of the mature egg in the middle of the menstrual cycle 3 hormones are involved in the menstrual cycle: oestrogen, LH and FSH. Here’s how: 14/03/2016 Worksheet FSH • FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) • Secreted by the pituitary gland • Causes eggs to mature in the ovaries • Stimulates the ovaries to produce oestrogen Oestrogen • Secreted by the ovaries • Stimulates the lining to be made • Stops productions of FSH so no more eggs mature • Causes the release of LH which causes an ovum to be released (ovulation) Progesterone • A high level of Progesterone maintains the lining of the uterus • When the level of progesterone falls the uterus lining breaks down resulting in menstruation (a period) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Quick Quiz Give 2 differences between the way information travels by nerves and hormones Give 2 reasons the menstrual cycle is important Which hormone is responsible for maintaining the lining of the uterus? Which hormone causes the ovum to mature? Which hormone is associated with the release of an ovum (ovulation)? On which day is a woman most likely to get pregnant? • http://www.nelsonthornes.com/4u resources/resources/Biology/AQA/i nteractives/B1a1/Menstrual_cycle_animation/inter face.swf