Chapter8

Chapter 8. Impact of
Noise
Husheng Li
The University of Tennessee
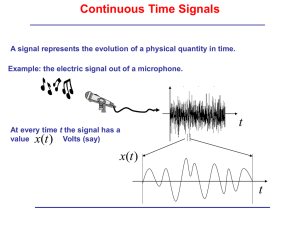
White Noise
When the noise spectrum is flat, we call it white noise.
The spectral density is given by
Filtered (Colored) Noise
When passed through a LTI filter with transfer function H(f), we have
Example: noise passed through RC network
Noise Equivalent Bandwidth
Average noise power:
Noise equivalent bandwidth:
What about the
RC circuit?
The filtered noise is
Illustration of Equivalent
Bandwidth
Bandpass Noise
Bandpass noise results when white noise passes through a bandpass filter.
SNR
The predetection signal-to-noise ratio is given by
We also define a system parameter (W is the low pass filter bandwidth)
Destination
SNR
Quadrature Components
The bandpass noise can be written as
The power spectral densities are identical lowpass functions related to G_n(f):
Impact on AM (Synchronous
Detection)
For DSB, the detected signal is given by
Then, the destination SNR is given by
Impact on AM (Synchronous
Detection)
For generic AM, we have
For SSB, we have
For VSB, we have
Summary
The message and noise are additive at the output if they are additive at the input.
If the predetection noise spectrum is reasonably flat over the transmission band, then the destination noise spectrum is essentially constant over the message band.
Relative to (S/N)_D, SSB has no particular advantage over DSB.
Making due allowance for the wasted power in unsuppressed-carrier systems, all types of linear modulation have the same performance as baseband transmission on the basis of average transmitted power and fixed noise density.
Envelop Detection
When envelop detector is used for the demodulation of AM, the noise can affect the amplitude.
Two Extreme Cases
When the SNR is high, we have
When the SNR is low, then the signal modulates the noise.
Threshold Effect
There is some value of SNR above which message corruption is negligible and below which system performance rapidly deteriorates.
We define the threshold level as that value of
SNR_R for which A_c>A_n with probability 0.99.
The threshold effect is usually not a serious limitation for AM broadcasting.
Angle Modulation with
Noise
Now (S/N)_R is often called carrier-to-noise ratio
(CNR).
The phasor construction shows
Noise Spectrum in PM and
FM
When the signal is 0, the noise is given by
PM FM
SNR Gain of PM and FM
Both PM and FM give SNR gains over the base band transmissions:
Threshold Effect in FM
When the system is operating near the threshold, small variations of received signal power cause sizable changes in the output signal --- one moment it is there and the next moment it is gone.
Comparison of Continuous
Waveform Modulations
Review for Final Exam
Nyquist criterion
Aliasing
Flat top sampling and aperture effect
PAM, PPM and PDM (how to generate them? How to recover the original signal?
What is the superhet principle? What are the frequency conversion procedure? How to determine the image frequency?
Specifications of frequencies
Tradeoff in spectrum analyzer
What types of multiple access schemes do we have? What are their major concerns?
Review
How to derive the dynamics of phase locked loop?
How to analyze the steady state of phase locked loop? Need to write down the details
What if there is no carrier in the signal (say, DSB) for phase locked loop?
What are the SNR properties of AM, FM and PM (just need to remember the qualitative conclusions)?
What happens to the noise when envelop detection is used for demodulating AM signals?
What are the noise spectrum shapes of FM and
PM?
Review