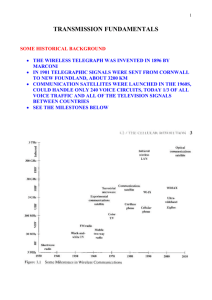
Optical Communication - Lecture Slides for Optical Communication
advertisement

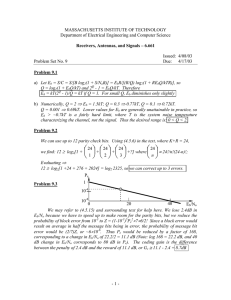
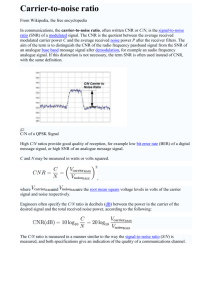
Information Capacity and Communication Systems By : Mr. Gaurav Verma Asst. Prof. ECE Dept. NIEC SHANNON’S LAW Shannon's law is any statement defining the theoretical maximum rate at which error free digits can be transmitted over a bandwidth limited channel in the presence of noise Shannon’s Theorem (Shannon’s Limit for Information Capacity) Claude Shannon at Bell Labs figured out how much information a channel could theoretically carry: Note that the log I = B log2 (1 + S/N) is base 2! Where I is Information Capacity in bits per second (bps) B is the channel bandwidth in Hz S/N is Signal-to-Noise ratio (SNR: unitless…don’t make into decibel: dB) 3 Signal-to-Noise Ratio S/N is normally measured in dB (decibel). It is a relationship between the signal we want versus the noise that we do not want, which is in the medium. It can be thought of as a fractional relationship (that is, before we take the logarithm): 1000W of signal power versus 20W of noise power is either: 1000/20=50 (unitless!) or: about 17 dB ==> 10 log10 1000/20 = 16.9897 dB 4 Example If the SNR is 20 dB, and the bandwidth available is 4 kHz, which is appropriate for telephone communications, then C = 4 log2(1 + 100) = 4 log2 (101) = 26.63 kbit/s. Note that the value of 100 is appropriate for an SNR of 20 dB. Example If it is required to transmit at 50 kbit/s, and a bandwidth of 1 MHz is used, then the minimum SNR required is given by 50 = 1000 log2(1+S/N) so S/N = 2C/W -1 = 0.035 corresponding to an SNR of -14.5 dB. This shows that it is possible to transmit using signals which are actually much weaker than the background noise level. Communication systems Digital Analog The block diagram on the top shows the blocks common to all communication 7 systems We recall the components of a communication system: Input transducer: The device that converts a physical signal from source to an electrical, mechanical or electromagnetic signal more suitable for communicating Transmitter: The device that sends the transduced signal Transmission channel: The physical medium on which the signal is carried Receiver: The device that recovers the transmitted signal from the channel Output transducer: The device that converts the received signal back into a useful quantity 8 9