Trends-Proficient
Periodic Trends
Ionization energy, atomic radius, ionic radius, electronegativity
By Oscar Trejo
Period 2
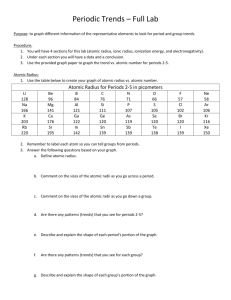
Ionization Energy (Periods)
As you go across the periodic table the ionization energy increases.
Boron has 800.6 and across from it nitrogen has an ionization energy of 1402.
Ionization Energy (Groups)
As you go down the periodic table the ionization energy decreases. Boron 800.6 to Thallium's
589.4.
Atomic Radius (Periods)
Atomic radius across the periodic table decreases. Gallium is
130 and across the period to Arsenic which has an atomic radius of 125.
Atomic Radius (Groups)
Atomic radius in the groups of the periodic table increase as they go down. Arsenic 125 increases to 143 in Bismuth.
Ionic Radius (Period)
As you go across the periodic table the ionic radius in a period increases.
The element nitrogen has an ionic radius of
25 to fluorine’s 133.
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
Ionic radius
Ionic Radius (Groups)
Arsenic
Bismuth
3-D
Column 3
The ionic radius in the periodic table tends to increase as you go down the families.
Arsenic has an ionic radius of 78, which increases to Bismuth’s
103.
Electronegativity (Periods)
Electronegativiy in the periodic table increase along the periods.
Gallium’s electronegativity is
1.81 it increases along the period to arsenic’s
2.2
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
0 gallium arsenic bromine
Electronegativity (Groups)
In the electronegativity of the periodic table, the groups decrease as you go down them.
Boron 2.04, gallium
1.81, thallium 1.62 as you can see elements electronegativity does decrease.
Density (Periods)
Density across the periodic table for the most part does decrease.
Boron has a density of 2.34, Nitrogen has a density of 1.25, while fluorine is 1.70.
10
5
0
Density
Nitrogen
Arsenic
Bismuth
Density (Groups)
Going down the element families the density increases as you go down them. Nitrogen 1.25,
Arsenic 5.73, Bismuth 9.75.
The Periodic Trends
Ionization energy in periods increases, but in groups decrease.
Atomic radius in periods decrease while in groups the radius in elements increases.
The same can be said for density.
Ionic radius in periods increases and the ionic radius decreases in groups.
Electronegativity increase in periods and decrease in groups.