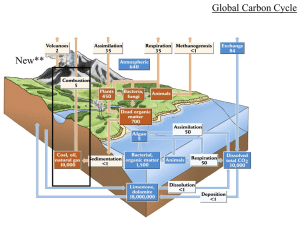
Chapter 11
Properties of Solutions
Section 11.4
The Vapor Pressures of Solutions
An Aqueous Solution and Pure Water in a Closed Environment
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
2
Section 11.4
The Vapor Pressures of Solutions
Liquid/Vapor Equilibrium
To play movie you must be in Slide Show Mode
PC Users: Please wait for content to load, then click to play
Mac Users: CLICK HERE
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
3
Section 11.4
The Vapor Pressures of Solutions
Vapor Pressure Lowering: Addition of a Solute
To play movie you must be in Slide Show Mode
PC Users: Please wait for content to load, then click to play
Mac Users: CLICK HERE
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
4
Section 11.4
The Vapor Pressures of Solutions
Vapor Pressures of Solutions
Nonvolatile solute lowers the vapor pressure of
solvent.
Raoult’s Law: Psoln = solv Psolv
Psoln
solv
Psolv
=
=
=
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
a
observed vapor pressure of solution
mole fraction of solvent
vapor pressure of pure solvent
5
Section 11.4
The Vapor Pressures of Solutions
A Solution Obeying Raoult’s Law
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
6
Section 11.4
The Vapor Pressures of Solutions
Nonideal Solutions
Liquid-liquid solutions where both components are
volatile.
Modified Raoult’s Law:
PTotal = APA + BPB
Nonideal solutions behave ideally as the mole fractions
approach 0 and 1.
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
7
Section 11.4
The Vapor Pressures of Solutions
Vapor Pressure for a Solution of Two Volatile Liquids
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
8
Section 11.4
The Vapor Pressures of Solutions
Summary of the Behavior of Various Types of Solutions
ΔT for Solution
Formation
Deviation
from
Raoult’s
Law
Example
Zero
Zero
None (ideal
solution)
Benzenetoluene
A A, B B < A B
Negative
(exothermic)
Positive
Negative
Acetonewater
A A, B B > A B
Positive
(endothermic)
Negative
Positive
Ethanolhexane
Interactive Forces Between
Solute (A) and Solvent (B)
Particles
ΔHsoln
A A, B B A B
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
9
Section 11.4
The Vapor Pressures of Solutions
CONCEPT CHECK!
For each of the following solutions, would you expect it
to be relatively ideal (with respect to Raoult’s Law),
show a positive deviation, or show a negative deviation?
a) Hexane (C6H14) and chloroform (CHCl3)
b) Ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) and water
c) Hexane (C6H14) and octane (C8H18)
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
10