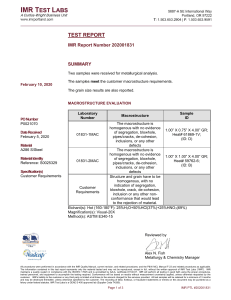
The Demographic Transition Model
advertisement
The Demographic Transition Model The Demographic Transition Model • generalization that depicts a countries development from a pre-industrial society to a post-industrial society and beyond • Describes changing levels of fertility and mortality as well as general levels of population growth • Based on known facts rather than general assumption The Demographic Transition Model As we go through, consider these questions: What countries might be in each stage? Where are the core, periphery and semi-periphery countries? Stage 1: High Stationary / Pre-Transition • High birth rate and high death rate • Two rates are nearly equal • Death rate fluctuating likely due to war and disease • Involves a low-income agricultural economy • Children are less of an expense and more of a commodity • Population growth is very slow • Population resides in rural areas • Countries? Core, periphery or semiperiphery? Stage 2: Expanding Stage / Early Transition • • • • Birth rate remains high Death rate begins to fall rapidly Results in population explosion Early industrialization paralleled with medical and health advances • Infant mortality declines, life expectancy increases • This stage characterizes nations in early development • Countries? Core, periphery or semi-periphery? Stage 3: Late Expanding Stage / Late Transition • Principle feature is a declining birth rate which is the result of voluntary decisions to reduce family size and the availability of contraceptives • Increased standards of living • Rate of Natural Increase is falling • The cost of children is increasing • Medical advancements continuing to decrease death rate • Population still increasing relatively quickly • Countries? Core, periphery or semi-periphery? Stage 4: Low Growth Stage / Post Transition • Birth rate remains slightly above the death rate • Rate of Natural Increase is low • Population growth is low and stable • Women entering workforce, couples postponing families while educational goals are sought • Population viewed as ‘greying’ or ‘aging’ • Canada would fall into this stage of the DTM • Countries? Core, periphery or semi-periphery? Stage 5: Deindustrialization / Declining • The population is declining • Characterizes countries with present and predicted negative population growth rates such as Russia and many European countries • Death rate begins to exceed the birth rate • Countries? Core, periphery or semi-periphery? Relationship to Population Pyramids • By analyzing population pyramids, one can decipher fairly accurately the stage of the demographic transition model that that particular country is in and vice versa • In combination with each other and if the model holds true, a countries future growth and development can be predicted • Shortcoming of the Demographic Transition Model: does not provide a bold hypothesis about future growth or decline Stage 1: Pre-Transition and Unstable Stage 2: Expanding / Early Transition Stage 3: Stable / Late Transition Stage 4: Stationary / Post-Transition Stage 5: Deindustrialization / Declining BR 10.68; DR 8.09; IMR 4.85; FR 1.59, LE 81.48; DT 89.3 BR 13.68; DR 8.39; IMR 5.98; FR 2.06, LE 78.48; DT 77.9 • BR 12.31; DR 7.17; IMR 15.62; FR 1.55, LE 74.84; DT 145.5 • BR 20.6; DR 7.43; IMR 67.14; FR 2.58, LE 67.14; DT 53.3 • BR 17.8; DR 6.3; IMR 26.99; FR 2.23, LE 71.62; DT 67.3 • BR 17.5; DR 6.4; IMR 20.5; FR 2.16, LE 71.62; DT 72.8 • BR 18.9; DR 5.0; IMR 16.77; FR 2.27, LE 76.66; DT 64.5 • BR 15.8; DR 2 IMR 11.59; FR 2.38, LE 76.71; DT 22.9 • BR 12.3; DR 6.9 IMR 4.55; FR 2.38, LE 81.9; DT 62.2 • BR 39.3; DR 2 IMR 14.6; FR 121.6, LE 49.7; DT 31.5 • BR 9.06; DR 9.93 IMR 3.4; FR 1.4, LE 81.9; DT 184.21