Introduction to Debt Market - Learning Financial Management
advertisement

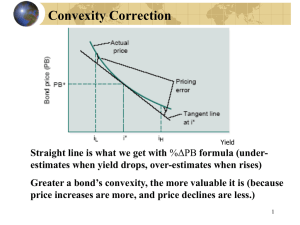
AGENDA Introduction of Debt Market Participants and products of debt market Few terms in Debt Market Types of Bonds Repo and Reverse Repo Duration in Bond Market Relation between YTM and Bond Price Introduction To Debt Market o Debt market : A market where fixed income securities are issued and trade o Share of debt market is much larger than equity market in US, i.e. is close to $31.4 trillion which is nearly equal to the total GDP of all countries taken together o Total size of Indian debt market is in the range of $92 billion to $100 billion i.e. approximately 30% of Indian GDP. o Debt market consists of three segments – Government security market – Public sector undertaking bond market(PSU) – Corporate security market o Govt. securities market accounts for more than 90% of the total turnover 3 Few terms in Debt Market o Maturity o Coupon rate o Principle o Yield to Maturity (YTM) o Current yield Debt Instruments & Features Contract between lender and the borrower Bonds Debentures Features Maturity Coupon Principal 5 Modifying Coupon Zero Coupon Bond Treasury Strips Floating Rate Bond Others 6 Cont. Term to Maturity Callable Bonds Puttable Bonds Convertible Bonds Principal Repayment Amortizing Bonds Bonds with sinking fund Provisions 7 Indian Debt Market Market Segments Government Securities PSU Bonds Corporate Securities Participants Government, RBI, PDs, PSUs, FI s, Corporates, Banks, Mutual funds, FII s, Provident Funds, Trusts. Secondary Market NSE-WDM only formal trading platform (NEAT) 8 Indian Debt Market Issuer Instrument Maturity Investors Central Government Dated Securities 2-20 Years RBI,Banks,Insurance Co., PFs, MFs, PDs, Central Government T-Bills 91/364 days RBI,Banks,Insurance Co., PFs, MFs, PDs,Individuals State Government Dated Securities 5-10 Years Banks,Insurance Co.,PFs. PSUs Bonds 5-10 Years Banks,Insurance Co., PFs, MFs, PDs,Individuals, Corporates Corporates Debentures 1-12 Years Banks, Mutual Funds, Corporates,Individuals Corporates, PDs Commercial paper 3 months to 1 Year Banks, Mutual Funds, FI s, Corporates,Individuals Banks Certificates of Deposit 3 months to 1 Year Banks, Corporates 9 Central Government Securities: Bonds Primary Issuance Process – Auction based Enable Higher Auction Volumes Broadening participation Ensuring efficiency Types of Auctions Discriminatory / Uniform Price Auction Yield / Price Based Auction Participants Banks, PFs, Insurance Co., PDs, MFs. 10 Cont.. Primary Dealers Introduced in 1995 and at present 19 Act as underwriters and market makers To Strengthen Infrastructure To divest responsibilities of RBI To facilitate Open Market Operations Eligibility 11 Cont. Satellite Dealers Second Tier in Trading and Distribution Provide a retail outlet 12 T - Bills Short Term borrowing Issued at discount 91 / 364 Days T – Bills Abolition of Ad Hoc T-Bills Issuance Process through Auction Banks and PDs Non Competitive Bids Calendar 91 days Weekly 250 Cr. Wednesday Thursday 364 days Fortnightly 750 Cr. Wednesday Thursday 13 Usually held till maturity 5.5% of total secondary market T-Bills Cut off Yields Yield given Price= ((100-Price)*365/(Price*No. of days to maturity) Price given Yield= 100/1+(yield%*(No.of days to maturity/365)) For Example: 14 A 182 day T-Bill auctioned on January 18 at a price of 95.510 would have an implicit yield of 9.4280% computed as follows: ((100-95.510)*365)/(95.510*182) State Government Bonds Represent market borrowimg to finance GFD Currenrly at 13% of GFD Averages about 12000 Cr. 84000 Cr. Outstanding Managed by RBI, States upto 35% Coupon fixed at 25 bps above Central Government 15 securities PDs allowed to particiapte SBI owns the largest chunk Low risk weight of 20% State Government Guaranteed Bonds Call Money Markets Short Term funds ranging from overnight funds to 14 days Banks and PDs allowed to borrow/lend UTI, FI s, MF s, Corporates allowed to lend Is around 32% of reserve requirements Call Rates Deposit mobilization of Banks, capital 16 flows,CRR on supply side Tax outflows, Government borrowing,Credit Off Take Corporate Debt: Bonds 17 Bonds issued by PSU, FI, and Corporates PSU bonds can be taxable or taxfree Issue Process Authority for the issue Appointment of Debenture Trustees Offer Document Creation of DRR Account Creation of charge Credit rating Listing Criteria on NSE WDM Form of Holding Corporate Debt: Bonds Issue management & Book building Managed by consortium of lead 18 manager, co-managers, underwriters and brokers. Investors indicate the amount at different coupon rates or the amount at cut-off coupon rate Oversubscribed Corporate Debt: Bonds 19 Terms of debenture Issue Face Value Price Credit rating Deemed date of allotment Applicable interest rate Interest on application money Interest payment Redemption Put/call option Letter of Allotment and Debenture Certificate Security Current Yield = Annual coupon pyt. Current price Capital Gains yield = Change in price Beginning price Exp. Exp. Cap. Exp. Total = YTM = Curr. Yld. + gains yld. Return 20 Find current yield and capital gains yield for a 9%, 10-year bond (F.V. Rs. 1000) when the bond sells for Rs.887 and YTM = 10.91%. Current yield 21 = Rs.90 Rs.887 = 0.1015 = 10.15%. Yield to Maturity The yield-to-maturity (YTM) is the measure of a bond’s rate of return that considers both the interest income and any capital gain or loss. 22 What is the YTM on a 10-year, 9% annual coupon, Rs.1,000 par value bond, selling for Rs.887? Must find the kd that solves this model: Bn INT INT B0 ... 1 n n (1 k d ) (1 k d ) (1 k d ) 90 90 1,000 Rs.887 ... 1 10 10 (1 k d ) (1 k d ) (1 k d ) YTM K d 10.91 23 YTM = Current yield + Capital Gains yield. Cap Gains yield = YTM - Current yield = 10.91% - 10.15% = 0.76%. 24 Coupon Rate, YTM, MP, and Par Value If MP = Par(Red.) Value, then YTM = Coupon Rate If MP > Par (Red.) Value, then YTM < Coupon Rate If MP < Par (Red.) Value, then YTM > Coupon Rate Thank You Neeraj Goyal Shreyance Jain Piyush Goel Priya Luthra Priyanka Chadha Pallavi Tripathi Sudhir Sharma Swati 26