Quantum no and orbitals
advertisement

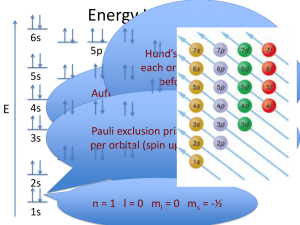
Quantum Numbers and Electron Configuration Hyperfine Spectral Lines http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/hyde.html In the hydrogen atom, you observe in an emission spectrum occur. What will you see? http://www.giangrandi.ch/optics/spectrum/visible-a.jpg 3 lines at exactly •656 nm, •434 nm, and •410 nm???? 1936 -- Neils Bohr and Arnold Summerfeld – found hyperfine lines made up the large principal spectral lines What does this mean? • The presence of hyperfine lines indicated that there are sublevels within each principal quantum level! Locating an electron • If there are multiple levels within each principal quantum level, how do we specify where (in a general sense) the electrons are? • How do we locate where YOU are? – How many pieces of information do we need? Quantum Numbers Preview • Four Quantum Numbers: – Principal Quantum # – Angular Momentum Quantum # – Magnetic Quantum # – Spin Quantum # Principal Quantum Numbers • Principal Quantum Number – Symbolized by n – Main energy level occupied by an electron – Values of n are positive 1, 2, 3, etc. – As n ↑ so does the energy Angular Momentum Quantum #s • Angular Momentum Quantum #s – Symbolized by l – Often referred to as sublevels – Indicates the shape of the orbital • Orbital: 3-D region around the nucleus that indicates the probable location of the electron – Values of l less than or equal to n-1 • Examples: – n=1, then l = 0 (one orbital shape) – n=2, then l = 1 and 0 (two orbital shapes) – n=3, then l = ? • Balloons as a visual aid l Letter Designation 0 s 1 p 2 d 3 f • What do s, p, d, and f actually stand for? – Free point for the first person who finds the naming scheme. – A second free point if you find the second naming scheme. Magnetic Quantum #s • Magnetic Quantum Number – Symbolized by m – Indicates the orientation of the orbital – For a given l, there are (2 l +1) integral values of m – from - l, (- l +1),. . . 0. . . (+ l -1), + l • Examples: – For the d orbital, l = 2 so m = -2, -1, 0, 1, 2 s orbitals Which one represents the highest energy level? Electron density plot The lowest? s Orbital shape Each s sublevel holds 2 electrons From Zumdahl, Chemistry 5th edition p orbitals Each p orbital holds: 2 electrons x 3 orientations = 6 total electrons in the p sublevel. d orbitals Each d orbital holds: 2 electrons x 5 orientations = 10 total electrons in the d sublevel. f orbitals Each f orbital holds: 2 electrons x 7 orientations = 14 total electrons in the f sublevel. Spin Quantum # • Spin Quantum # – Electrons are spinning on an internal axis which creates a magnetic field – There are 2 possible spins • +½ • -½ – How do magnets work? Back to the original question • How do we specify where (in a general sense) the electrons are? • Electron configuration: the arrangement of electrons in an atom. • Rules governing electron configuration – Aufbau Principle – Pauli Exclusion Principle – Hund’s Rule Aufbau Principle • Aufbau Principle: an electron will occupy the lowest-energy orbital that can receive it. http://chemed.chem.purdue.edu/genchem /topicreview/bp/ch6/graphics/6_22.gif Pauli Exclusion Principle • Pauli Exclusion Principle: no two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. – Example: For the electrons in He (ground state), what are: • the principal quantum number(s), • orbital type, and • Spin? Hund’s Rule • Hund’s Rule: orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin. – The school bus analogy • Example: – What are the spin quantum numbers for the electrons in the 2p orbital of oxygen? What is the electron arrangement for Nitrogen? 1. How many electrons does Nitrogen have? Principal Total e(2n2) Orbital (sublevel) Max # ein sublevel Total e- in sublevel Spin What is the electron arrangement for Nitrogen? 1. How many electrons does Nitrogen have? (7 e-) 2. Electrons in the first quantum level? Principal Total e(2n2) Orbital (sublevel) Max # ein sublevel Total e- in sublevel Spin What is the electron arrangement for Nitrogen? 1. How many electrons does Nitrogen have? (7 e-) 2. Electrons in the first quantum level? 3. Electrons in the second quantum level? Principal Total e(2n2) Orbital (sublevel) Max # ein sublevel Total e- in sublevel Spin 1 2 1s 2 2 +1/2, -1/2 What is the electron arrangement for Nitrogen? 1. How many electrons does Nitrogen have? (7 e-) 2. Electrons in the first quantum level? 3. Electrons in the second quantum level? Principal Total e(2n2) Orbital (sublevel) Max # ein sublevel Total e- in sublevel Spin 1 2 1s 2 2 +1/2, -1/2 2 8 1s 2 2 +1/2, -1/2 2p 6 3 +1/2, -1/2 Nitrogen: Nitrogen: Daily Questions 1. In what orbitals (sublevels) can you find electrons in the ground state of oxygen? 2. What are the quantum spin #s for the 2 outermost electrons in magnesium? 3. What are the quantum spin numbers for the electrons in the 3d orbital of titanium? 4. How many electrons are in the 2p orbital of neon? 5. Which principal energy level can hold 18 electrons? 6. Do the 2 electrons in the 3s orbital of calcium have the same or different spin quantum number? Why? Do the 2 electrons in the 2p orbital of carbon have the same or different spin quantum number? Notations for Electron Configuration • There are 3 ways to show electron configuration – Orbital Notation Model – Electron Configuration Model – Lewis Dot (Electron Dot) Notation Orbital Notation Model 1s 2s 2p or 1s 2s Closer to the nucleus What are the advantages and disadvantages of this notation? Each arrow represents a spinning electron 2p Further from the nucleus Each box represents an orbital Electron Configuration Notation 1s2 1s 2s # of electrons in the orbital 2p Angular momentum quantum # Principal Quantum # Another example: 1s22s22p3 1s 2s 2p What element is this? What are the advantages and disadvantages of this notation? The Ultimate Cheat-sheet What is the electron configuration notation for: Carbon? Potassium? Chromium? Neodymium? Daily Questions 1. Use the orbital notation model to represent the electron arrangement in fluorine. 2. What is the orbital notation for sodium? 3. Use the electron configuration notation to represent vanadium. 4. Use the electron configuration notation to represent iron. 5. What element has its 4 outermost electrons in the 3d orbital? A Short Cut • Noble Gas Configuration – Can shorten the notation by beginning with the last completed noble gas, then adding what is left: • For example: Mg – Long version: 1s22s22p63s23s2 – Short version: [Ne] 3s2 – Imagine the time you’ll save when you have to do Uranium. . . Lewis Dot (Electron Dot) • Only represents the outer-most s & p sublevel electrons (these are called valence electrons). • Represents the electrons as dots in pairs (or orbitals) around the element symbol. • Example: – Oxygen: O – Boron: B s d p f Daily Questions 1. Use the Noble Gas electron configuration notation to represent Titanium. 2. Use the Lewis Dot notation to represent Carbon. 3. Use the Lewis Dot notation to represent Fluorine. 4. Use the (Noble Gas) electron configuration notation to represent gold (Au). 5. Use the Noble Gas electron configuration notation to represent Neodymium (Nd). 6. Use the Lewis Dot notation to represent Selenium (Se).