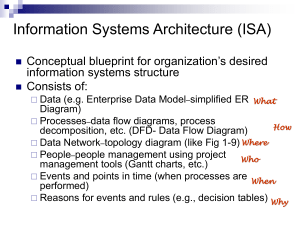
Electron Configuration
advertisement
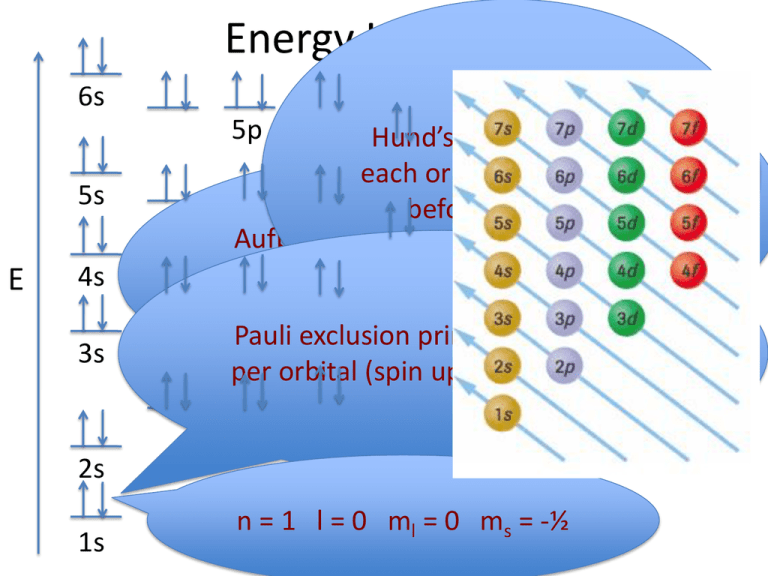
Energy Level Diagrams 6s 5p 5s E 4s 3s Hund’s rule – e- half-fill 4d eachPictorial orbital inrepresentation a sublevel of electron distribution before pairing up 4p Aufbau principle – e- occupy the in orbitals 3d lowest energy orbital available p. 188 in text 3p Pauli exclusion principle – max 2 eper orbital (spin up and spin down) 2p 2s 1s n = 1 l = 0 ml = 0 ms = -½ Orbitals Being Filled 1 Periods 1 1s 8 Groups 2 3 4 5 2 2s 2p 3 3s 3p 4 4s 3d 4p 5 5s 4d 5p 6 6s La 5d 6p 7 7s Ac 6d Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste, World of Chemistry 2002, page 345 6 7 1s 4f Lanthanide series 5f Actinide series Energy Level Diagrams 6s 5p 4d 5s E 4p 3d 4s 3p 3s 2p 2s 1s Anions - Add e- to lowest energy sublevel available. Energy Level Diagrams 6s 5p 4d 5s E 4p 3d 4s 3p 3s 2p 2s 1s Cations - Remove e- from sublevel with highest value of n. Energy Level Diagrams 6s 5p 4d 5s E 4p 3d 4s 3p 3s 2p 2s 1s Cations - Remove e- from sublevel with highest value of n. Energy Level Diagram of a Many-Electron Atom 6s 6p 5d 5s 5p 4d 4s 4p 3s 3p 2s 2p 3d Arbitrary Energy Scale 1s NUCLEUS O’Connor, Davis, MacNab, McClellan, CHEMISTRY Experiments and Principles 1982, page 177 4f 28 Orbital Diagrams for Nickel 1s 2 2s 2 6 2p 3s 2 6 3p 2 4s 3d Ni 58.6934 8 Excited State 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p6 4s1 3d 9 Pauli Exclusion 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d Hund’s Rule 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d Homework • p. 191 #3alt,4 • p. 197 #5 Electron Configuration • H 1s1 • Ca 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 • Pb 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d105p66s24f145d106p 2 • • • • • • Cl- 1s22s22p63s23p6 Fe2+ 1s22s22p63s23p63d6 Fe3+ 1s22s22p63s23p63d5 Ca [Ar]4s2 Shorthand: [noble gas] Cl[Ar] Fe2+ [Ar]3d6 Electron Filling in Periodic Table s s p 1 2 d 3 4 K 4s1 Ca 4s2 Sc 3d1 Ti 3d2 4f Energy n=4 n=3 V 3d3 Cr 3d54 Mn 3d5 Fe 3d6 Co 3d7 Ni 3d8 Cu 9 3d 3d10 Cr Cu 4s13d5 4s13d10 Zn 3d10 Ga 4p1 Ge 4p2 As 4p3 Se 4p4 Br 4p5 Kr 4p6 4d 4p 3d 4s 3p 3s Cr 4s13d5 4s 3d 2p n=2 2s n=1 Cu 1s 4s13d10 4s 3d Homework • p. 194 #6-11 • p. 197 #1,2,6-10,13 Anomalous e- Configurations Ferromagnetic – Fe, Co and Ni are smaller, closely packed atoms able to orient themselves in a magnetic field (group of these atoms oriented in the same direction – domain theory) , explains full magnetism Paramagnetism – substances exhibit a weak magnetic attraction believed to be caused by the presence of unpaired electrons Q: Which substances containing calcium, zinc, copper (II) and manganese(II) ions are paramagnetic? CaSO4(s) ZnSO4(s) CuSO4(s) MnSO4(s) Quantum Challenge The arrangement of elements in the periodic table is a direct consequence of the allowed values for the four quantum numbers. If the laws of physics allowed these numbers to have different values, the appearance of the periodic table would change. Suppose, in a different universe, the quantum number ml has the allowed values of ml = 0,1,…+l. All other allowed values are unchanged so the set of allowed values is: n = 1,2,3… l = 0,1,2…n-1 ml = 0,1…+l ms = ½,-½ Task: 1. Design the periodic table for the first 30 elements. 2. Label the s,p and d block elements. 3. Shade or colour the noble gas-like elements. Show your work!!