ppt格式
advertisement

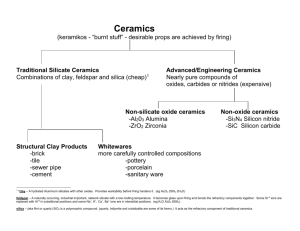
Ceramic Materials — Structures and Properties Ceramic Materials 陶瓷材料 • Inorganic materials 無機材料 • Nonmetallic materials 非金屬材料 • Most ceramics are compounds between metallic and nonmetallic elements • Composed of at least two elements, and often more • Atomic bonding in ceramics ranges from purely ionic to totally covalent ionic character 1 e Material CaF2 MgO NaCl Al2O3 SiO2 Si3N4 ZnS SiC X AXB 2 Ionic Character 89% 73% 67% 63% 51% 30% 18% 12% 2 Electronegativity 電負度、陰電性 Stable and unstable cation-anion coordination configuration - + - - stable - - + - - - - stable + - - unstable Cations are ordinarily smaller than anions cation 陽離子 anion 陰離子 Coordination Number 配位數 Coordination Number 配位數 2 3 4 6 Cation-Anion Radius Ration r<0.155 C/rA 0.155-0.225 0.225-0.414 0.414-0.732 8 0.732-1 rC/rA > 1 配位數12 Crystal Structures • AX Type – Rock Salt Structure 岩鹽結構 – Cesium Chloride Structure 氯化銫結構 – Zinc Blende (Sphalerite) Structure 閃鋅礦結 構 • AX2 Type – Fluorite Structure 螢石結構、氟石結構 • ABX3 Type – Perovskite Structure 鈣鈦礦結構 • AB2X4 Type – Spinel Structure 尖晶石結構 Rock Salt Structure 岩鹽結構 • NaCl, MgO, MnS, LiF, FeO rNa+ = 0.102 nm rCl = 0.181 nm rNa+/rCl = 0.564 Cesium Chloride Structure 氯化銫結構 • CsCl rCs+ = 0.170 nm rCl = 0.181 nm rCs+/rCl = 0.939 Zinc Blende Structure 閃鋅礦結構 • ZnS, ZnTe, SiC, ZnO rZn2+ = 0.074 nm rO2 = 0.140 nm rZn+2/rO2 = 0.529 Fluorite Structure 螢石結構 • CaF2, ZrO2, UO2, PuO2, ThO2 rCa2+ = 0.100 nm rF = 0.133 nm rCa+2/rF = 0.8 Perovskite Structure 鈣鈦礦結構 • BaTiO3, SrZrO3, SrSnO3 Interstitial position 填隙位置、間隙位置 • Tetrahedral position 四面體位置 • Octahedral position 八面體位置 close-packed structure 最密堆積結構、緊密堆積結構 Crystal structure • Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP) 六方最密堆積 A sites – ABAB... Stacking Sequence c B sites A sites a • Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) 面心立方 – ABCABC... Stacking Sequence A B C Determine Crystal Structures 1. Stoichiometry 化學計量 Charge Neutrality 2. Cation-anion radii ratios (coordination number) 3. Covalent character Ceramic Density Computation Number of formula units/unit cell n ( A C A A ) VC N A AC: atomic weight of cation AA: atomic weight of anion VC: Volume of unit cell NA: Avogadro’s number Silicate Ceramics 矽酸鹽陶瓷 Silica 矽石、二氧化矽 • Crystalline structure of Silica – Quartz 石英 – Cristobalite (Crystobalite) 白矽石、方矽石 – Tridymite 鱗石英、鱗矽石 • The strong Si-O bond leads to a strong, high melting temperature (1710C) Cristobalite (Crystobalite) 白矽石、方矽石 Silica Glass 矽石玻璃 • fused silica or vitreous silica 熔凝矽石或 玻化矽石 • B2O3 and GeO2 – Network former • CaO and Na2O – Network modifier • TiO2 and Al2O3 – Intermediate • Modifiers and Intermediates lowers the melting point and viscosity of a glass Crystalline silicon dioxide Noncrystalline silicon dioxide Silicate 矽酸鹽 Two-dimensional silicate sheet structure (Si2O5)2 Layered Silicates • Can change the counterions (相對離子) – this changes layer spacing – the layers also allow absorption of water • Mica 雲母 KAl3Si3O10(OH)2 • Bentonite 膨土、火山黏土 – – – – used to seal wells packaged dry swells 2-3 fold in H2O pump in to seal up well so no polluted ground water seeps in to contaminate the water supply Structure of kaolinite clay 高嶺黏土 Carbon 碳 • Diamond 鑽石 – metastable state 介穩態、準穩態 • Graphite 石墨 • Fullerene 芙、芙樂、富勒、芙樂烯、富勒烯 • C60 – Buckminsterfullerenes 巴克明斯特芙樂烯 – Buckyball 巴克球 Diamond cubic crystal structure Structure of Graphite Structure of a C60 Molecule Structure of a Carbon Nanotube Imperfections in Ceramic • Imperfection 缺陷 • Electroneutrality 電中性 • Atomic Point Defect – Vacancy 空位 – Interstitial 填隙、間隙 • Defect Structure – Frenkel defect 夫倫克耳缺陷 – Schottky defect 肖特基缺陷 • Stoichiometry or Nonstoichiometry Defect Structure Schottky defect Frenkel defect Impurities in Ceramics • Electroneutrality 電中性 • Solid solution 固溶體 – substitutional type – interstitial type Diffusion in Ionic Materials • Diffusion in ionic materials usually occurs by a vacancy mechanism • Electroneutrality 電中性 Ceramic Phase Diagrams MgO-Al2O3 Brittle Fracture of Ceramics • • • • • brittle fracture 脆性斷裂 plastic deformation 塑性形變 fractography 斷口形像學 crack 裂痕、裂紋、裂縫 branch or bifurcate 分叉 Stress-Strain Behavior • Stress 應力 • Strain 應變 • flexural strength 抗彎強度、抗撓強度、 撓曲強度 • modulus of rupture 破壞模數 • fracture strength 破裂強度 • bend strength 彎曲強度 Plastic Deformation • Crystalline ceramics • Noncrystalline ceramics – Viscosity 黏度、黏性