Intrinsic and ActiveX Controls
advertisement

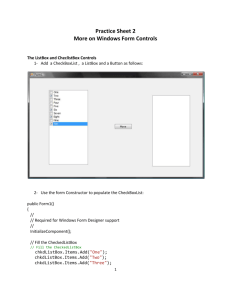
Working with Intrinsic Controls and ActiveX Controls Project 2 Introduction Intrinsic Controls – the basic set of twenty controls in the toolbox. Are a part of the .exe VB program. ActiveX Controls – exists as separate files. Files have a .ocx extension. Introduction cont………. Many routines and procedures are built into applications that are not designed for the end user. Creating the Interface Consists of sizing and locating the GUI and then adding the controls necessary for the user to use the form. Form Size and Position Height and Width property values can change the size of the form. Top and Left property values change the position of the form. AutoSize and BackStyle Properties AutoSize – when set to True, the size of the control (label) will depend on the size of the caption property. BackStyle – when set to Transparent, the color of the control below the label displays within the label’s border. Copying Controls You can copy and paste controls. A message will ask you if you want to create a control array. Click “NO” if you just want a copy of the control. We will work with control arrays later on. ListBox and ComboBox Controls Used to present the end user with choices from a list. When a list is longer than the list box, scroll bars automatically appear. ListBox and ComboBox Control Appearance of List Selection From List ListBox List always shows, Click item in list scroll bars added if list is longer than box. ComboBox(Style = 0) Drop-down list Click item in list or type directly in box. ComboBox(Style=1) List always shows, scroll bar added if list is longer than box. Click item in list or type directly in box. ComboBox(Style=2) Drop-down list Click item in list Shape Control Used to add shapes to the form Square Circle Rectangle CheckBox Control Used to turn controls on or off. Indicate the selection of deselection of check boxes on a form. Frame Control Used as a container for other controls, such as option buttons. A frame can only have a rectangle shape. A frame can have a caption. When option buttons are added to the frame, only one can be selected at a time. Option Button Control Presents a set of choices. Placed in groups, such as on a frame control. Must be drawn directly on the frame to be a part of the group. CommonDialog Control Allows you to add the Open, Save As, Color, Print and Font commands. Not visible during run time. Activate the CommonDialog control by using one of the Show methods. Aligning Controls Used to align controls in the form. Vertically Horizontally Format menu Naming Controls The name of a control is a property of a control. Helps the programmer know what control he/she is working with when writing code. Table 2-2 Writing Code Project 2 Changing Control Properties Basic Format controlname.property = value Variables Temporary storage locations. Each variable has a Name Type – determines the type of data the variable can hold. Data Variables cont……….. Must follow these rules when choosing names for variables. The name must begin with a letter. The name cannot be more than 255 characters. Then name cannot contain punctuation or blank spaces. Declaring Variables You must declare, or create, a variable. This will be done by Explicitly Declaring them. Dim variablename As datatype There can be a wide variety of different data types Byte, date, string, integer, variant, double Assigning values to a variable Variables can hold one value at a time. We use assignment statements to give variables a value. dblRate = 10.5 strName = “Mr. Preheim” Variable Scope Refers to whether or not the variable is visible to other sub routines. Variables declared in a sub routine are not visible by other sub routines in the program. Variables declared in the General Declarations are visible to all subroutines for that form. Arithmetic Expressions Code that contains statements to perform mathematical operations. Order of Precedence – the order in which the calculation will take place. Can change the order of precedence by using parentheses. Refer to table 2-7 Arithmetic Expression Examples dblPayRate = dblHours * curWage dblTotal = intNumber1 + 100 If..Then…Else Statements Used to execute one statement or another based on whether a condition is True or False. A condition is made up of a 2 expressions and a comparison operator. =, <, >, <=, >=, <> Key words in an If…Then…Else Statement If Then Else End If If Statement Structure If condition Then Block of code if the condition is True Else Block of code if the condition is False End If If Structure Flowchart Example F Price = 5 Is Matinee Check Box Checked T Price = 3.5 If Structure VB Code Example If chkMatinne.Value = 1 Then Price = 3.5 Else Price = 5 End IF Constants Similar to a variable in the idea that it uses space in memory. However, the value of a constant does not change. Defined by using the Const statement in the General Declarations. Concatenation The process of adding strings together is called concatenation. Performed by using the ampersand (&) character. Example: textRecord.Text = num & “ ” & cboShow.Text & vbNewLine & txtRecord.Text Items in a ComboBox When items are added to a ComboBox, they are assigned an Index number. The first item is assigned an index of 0. When an item is selected from the list during runtime, that index number is assigned to the ListIndex property. Writing Code for the Common Dialog Control To display the Color dialog box, you will apply the ShowColor method.


![[#EDS-26] Investigate diferentiating screen readers](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007260464_1-1f28ff9487a765c00f51111f692147a9-300x300.png)