- Peterson-Kaiser Health System Tracker
advertisement

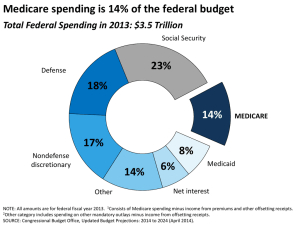
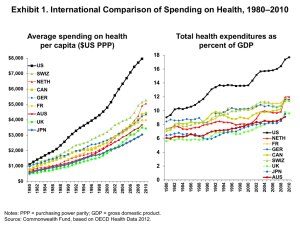
What is behind the recent slowdown in health spending? Peterson-Kaiser Health System Tracker U.S. health care spending per capita has risen at historically low rates in recent years Average annual growth rate of health spending per capita for 1970’s – 1990’s; Annual change in actual health spending 2000 – 2013 and projected (2014 – 2023) 14% 12% 10% Change in Spending Projected Change in Spending 12.0% 9.9% 8.6% 8% 7.4% 7.6% 6.2% 6.1% 6% 5.5% 5.8% 5.5% 5.3% 4.7% 4.7% 3.8% 4% 3.2% 3.4% 2.9% 3.1% 2.9% 3.7% 5.1% 5.5% 5.6% 5.3% 5.3% 5.2% 4.0% 2% 0% 1970's 1990's 2001 2003 2005 2007 2009 2011 2013 2015 2017 2019 2021 2023 Source: Kaiser Family Foundation analysis of National Health Expenditure (NHE) data from Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, Office of the Actuary, National Health Statistics Group Peterson-Kaiser Health System Tracker Health spending growth has slowed in the U.S. and in comparable countries Average annual growth rate in total health expenditures per capita, U.S. dollars, PPP adjusted Comparable country average 8% United States 7.4% 7% 6.1% 6% 5.3% 5.3% 5.8% 5.1% 5% 4.0% 4% 2.9% 3% 2% 1% 0% 1990's 2000-2004 2004-2008 2008-2012 Source: Kaiser Family Foundation analysis of 2013 OECD data: "OECD Health Data: Health expenditure and financing: Health expenditure indicators", OECD Health Statistics (database). doi: 10.1787/data-00349-en (Accessed on June 25, 2014). Notes: Data unavailable for: Australia and the Netherlands in 2012; France from 1981 through 1984 and 1986 through 1989; and Germany in 1991. OECD reports a break in series for: Belgium in 2003; Canada in 1975 ; France in 2003; and the Netherlands in 2005. Canada and Switzerland data are reported as estimated values for 2012. Peterson-Kaiser Health System Tracker Low growth rates have persisted for five years, sparking researchers to look for the causes Annual change in U.S. per capita health spending 2000 – 2013 10% 9% 8% 7% 6% 6.06% 5% 4% 3% 2.88% 2% 1% 0% 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 Source: Kaiser Family Foundation Analysis of National Health Expenditure (NHE) data from Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, Office of the Actuary, National Health Statistics Group Peterson-Kaiser Health System Tracker Exhibit 4 What types of structural changes in the health care system may be contributing to the slowdown? • Changes in insurance – Higher deductibles and cost sharing – Shifts from employer-sponsored coverage to lower-paying public coverage and in uninsurance • Changes in Medicare and Medicaid payment policies and limits on provider reimbursements • Slower diffusion of new medical technology, as examples: – Few new high-cost prescription drugs, combined with existing brands moving to generic status – Slowing use of advanced imaging and expensive heart procedures • Increased efficiency of health care providers Peterson-Kaiser Health System Tracker Medicare spending slowed for different reasons than private spending CBO projections of Mandatory outlays per Medicare beneficiary, predicted based on baseline year $16,000 2010 baseline 2014 baseline $14,913 per enrollee (based on 2010 projections) $15,000 $14,000 $13,000 $12,545 per enrollee (based on 2014 projections) $12,376 $12,000 $11,000 $11,328 $10,000 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 Source: Kaiser Family Foundation analysis of mandatory Medicare outlays and Medicare enrollment data from CBO Medicare baseline projections, 20102014: https://kaiserfamilyfoundation.files.wordpress.com/2014/07/medicare-spending-figure-1.png Notes: Grey lines represent 2011 – 2013 baseline projections. Peterson-Kaiser Health System Tracker An annual percentage point difference in growth rates makes a very large difference in spending over time Projected annual change in U.S. per capita health spending 2014 – 2023, alternative scenarios Projected NHE Per Capita Projected Plus 1 Percentage Point Projected Minus 1 Percentage Point $18,000 $16,430 $16,000 $14,944 $13,580 $14,000 $12,000 $10,000 $8,000 $6,000 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 Source: Kaiser Family Foundation analysis of National Health Expenditure (NHE) data from Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, Office of the Actuary, National Health Statistics Group Peterson-Kaiser Health System Tracker