–2010 Exhibit 1. International Comparison of Spending on Health, 1980
advertisement

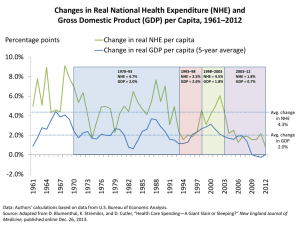
1 Exhibit 1. International Comparison of Spending on Health, 1980–2010 Average spending on health per capita ($US PPP) Total health expenditures as percent of GDP 18 $8,000 US $7,000 16 SWIZ NETH $6,000 14 CAN 12 GER FR 10 AUS UK 8 JPN US NETH FR GER CAN SWIZ UK JPN AUS Notes: PPP = purchasing power parity; GDP = gross domestic product. Source: Commonwealth Fund, based on OECD Health Data 2012. 2004 2002 2000 1998 1996 1994 1992 1990 1988 1986 1984 1982 2010 2008 2006 2004 2002 2000 1998 1996 1994 1992 1990 0 1988 $0 1986 2 1984 $1,000 1982 4 1980 $2,000 1980 6 2010 $3,000 2008 $4,000 2006 $5,000 Exhibit 2. Projected U.S. National Health Expenditures (NHE) by Source, 2013–2023 NHE in $ billions 6000 $5.5 trillion Federal government 5000 $4.0 trillion 32% State and local government 4000 $2.9 trillion 31% 28% 18% 3000 2000 18% 24% 18% 25% 1000 26% 26% 28% 26% 2013 2018 2023 17.9% 18.7% 20.5% 0 % GDP: Note: GDP = gross domestic product. Source: Estimates by Actuarial Research Corporation for The Commonwealth Fund. Private employers (including "other private revenue") Households Exhibit 3. Medicare Spending per Enrollee Projected to Increase More Slowly Than Private Insurance Spending per Enrollee and GDP per Capita Annual rate of growth (percent) 8.0 GDP per capita 7.0 6.0 Medicare spending per enrollee Employer-sponsored insurance spending per enrollee 5.0 3.7 4.0 3.0 4.6 4.5 3.8 2.9 2.7 2.0 1.0 0.0 2008–2011 2011–2021 (projected) Note: GDP = gross domestic product. Source: CMS Office of the Actuary, National Health Expenditure Projections, 2011–2021, updated June 2012. Exhibit 4. Rising Health Spending Crowds Out Other Priorities Massachusetts State Budget, FY 2001 vs. FY 2011 State spending ($ billions) FY2001 FY2011 $16 $14 $12 +$5.1 B (+59%) -$4.0 B (-20%) $10 -15% $8 $6 -13% $4 -23% $2 -38% -33% Public health Mental health -11% -50% $0 Health care coverage (state employees/GIC; Medicaid/health reform) Note: GIC = Group Insurance Commission. Source: Massachusetts Budget and Policy Center Budget Browser. Education Infra- Human struc- services ture/ housing Local aid Public safety Exhibit 5. Premiums Rising Faster Than Inflation and Wages Cumulative changes in insurance premiums and workers’ earnings, 1999–2012 Projected average family premium as a percentage of median family income, 2013–2021 Percent Percent 200 Health insurance premiums 175 180% Workers' contribution to premiums 150 Workers' earnings 125 Overall inflation 35 30 172% 25 22 23 20 100 15 12 13 75 50 25 47% 10 38% 5 15 17 18 18 18 18 19 24 26 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 20 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 0 0 Projected Sources: (left) Kaiser Family Foundation/Health Research and Educational Trust, Employer Health Benefits Annual Surveys, 1999– 2012; (right) author’s estimates based on CPS ASEC 2001–12, Kaiser/HRET 2001–12, CMS OACT 2012–21. Exhibit 6. Cumulative Impact of Comprehensive Strategy on Health Spending, 2013–2023: Medicare, Federal, and NHE Net impact in $ billions Medicare Federal NHE Provider payment reforms –$587 $788 –$1,333 Provide and support highvalue choices by consumers –$70 –$71 –$189 Make markets work better –$104 –$177 –$481 Cumulative impact –$761 –$1,036 –$2,004 Note: NHE = national health expenditures. Components may not add to total because of rounding. Source: Estimates by Actuarial Research Corporation for The Commonwealth Fund. Exhibit 7. Cumulative Impact of Comprehensive Strategy on Health Spending, 2013–2023, by Payer Net impact in billions Federal Total NHE government 2013–2023 –$2,004 –$1,036 State and local government Private employers Households –$242 –$189 –$537 Note: NHE = national health expenditures. Components may not add to total because of rounding. Source: Estimates by Actuarial Research Corporation for The Commonwealth Fund. Exhibit 8. Projected National Health Expenditures (NHE), 2013–2023: Potential Impact of Synergistic Strategy NHE in $ trillions $6.0 Current baseline NHE projection $5.5 Projected NHE net of policy impacts $5.0 $5.1 $4.0 $2.9 $3.0 $2.0 $1.0 NHE as percentage of GDP— Current projection: 18% in 2013→21% in 2023 Under unified strategy: 18% in 2013→19% in 2023 Cumulative NHE savings under synergistic strategy: $2.0 trillion $0.0 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 Note: GDP = gross domestic product. Source: Estimates by Actuarial Research Corporation for The Commonwealth Fund. Current baseline projection assumes that the cuts to Medicare physician fees under the sustainable growth rate (SGR) formula are repealed and basic physician fees are instead increased by 1% in 2013 and held constant from 2014 through 2023.