Slides - Projects In Knowledge
advertisement
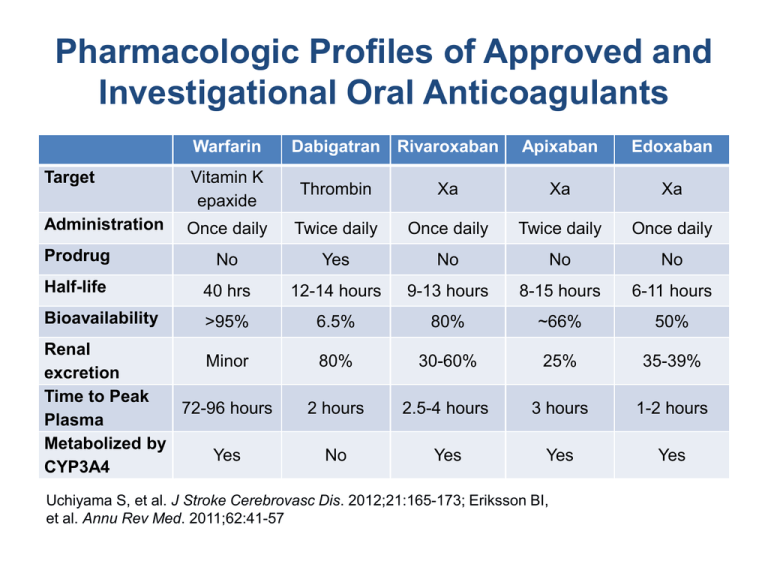
Pharmacologic Profiles of Approved and Investigational Oral Anticoagulants Warfarin Dabigatran Rivaroxaban Apixaban Edoxaban Target Vitamin K epaxide Thrombin Xa Xa Xa Administration Once daily Twice daily Once daily Twice daily Once daily Prodrug No Yes No No No Half-life 40 hrs 12-14 hours 9-13 hours 8-15 hours 6-11 hours Bioavailability >95% 6.5% 80% ~66% 50% 80% 30-60% 25% 35-39% 2 hours 2.5-4 hours 3 hours 1-2 hours No Yes Yes Yes Renal Minor excretion Time to Peak 72-96 hours Plasma Metabolized by Yes CYP3A4 Uchiyama S, et al. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012;21:165-173; Eriksson BI, et al. Annu Rev Med. 2011;62:41-57 Dosing Recommendations of FDA Approved New Oral Anticoagulants by Degree of Renal Function CrCl Dosing Recommendations > 30 mL/min 150 mg BID 15-30 mL/min 75 mg BID > 50 mL/min 20 mg/day* 15-50 mL/min 15 mg/day* Dabigatran Rivaroxaban *With evening meal Abbreviations: BID, twice daily; CrCl, creatinine clearance Pradaxa® (dabigatran etexilate mesylate) [package insert]. Ridgefield, CT: Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2012. Xarelto® (rivaroxaban) [package insert]. Raritan, NJ: Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2012. RE-LY Randomized Evaluation of Long-Term Anticoagulation Therapy • Study Design: PROBE (N = 18,113) • Primary Efficacy: All stroke or systemic embolism • Primary Safety: Major bleeding • Mean Follow-up: 2 years • Inclusion: NVAF and ≥ 1 risk factor* • Exclusion for Renal Impairment: CrCl < 30 mL/min • Mean CHADS2 Score: 2.1 – CHADS2 score of ≥3: 33% • Mean TTR: 64% Warfarin Dabigatran 150 mg BID Event Rate Event Rate (%/y) (%/y) RR (95% CI)† P Value Efficacy Stroke or Systemic Embolism 1.7% 1.1% 0.66 (0.53–0.82) <.001‡ Hemorrhagic Stroke 0.38% 0.10% 0.26 (0.14–0.49) <.001 3.4% 3.1% 0.93 (0.81–1.07) .31 0.74% 0.30% 0.40 (0.27–0.60) <.001 Safety Major Bleeding Intracranial Bleeding *Risk factors: prior stroke/TIA; LVEF < 40%; NYHA Class ≥ II; aged ≥ 75 years, or aged 65-74 years with DM, HTN, or CAD †vs dose-adjusted warfarin; ‡for both inferiority and superiority Abbreviations: BID, twice daily; CI, confidence interval; CAD, coronary artery disease; CHADS 2, congestive heart failure, hypertension, age, diabetes, prior stroke; DM, diabetes mellitus; CrCl, creatinine clearance; DM, diabetes mellitus; HTN, hypertension; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; NVAF, nonvalvular atrial fibrillation; NYHA = New York Heart Association; PROBE, prospective, randomized, open-blinded, end-point evaluation; RR, relative risk; TIA, transient ischemic attack; TTR, time in therapeutic range Connolly SJ, et al. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1139-1151 ROCKET-AF Rivaroxaban Once Daily Oral Direct Factor Xa Inhibition Compared With Vitamin K Antagonism for Prevention of Stroke and Embolism in Atrial Fibrillation • Study Design: Randomized, double-blind, double-dummy (N = 14,264) • Primary Efficacy: Composite of all stroke and systemic embolism • Primary Safety: Composite of major and nonmajor clinically-relevant bleeding events • Mean Follow-up: 1.9 years • Inclusion: NVAF and prior stroke/TIA or ≥ 2 risk factors* • Exclusion for Renal Impairment: CrCl < 30 mL/min • Mean CHADS2 Score: 3.5 – CHADS2 score of ≥3: 87% • Mean TTR: 55% Warfarin Rivaroxaban 20 mg/day Event Event Rate Rate (%/y) (%/y) HR (95% CI)† P Value Efficacy: Stroke & Systemic Embolism Per Protocol Analysis 2.2% 1.7% 0.79 (0.66–0.96) <.001‡ By ITT 2.4% 2.1% 0.88 (0.74–1.03) <.001‡ .12§ Major & Non-major Bleeding 14.5% 14.9% 1.03 (0.96–1.11) .44 Intracranial Bleeding 0.7% 0.5% 0.67 (0.47–0.93) .02 Safety *Risk factors: HF or LVEF ≤ 35%, HTN, aged ≥ 75 years, or DM (i.e., a CHADS2 score ≥ 2, on a scale ranging from 1 to 6, with higher scores indicating a greater risk of stroke). †vs dose-adjusted warfarin; ‡for noninferiority; §for superiority Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; CHADS2, congestive heart failure, hypertension, age, diabetes, prior stroke; CrCl, creatinine clearance; DM, diabetes mellitus; HR, hazard ratio; HTN, hypertension; ITT, intent-to-treat; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; NVAF, nonvalvular atrial fibrillation; TIA, transient ischemic attack; TTR, time in therapeutic range Patel MR, et al. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:883-891. ARISTOTLE Apixaban for Reduction in Stroke and Other Thromboembolic Events in AF • Study Design: Randomized, double-blind, double-dummy (N = 18,201) • Primary Efficacy: All stroke or systemic embolism • Primary Safety: Major bleeding (ISTH criteria) • Mean Follow-up: 1.8 years • Inclusion: NVAF and ≥ 1 risk factor* • Exclusion for Renal Impairment: CrCl < 25 mL/min • Mean CHADS2 Score: 2.1 – CHADS2 score of ≥3: 30% • Mean TTR: 62% Warfarin Apixaban 5 mg BID Event Event Rate Rate (%/y) (%/y) HR (95% CI)† P Value Efficacy Stroke or Systemic Embolism 1.6% 1.3% 0.79 (0.66–0.95) <.001‡ .01§ Hemorrhagic Stroke 0.47% 0.24% 0.51 (0.35–0.75) <.001 3.1% 2.1% 0.69 (0.60–0.80) <.001 0.8% 0.3% 0.42 (0.30–0.58) <.001 Safety Major Bleeding Intracranial Bleeding *Risk factors: aged ≥ 75 years; prior stroke/TIA; symptomatic HF or LVEF ≤ 40%; DM; HTN (ontreatment); †vs dose-adjusted warfarin; ‡for noninferiority; §for superiority Abbreviations: BID, twice daily; CI, confidence interval; CHADS2, congestive heart failure, hypertension, age, diabetes, prior stroke; CrCl, creatinine clearance; DM, diabetes mellitus; HR, hazard ratio; HTN, hypertension; ISTH, International Society of Thrombosis and Haematosis; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; NVAF, nonvalvular atrial fibrillation; TIA, transient ischemic attack; TTR, time in therapeutic range Granger CB, et al. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:981-992.