Nasla Polyps-ENT
advertisement

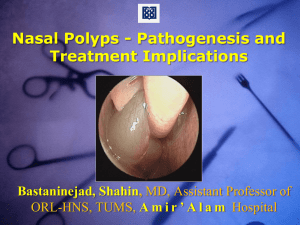
Nasal Polypi Definition non neoplastic edematous nasal or sinus mucosa. Nasal polyps are abnormal lesions that originate from any portion of the nasal mucosa or paranasal sinuses. Polyps are an end result of varying disease processes in the nasal cavities. malignant tumours. Introduction Nasal polyps are abnormal lesions that originate from any portion of the nasal mucosa or paranasal sinuses. Polyps are an end result of varying disease processes in the nasal cavities. Benign polyps. Other benign or malignant tumours. Classification: 1/ Bilateral Ethmoidal polyps 2/ Antrochoanal Polyps 3/ Neoplastic Pathology: Histologically, nasal polyps are characterized by a pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium, thickening of the epithelial basement membrane, and few nerve endings. The stroma of nasal polyps is edematous. Eosinophil cells are the most commonly identified inflammatory cell, occurring in 8090% of polyps. Neutrophils in 7% of polyps Multiple polyps can occur in children with chronic sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, cystic fibrosis (CF), or allergic fungal sinusitis (AFS). An individual polyp could be an antral-choanal polyp, a benign massive polyp, or any benign or malignant tumor (eg, encephaloceles, gliomas, hemangiomas, papillomas, juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas, rhabdomyosarcoma, lymphoma, neuroblastoma, sarcoma, chordoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, inverting papilloma). Evaluate all children with benign multiple nasal polyposis for CF and asthma. • Next Section: Pathophysiology • Ethmoidal polyps arise from Middle meatus • Insensitive to touch • blood supply is poor.(Pale colour) • When unilateral Exclude malignancy. Causes As described in Pathophysiology, chronic inflammation (from whatever source) apparently has an initial role in the pathogenesis of nasal polyps. Multiple polyps occur in children with chronic sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, CF, and AFS. An isolated polyp could be an antralchoanal polyp , a benign massive polyp, a nasolacrimal duct cyst or any congenital lesion or benign or malignant tumor . Simple polyps can arise any time after age 2yrs, before this suspect meningocele,encephalocoel.(do ct. scan) Before age 10 yrs. rare if found suspect cystic fibrosis,(do sweat test Frequency Adults 1-4% Children 0.1% All races and social classes M/F 2-4:1 in adults Increasing incidence with age Associated with allergic conditions 20-50% have asthma Allergic rhinitis 8-26% have aspirin intolerance 50% have alcohol intolerance Various theories Bernstein theory Vasomotor theory Epithelia rupture theory Bernstein theory Inflammatory changes in lateral nasal wall or sinus mucosa Polyps originate from contact area Ulceration, reepithelialisation and new gland formation Inflammatory processes from epithelial cells, endothelium and fibroblasts Integrity of sodium channels affected Clinical Presentation Airway obstruction Postnasal drip Dull headaches Snoring Rhinorhoea Hyposmia / Anosmia Epistaxis (often other lesion) Obstructive sleep apnoea Coronal CT scan MRI scan Flexible nasendoscopy Rigid nasendoscopy Coronal CT scan through anterior sinuses. Opacification of left maxillary sinus, opacification of inferior half of nasal cavity. Due to antro coanal polyp. Antrochoanal Polyp;arise from maxillary sinus. 3 parts channel,nasal, antrum. end result of prolong sinus infection unilateral differential diagnosis, 1/ hypertrophied middle turbinate, probe test, 2/ Angiofibroma other neoplasm, fleshy appearance.fiable tissue and bleed easily. e.g. squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma Fiber optic Nasophyrangoscopy. Coronal CT scan MRI scan 20 Investigations Sweat test.(Cystic fibrosis) RAST(radioallergosorbent test/ skin testing Nasal smear Microbiology Eosinophils (allergic component) Neutrophils (chronic sinusitis) Clinical Presentation Airway obstruction Postnasal drip Dull headaches Snoring Rhinorhoea Hyposmia / Anosmia Epistaxis (often other lesion) Obstructive sleep apnoea Management: Conservative : Oral steroid. Prednisolon 30mg for 3 days,20mg for 3 days,10mg for 3 days. Surgery 1/ simple polypctomy 2/ Nasal polytectomy (With debrider and FESS. Endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) is a better technique that not only removes the polyps but also opens the clefts in the middle meatus, where they most often form, which helps decrease the recurrence rate. Nasal Polypectomy Microdebrider entering left middle meatus Summary Common condition in adults Aetiology not fully understood Majority are not allergic in nature Medical treatment can be effective Even with surgery, recurrence is common Thank You Questions: 10 yrs. old boy with nasal polyps, the child suffers from recurrent lung infections with thick, sticky sputum and his skin tastes salty. whats your diagnosis Name one test to confirm your diagnosis. Question 2: A 40yrs male suffer from unilateral Nasal obstruction,and symptoms of sinusitis.Anterior rhinoscopy reveals nasal Polyp. 1/ what radiological investigation you will request.explain why. 2/ treatment option 3/ would you send specimen for histology ,explain why.