Nasal Polyp
advertisement

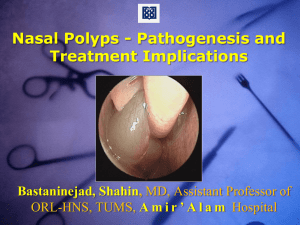
TOPIC – NASAL POLYP CONTENTS • • • • • • • • • • DEFINITION CAUSES SIGN AND SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT COMPLICATION HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICINES MANAGEMENT CASE BIBLIOGRAPHY DEFINATION• Nasal Polyp are the most common benign growths in the nasal cavity. CAUSES • Nasal Polyps are more common in adults than in children. Polyps are seen with greater frequency in people with asthma, allergic rhinitis (hay fever), vasomotor rhinitis (may be caused by emotional upset or sexual arousal), and certain kinds of drug use, chronic sinus infections, and cystic fibrosis. They can be a sensitivity reaction to aspirin. About one out of four people with cystic fibrosis has nasal polyps. Frequently, no specific cause can be found. Signs & Symptoms • Usually in both sides of the nose, polyps are essentially outgrowths of the nasal mucosa. The polyps are smooth, gelatinous, semi-translucent, pear-shaped, and pink to white in color. The polyps originate near the ethmoid sinuses (located at the top of the nose on both sides of the nasal cavity) and grow into the open areas of the nasal cavity. They sometimes grow large and numerous enough to cause nasal obstruction. Diagnosis • Nasal Polyps can occasionally be seen on exam with a nasal speculum. Sometimes they can only be seen with special equipment. Since polyps are devoid of sensation, they can be distinguished from other swollen tissues by a lack of pain on probing. The clinical features of nasal polyps include nasal congestion (100%), loss of smell and/or taste (75%), sneezing and runny nose (60%), post-nasal drip (65%), facial pain (35%), and itchy eyes (25%). Treatment • MEDICINAL TREATMENT Conventional medical treatment with a nasal steroid spray and/or a short course of oral corticosteroids is usually effective, shrinking or eliminating the polyps. Surgery to remove the polyps and infected material is recommended if the medical treatment is not successful. The problem with these approaches is that they are not addressing the cause. The best form of treatment would be to find out what the patient is allergic to and try to eliminate it. This does not only mean what can be inhaled, it can also be an allergy to food substances as well. Complete allergy testing for inhaled substances and foods should be carried out. Electric acupuncture has also shown some positive results in the treatment of nasal polyps. • SURGICAL TREATMENT - POLYPECTOMY Complications • A single, small nasal polyp rarely causes complications, but a large polyp or many smaller polyps (polyposis) may lead to the following: • Acute or chronic sinus infections. • Obstructive sleep apnea — a potentially serious condition in which you stop and start breathing a number of times during sleep. • Altered facial structure leading to double vision or unusually wide-set eyes. This complication is rare and is most likely to occur in people with cystic fibrosis. HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICINES • • • • • • • • • • • • • • TUBERCULINUM BARYTA CARB ALLUMINA CALC. PHOS CONIUM CALC. FLOUR SILICEA PHOSPHORUS TEUCRIUM MARUM LACHESIS CALC. IOD SANGUNERIA LEMNA MINOR KALI BICHROME HOMOEOPATHIC MANAGEMENT • TEUCRIUM MAR - IT IS ONE OF THE BEST REMEDIES FOR POLYP OF NOSE - 3-4 DOSES REPEATED AFTER AN INTERVAL OF 15 DAYS USUALLY CURES PERMANENTLY - BLOCKAGE OF NOSE ON THE SIDE PATIENT LIES ON - POLYP IS SOFT AND GELLY LIKE CONSISTENCY • LEMNA MINOR - NASAL POLYPI - SWOLLEN MUCOUS MEMBRANE OF THE NOSE - ATROPHIC RHINITIS - FOETID SMELL - REDUCES THE OBSTRUCTION OF NOSE BY REDUCING THE SWELLING • CALC. CARB - A GOOD REMEDY FOR POLYP OF NOSE, EAR, BLADDER, UTERUS ETC - IT SHOULD BE REPETED AFTER 7 DAYS - MUCOUS POLYPS WHICH BLEED EASILY • PHOSPHOROUS - NASAL POLYP BLEED EASILY - HANKERCHIEF IS ALWAYS BLOODY - IMAGINARY ODOURS - CRAVING FOR COLD DRINKS - SNEEZING - POLYP OF THE UTERUS • SANGUNARIA - POLYP OF THE NOSE OR LARYNX - SMARTING AND BURNING IN NOSE AND THROAT - NOSE OBSTRUCTED - BLEEDING FROM REMOVAL OF CRUSTS BIBLIOGRAPHY • • • • WWW.GOOGLE.COM TEXTBOOK OF ENT DHINGRA ILLUSTERED-KHANEJA MATERIA MEDICA- BORIECKE