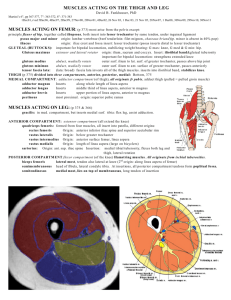
Insertion
advertisement

Teres Major • • • • • Meaning: teres- long and rounded shape Origin: lateral border of scapula Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus Action: lateral rotation at shoulder Stretch: Teres Minor • Meaning: same as teres major • Origin: inferior angle of scapula • Insertion: intertubercular groove of the humerus • Action: adduction and medial rotation at the shoulder (rotator cuff muscle) • Stretch: Deltoid Muscle By: Hannah Thomas Delta = Triangle, so it is triangular shaped Origin: Clavicle and Scapula (Acromion and Adjacent Scapular Spine) Insertion: Deltoid Tuberosity of Humerous Primary Actions: Abduction at Shoulder Stretches: Arm cross, shoulder roll Pectoralis Major Hillary Pyatt “pectoralis major”- large pectoral muscle Origin- cartilege of ribs 2-6, body of sternum and clavicle. Insertion- greater tubercle of humorous Action- flexion, adduction, and medial rotation at shoulder. Exercise- pushup Levator Scapulae • Levator means to lift – lifts the scapula • Origin: Transverse Process of first 4 cervical vertebrae • Insertion: Vertebral border of scapula • Primary action: Elevate scapula • Stretch: Sit with feet flat on the floor, relax shoulders, bring chin back towards shoulders, eyes look straight ahead • • • • Tensor=to stretch; Fascia=band; Latae=side Origin: Iliac crest Insertion: Iliotibial tract Action: Flexion, abduction, and medial rotation at hip Adductors • An athlete pulls one of these muscles when strains his/her groin – Adductor brevis – Adductor longus – Adductor magnus – Pectineus – Gracilis ADDUCTORS ORGIN INSERTION ACTION Adductor Brevis: Inferior ramus of the pubis Linea aspera of pubis Adduction, flexion, and medial rotation at hip Adductor Longus: Inferior ramus of pubis posterior to adductor brevis Linea aspera of pubis Adduction, flexion, and medial rotation at hip Adductor Magnus Inferior ramus of pubis posterior to adductor brevis Linea aspera of pubis Adduction at hip joint; superior portion produces flexion, inferior portion produces extension Pectineus Superior ramus of pubis Inferior to lesser Adduction, flexion, trochanter of femur medial rotation at hip joint Gracillis Inferior ramus at pubis Medial surface of tibia inferior to medial condyle Flexion at knee; adduction and medial rotation at hip Transverse Abdominis Mackenzie Gordon •Name: ‘Transverse’ refers to going across •‘Vacuum’ excercise Shape: Resembles the Big Dipper on its side Location: Deepest of the abdominals, lateral to the rectus abdominis Origin: Lateral inguinal ligament, iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia, cartilage of lower 6 ribs Insertion: Abdominal aponeurosis to linea alba Primary Actions: Compresses abdominal contents, assists respiration Rectus Abdominis •Name: ‘Rectus’ means strait •Back bend Shape: ‘Six pack’, vertical strip Location: Superficial, medial to the external oblique Origin: Pubic crest and pubic symphysis Insertion:Cartilage of 5th, 6th, 7th ribs, and xiphoid process Primary Actions: Flexes the vertebral column (allows you to stand up strait) Vastus Intermedius • Origin- anterior and lateral surface of femur along linea aspera • Insertion- tibial tuberosity by way of patellar ligament • Primary actions- extension at knee • Exercise- quad stretch Vastus Lateralis • Origin- anterior and inferior to greater trocanter of femur and along linea aspera • Insertion- tibial tuberosity by way of patellar ligament • Primary actionsextension at knee • Exercise- quad stretch Vastus Medalis • Origin- entire length of linea aspera of femur • Insertion- tibial tuberosity by way of patellar ligament • Primary actionsextension at knee • Exercise- quad stretch SartoriusLatin root-Sartor (meaning tailor)-reference to the cross legged position in which tailors sit. Origin-Anterior superior spine of illeum. Insertion-Medial surface of tibia, near tibial tuberocity. Action-Flexion at knee; flexion and lateral rotation at hip. Stretch/Exercise- Climbing stairs Supraspinatus( above the spine) • Origin: supraspinous fossa of the scapula • Insertion: greater tubercle of the humerus • Primary actions: abduction of the arm at the shoulder (assists deltoid) Infraspinatus (below the spine) • Origin: infraspinous fossa of the scapula • Insertion: same as above • Primary actions: extension, horizontal (transverse) extension and lateral rotation of humerus at the shoulder joint • Origin – Spinous processes of the lower thoracic vertebrae, ribs, and lumbar vertebrae • Insertion – Intertubercular groove of humerus • Primary Actions – Extension, adduction, and medial rotation at shoulders The name derives from the Greek word "spléníon," which means bandage. Capitis means of the head, and cervicis means of the neck. Origin Spinous processes of lower cervical( 7th) and upper T3 or T4. Insertion Inserts under the Sternocleidomastoideus, into the mastoid process and into the occipital bone and between the upper cervical vertebrae. Action Extends and rotates cervical spine The splenius muscle is a prime mover for head extension. Stretch lateral flexion and rotation of the neck and hyper extending the neck. ORIGIN Spinous processes and supraspinous ligaments of T36. Insertion Posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C1-3. ACTION Extends and rotates cervical spine Stretch Internal and External Obliques •Internal obliques are under external ones •External: Origin—lower 8 ribs •Insertion—linea alba and iliac crest •Action—compresses abdomen, depresses ribs, flexes or laterally flexes vertebral column •Internal: Origin—Iliac crest, and adjacent connective tissues •Insertion—lower ribs, xiphoid of sternum and linea alba Internal and External Obliques •Internal obliques are under external ones •External: Origin—lower 8 ribs •Insertion—linea alba and iliac crest •Action—compresses abdomen, depresses ribs, flexes or laterally flexes vertebral column •Internal: Origin—Iliac crest, and adjacent connective tissues •Insertion—lower ribs, xiphoid of sternum and linea alba