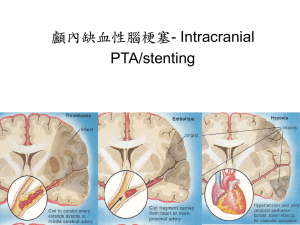
Facial Aesthetic Units
advertisement

Basic Principles of the Facial Plastic Surgery Bastaninejad, Shahin, MD, ORL & HNS, TUMS Amiralam Hospital Presentation Outline Suture Materials & Techniques Neurovascular Neighbours Relaxed Skin Tension Lines Facial Aesthetic Units Scar Revision Pearls Post-Op Cares Suture Materials and Techniques Suture material of choice for the skin surface of the face is 6−0 or 7−0 Nylon or Prolene® Monofilament on a very fine cutting needle For subcutaneous tissue: Vicryl or PDS 40 to 5-0 Simple interrupted suture is most commonly used For deep wounds we use SQ sutures and interrupted vertical mattress suture to coapt the wound edges We generally use continuous sutures for: lid area long traumatic wounds behind the ear in auricular reconstructions Neurovascular Neighbors 1 External carotid artery 2 Facial artery 2.1 Inferior labial artery 2.2 Superior labial artery 2.3 Angular artery 3 Transverse facial artery 4 Zygomatico-orbital artery 5 Superficial temporal artery 5.1 Frontal branch 5.2 Parietal branch 6 Occipital artery 7 Supraorbital artery 8 Supratrochlear artery 9 Dorsal nasal artery Relaxed Skin Tension Lines RSTL is the reflection of the molecular orientation in the dermal level They are usually run perpendicular to the muscular fibers beneath them Facial Aesthetic Units Major units are based on skin thickness, color, texture & underlying structural contour Precise planning of surgical incisions & reconstructions, require, analysis of the entire subunit Incisions parallel to RSTL & within unit or subunit borders result in the most favorable scars Facial Esthetic Units Indications for Scar Revision Widened Scars Perpendicular to RSTL Webbed Pin-cushioned Long & linear and misaligned with RSTL Hypertrophied Interrupting an aesthetic unit of the face Causing distortion of facial features or anatomic function After 2-3mo proceed with revision surgery Scar Revision Techniques Excision (2-3mo after scar maturation and thereafter) Expansion with Excision Irregularization Dermabrasion (6-8wk after injury or surgery) Steroid injection Excision With regards to the facial subunits, place incision in RSTL or pre-existing facial wrinkles Pearls: Fusiform shape with 30 degree Slight vertical bevel outward 1-2 cm undermining Buried SQ sutures Monofilament interrupted sutures For maximizing eversion, use mattress sutures vertical Examples of proper placement of fusiform incisions with 30 degree angled ends Tissue Expansion Tissue expansion is the ideal procedure for reconstruction of SCALP defects Rectangular expanders are mostly used Previous scars and incisions can be used for placement of the prostheses (do not harm your future flap designs) Create a subgaleal plan Care should be taken to fix the inflation reservior Expansion with N/S biweekly, starting 2wks post insertion (continue up to 6-8wks) Irregularization Makes scars less noticeable with human eyes! Techniques: Z-Plasty Classic 60 degree 75% scar lengthened 45 degree 50% “ “ 30 degree 25% “ “ W-Plasty Geometric Broken Line Closure (GBLC) 5-7mm arms, one arm must be parallel to the RSTL Attention to the W-plasty angles and the scar inclination Dermabrasion Candidates: Lighter complexions Avoid in HIV and Hepatitis Perform this procedure, 6-12mo after treatment with13-cis-retinoic acid Use antiviral prophylaxis for patient with a history of herpetic infection Penetrate a little bit more deeply than superficial papillary dermis (to see the strands of whitecolored collagen fibers) & ETC... Steroids In scar revision, in particular patients, whenever persistent tissue edema detracts from the wound’s appearance, you can use triamcinolone 10mg/ml, with ID or a plan between D & SQ route, injections Post-Op Cares Removing the sutures on postoperative day five, six, or seven Hydrocortisone ointment is massaged into the scar for 15 minutes in the morning and evening for 2weeks If the patient is prone to hypertrophic scarring, we will inject intralesional Triamcinolone 10mg/ml (use N/S for dilution) References Cummings ORL&HNS 5th edition-2010 Reconstructive Facial Plastic (Weerda-2001) Plastic Surgery (Mathes-2006) Facial Plastic Surgery (Park-2005) Surgery