anatomy3
advertisement

Anatomy
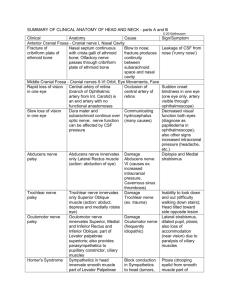
The face
The face is covered by:- 1- skin
2- Superficial-fascia
3- Periosteum
Imp. There is NO deep fascia
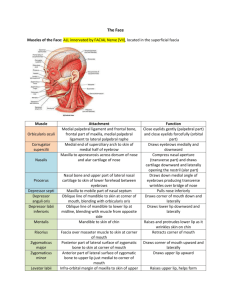
Muscles of facial expressions :1- Located in the superficial-fascia
2- Developed from the second pharyngeal-arch
3- Supplied by the 7th cranial nerve (facial nerve)
4- Originated from bone
5- Inserted into skin
6- Most located around orifices (such as orifices of eye,
mouth and nose) to act as dilators or sphincters
Arterial supply of the face:--mainly through the facial artery and the transverse facial artery .
--because of this rich supply of the face, when cut it will bleed
freely and heal quickly .
---Common carotid artery divides into:- External carotid artery(supply structures outside the
skull).
- Internal carotid artery(supply structures within the
skull).
External carotid artery:-
It has 8 branches:-
Some American ladies find Our Pyramids So Magnificent
The maxillary and the superficial-temporal are terminal branches
Facial artery originates from anterior aspect of (external carotid),
It’s course: - (It passes deep to the submandibular gland >then
appears at the lower border of the mandible >pass anterior to the
masseter muscle (where we can locate it’s pulse)>ascend up in a
tortuous course towards the medial angle of the eye(there it
forms angular-artery (through its pathway it gives branches to the
face like inferior, superior labial artery)).
Transverse facial artery:-
- It’s a branch from the superficial-temporal artery
- Passes anterior to cross the external masseter muscle
parallel to zygomatic arch and parallel to mandible-duct
- Supply the parotid duct
- The maxillary artery is bigger than the transverse.
Veins of the face: Note {the facial vein is POSTERIOR to the artery, Straighter than the
artery, anterior to the masseter muscle and valve-less, so blood can
flow in both directions}
### The course of the facial vein: - The beginning is at medial angle of
the eye formed by the union of (supraorbital-vein (laterally) &
supratrochlear-vein (medial)) to be called angular-vein>then crossing
the masseter muscle>at the angle of the mandible it unites with a
branch of retromandibular-vein>to drain into the internal-jugular-vein.
Retromandibular-vein: 1- Formed by (superficial-temporal vein & maxillary)
2- Formed behind the mandible(auricle of the ear)
-- Note “all the face, head, neck, brain are valve-less except at the
distal end of internal jugular vein”.
* Pterygoid venous plexus: 1- Located between medial and lateral pterygoid muscles inner to
the ramus of the mandible
2 – Facial vein (superficial) is connected to pterygoid-plexus
through a branch called deep-facial-vein.
3- Pterygoid-plexus connected up to cavernous-sinus (the
cavernous-sinus is dural venous sinus located on both sides
of the pituitary gland.
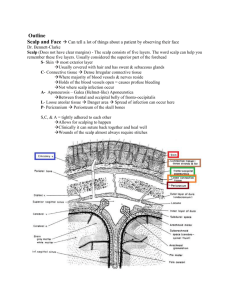
(Don’t squeeze acne in the area between the root of the nose and the mouth angles because when
squeezing sucking of germs will happen and meningitis or brain abscess).
Nerve supply: - cranial nerves are 12 pairs, nominated in roman
Nerve supply of the face: Facial nerve:
1- The nerve supply of the face is the facial nerve which is the cranial
nerve no.7.
2- Supply structures derived from second pharyngeal-arch(like the
muscles of facial expressions)
3- Mixed nerve so it has (large motor root{outside},small sensory
root{inside})
4- Course: - leaves the cranial-cavity through internal-auditorymeatus>exit outside the skull through stylomastoid foramen>once
out(near the parotid gland) it will be superficial>then enters the
parotid gland>there it divides into 5 branches (like the extended
abducted fingers) which are motor
5- The 5 branches are : - (1- temporal, 2- zygomatic, 3- buccal,4mandibular and 5- cervical )
6- 1-temporal: - *supplies muscles in the temple, forehead, supraorbital
areas.
2- Zygomatic: - * infra-orbital,
3- Buccal: - supplies muscles of the cheeks, corner of the mouth
muscles.
4- mandibular:- supply muscles of the lower lip
5- Cervical : - supplies platysma muscle
Clinical consideration:- Paralysis if happens then that person is done no
nerve supply is reaching
Palsy: 1- uni-Lateral, paralysis of facial muscles lesion of the facial nerve
commonly at stylomastoid foramen, direct blow (cold draft),
2- Losing the motor function of the whole side of the face, unusual
appearance, (can’t close his/her eye’s, mouth angle deviated, involuntary
salivation, chewing problems.
3- therapy: - artificial tears, needs a week to recover
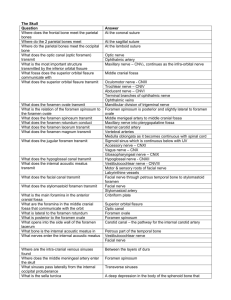
Parotid gland: 12345-
The largest salivary gland
Located on the side of the face
It developed from oral cavity(out-pouching from the mouth)
Saliva secreted into the mouth
Its wedged between ramus of the mandible &
sternocleidomastoid muscle, triangular in shape(base of it outside
while apex inside)
6- Surface anatomy: - to identify from outside(in the lab)
a- Inferior (angle of the mandible)
b- Superior (mid-point of the zygomatic arch)
c- Posterior (mastoid process)
7- Convex anterior border where the parotid duct emerges.
8- It has two capsules(the facial-nerve divides it into 2 lobes):a- Superficial
b- deep
9- Bones related to the parotid gland are sandwiched between
muscles
10- Contents
-
Facial nerve
Retromandibular vein
External carotid artery
Parotid lymph nodes