CASEPRESENTATION ON FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURE

PREPARED BY
DHANYA VIJAYAN
OPERATING ROOM
GENERAL APPEARANCE
Patient is conscious and coherent.
Looks weak and fatigue.
Unable to mobilize his left lower extremity.
VITAL SIGNS
BP :124/86mm of Hg
PR :82bpm
RR :20cpm
Temp :98.6F
SPO2 :98%
.
SKIN
•Skin is warm .
•Has swelling on rt leg.
• Noted abrasions on rt arm and lower limbs
HEAD
•Hair is equally disrtibuted.
• Absence of dandruff
EYES
• Able to move both eyes
• On inspection of eyes ,the rt eye is reddish and the eyelid has dark discouloration
.
EARS
• Patients pinna is same colour as fascial.
•
Able to hear sounds clearly
.
• No discharges.
MOUTH
• Lips are pink but dry.
• Teeth is propely aligned with no dentures.
NECK
• No tenderness of node
THORAX
• The Thorax Is Symmetric On Inspection
CARDIO VASCULAR
•Absence Of Chest Pain .
•Heart sounds are clear.
•Upon auscultation his Bp is 132/78mmof hg.
GENITO URINARY
•With foley catheter fr.16
.
GASTRO INTESTINAL
•No Tender Ness Of Abdomen and its soft .
•Had enema once and he was kept on NPO for 8hrs.
.
MUSCULOSKELE
TAL
•Unable To Mobilize His Lt Lower Limb.
•Has Pain During Examination.
•Cannot Perform ADL.
•Tenderness at site of fracture.
•Visible deformity.
•Lower extremity appear shortened.
•Crepitus noted with movement.
NEUROLOGIC
•Patient Is Mentally Alert And Oriented With
Circumstances.
•Able To Follow Commands.
•No neurovascular deficit.
PAST MEDICAL AND SURGICAL HISTORY
H/O Adenotonsilectomy 10yrs back
PRESENT MEDICAL HISTORY
Patient was brought in E.R on 17/12/12 by RED
CRESCENT due to R.T.A.After further investigations he was diagnosed with fracture on femoral shaft rt side.
PRESENT SURGICAL HISTORY
He underwent intramedullary nailing of lt femur on
18/12/12.
INVESTIGATIONS DONE FOR THE PATIENT
X-Ray Pelvic And Femur
CT lower extremity
CT lumbar and thoracic spine
Blood investigations like
o o
CBC
PT INR
o
SERUM ELECTROLYTES
o
RH TYPING
MEDICATIONS
Inj .Risek 40mg od
Inj:Augmentin1.2gm Bd
Inj.Amikacin 500mg bd
Inj.Perfelgan 1 gm.
TEST on 17/12/12
CBC
HB
HCT
RBC
PLT
sodium pottassium
PT
APTT
INR
RH typing
RESULT REFERENCE
RANGE
12.1g/dl
35.8g/dl
4.81
13.7-17.5g/dl
40.1-51.0g\dl
4.63-6.08 *10^6/ul
198
138
4.0
13.4
29.2
1.3
Ab+ve
163-337/ul
135-150 mmol/l
3.5-5.0mm0l/l
10.0
-
17.0sec
26.1-36.3sec
2.4theraputic
TOPIC PRESENTATION
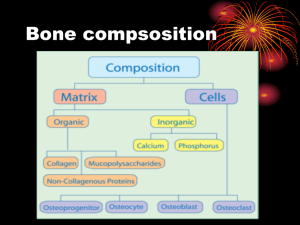
The femur is the anatomical name given to the thigh bone .It is the largest and strongest bone of the body. The long, straight part of the femur is called the femoral shaft.
When there is a break anywhere along this length of bone, it is called a femoral shaft fracture.
The most common types of femoral shaft fractures include:
Transverse fracture
.
In this type of fracture, the break is a straight horizontal line going across the femoral shaft.
b.Oblique fracture .
This type of fracture has an angled line across the shaft.
C.
Spiral fracture.
The fracture line encircles the shaft like the stripes on a candy cane.
A twisting force to the thigh causes this type of fracture.
d
.
Open or compound fracture
If a bone breaks in such a way that bone fragments stick out through the skin or a wound penetrates down to the broken bone, the fracture is called an open or compound fracture.
They have a higher risk for complications — especially infections — and take a longer time to heal.
e
.
Comminuted fracture
In this type of fracture, the bone has broken into three or more pieces.
open fracture
The femur is the longest and strongest bone in the skeleton, is almost perfectly cylindrical in the greater part of its extent It is divisible into a body and two extremities
.
T HE U PPER E XTREMITY ( PROXIMAL EXTREMITY ), presents a head, a neck, a greater and a lesser trochanter
The Head (caput femoris).
is globular and forms rather more than a hemisphere and fits in to the acetabulam (a cup shaped socket in the pelvis)
.
T HE N ECK ( COLLUM FEMORIS ).
— The neck is a flattened pyramidal process of bone, connecting the head with the body
The Greater Trochanter (trochanter major; great trochanter ) is a large, irregular, quadrilateral eminence, situated at the junction of the neck with the upper part of the body.
The Lesser Trochanter ( trochanter minor; small trochanter ) is a conical eminence it projects from the lower and back part of the base of the neck.
Running obliquely downward and medialward from the tubercle is the intertrochanteric line ( spiral line of the femur )
The Body or Shaft (corpus femoris).
— The body, almost cylindrical in form, is a little broader above than in the center, broadest and somewhat flattened from before backward below. it is strengthened by a prominent longitudinal ridge, the linea aspera.
The distal extremity of the femur (or lower extremity) is larger than the proximal extremity
It consists of two oblong eminences known as the condyles
Anteriorly, the condyles are slightly prominent and are separated by a smooth shallow called the patellar surface .
posteriorely they project considerably and a deep notch, the Intercondylar fossa of femur , is present between them.
The lateral condyle is the more prominent and is the broader both in its antero-posterior and transverse.
o The lateral condyle is the more prominent and is the broader both in its antero-posterior and transverse.
o Each condyle is surmounted by an elevation, the epicondyle o The medial epicondyle is a large convex eminence to which the tibial collateral ligament of the knee-joint is attached. o The lateral epicondyle, smaller and less prominent than the medial, gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-joint.
o The articular surface of the lower end of the femur occupies the anterior, inferior, and posterior surfaces of the condyles. Its front part is named the patellar surface and articulates with the patella.
THE FEMORAL ARTERY PASSES roundthe medial aspect of the femur to enter the popiliteal space where it becomes the
POPILITEAL ARTERY .
it supplies blood to the structures of the thigh.
Branches from the femoral artery
D EEP ARTERY OF THE THIGH
( ARTERIAPROFUNDA FEMORIS ) is the largest and main branch of the femoral artery and branches off the femoral artery about 2 to 5 cm below the inguinal ligament.
M EDIAL CIRCUMFLEX ARTERY AND LATERAL
CIRCUMFLEX ARTERY may arise from the deep artery or directly from the femoral artery.
Great saphenous vein joins the femoral vein about 3 cm below the inguinal ligament
Deep vein of the thigh ( profunda femoris vein ) joins the femoral vein about 8cm below the inguinal ligament.
The muscles in the front of the thigh are the
SARTORIUS and the QUADRICEPS FEMORIS .
T he quadriceps is actually a powerful muscle made of 4 parts – the rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis and
vastus intermedius. While the sartorius flexes both the hip and knee joints, the quadriceps femoris is an extensor of the knee joint.
The muscles in the inner aspect of the thigh are the
PECTINEUS , GRACILIS ,
ADDUCTOR LONGUS , ADDUCTOR MAGNUS ,
ADDUCTOR BREVIS , OBTURATOR EXTERNUS The adductor muscles also help rotate the thigh in an inward direction while the iliopsoas flexes the hip joint .
The back of the thigh holds the powerful hamstring muscles , the biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus. ND
THE ILIOPSOAS .
The hamstrings are all flexors of the knee joint.
T HE IMPORTANT NERVES OF THE THIGH ARE THE
FEMORAL AND THE SCIATIC NERVES
The femoral triangle is an anatomical region of the upper inner human thigh .
It is bounded by
:
( superiorly ) the inguinal ligament
• ( medially ) the medial border of the adductor longus muscle
( laterally ) the medial border of the sartorius muscle
The three compartments of the femoral sheath (From lateral to medial ):
• femoral artery and its branches
• femoral veins and its tributaries
• femoral canal , Which contains lymphatic vessels and some lymph nodes (Specifically, the deep inguinal lymph nodes
DUE TO A FALL
(
USUALLY FROM A HEIGHT AND OFTEN
ON TO HARD SURFACE
)
DUE TO DIRECT BLOW TO FEMUR SUCH AS RTA
OSTEO POROSIS OR MALIGNAN
Common Symptoms Are
BLEEDING
DEFORMITY OF THE LEG
INABILITY TO MOVE THE AFFECTED LEG
MUSCLE SPASMS
NUMBNESS Or TINGLING
SEVERE PAIN
SWELLING
SERIOUS SYMPTOMS THAT MIGHT INDICATE A LIFE
THREATENING CONDITION ARE.
CONTUSION OR LOC EVEN FOR A BRIEF MOMENT
HEAVY UNCONTROLLABLE BLEEDING
INAVBILITY TO MOVE LEG
HYPOTENSION
PROTRUDING FRAGMENTS OF BONE THROUGH THE s
KIN
Nonsurgical Treatment
Most femoral shaft fractures require surgery to heal. It is unusual for femoral shaft fractures to be treated without surgery. Very young children are sometimes treated with a cast.
Surgical Treatment
For the time between initial emergency care and surgery, doctor will place leg either in a long-leg splint or in skeletal traction. This is to keep broken bones as aligned as possible and to maintain the length of leg.
( S KELETAL TRACTION IS A PULLEY SYSTEM OF WEIGHTS AND COUNTERWEIGHTS THAT HOLDS
THE BROKEN PIECES OF BONE TOGETHER . I T KEEPS LEG STRAIGHT AND OFTEN HELPS TO
RELIEVE PAIN
.)
EXTERNAL FIXATION
External fixation is usually a temporary treatment for femur fractures. This device is stabilizing frame that holds the bones in the proper position so they can heal.
Extensive comminution and open fractures were considered to be relative indications for the use of femoral external fixation as a definitive treatment for femoral shaft fractures.
INTRAMEDULLARY NAILING .
It is the most common treatment for femoral shaft fractures in adults,An intramedullary nail can be inserted into the canal either at the hip or the knee through a small incision. It is screwed to the bone at both ends.
This keeps the nail and the bone in proper position during healing. to determine how
PLATE AND SCREWS
The use of plate fixation for the routine treatment of femoral shaft fractures has decreased with the increased use of intramedullary nails.
The main disadvantages associated with plate fixation when compared with intramedullary nailing are the need for an extensive surgical approach with its associated blood loss, infectious complications, and soft tissue insult.
Because the plate is a load-bearing implant, implant failure is expected if union does not occur.
PLATE AND SCREWS
IM NAILING
Complications from Femoral Shaft Fractures
The ends of broken bones are often sharp and can cut or tear surrounding blood vessels or nerves.
Acute compartment syndrome may develop.
(This is a painful condition that occurs when pressure within the muscles builds to dangerous levels. This pressure can decrease blood flow, which prevents nourishment and oxygen from reaching nerve and muscle cells. Unless the pressure is relieved quickly, permanent disability may result. This is a surgical emergency.)
Open fractures expose the bone to the outside environment. Even with good surgical cleaning of the bone and muscle, the bone can become infected . Bone infection is difficult to treat and often requires multiple surgeries .
Complications from Surgery.
Infection.
Injury to nerves and blood vessels.
Blood clots.
Fat embolism (bone marrow enters the blood stream and can travel to the lungs; this can also happen from the fracture itself without surgery).
Malalignment or the inability to correctly position the broken bone fragments.
Delayed union or nonunion (when the fracture heals slower than usual or not at all).
Hardware irritation (sometimes the end of the nail or the screw can irritate the overlying muscles and tendons.)
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
1.Provide emergency care if requires (hemostasis, respiratory care, prevention of shock).
2. Provide fracture fixation to prevent following injury of tissues.
3. Observe signs of fat embolism (especially during first 48 hours after the fracture).
4. Monitor fluids input and output continuously, insert IV catheter, urinary catheter.
5. Monitor client’s vital signs.
6. Monitor client’s laboratory tests results for abnormal values.
7. Administer IV therapy, analgesics, antibiotics, and other medications as prescribed.
8. Prepare client and his family for surgical intervention if required.
9. For client after surgical intervention provide routine postoperative care and teach about possible postoperative complications.
10. Provide care to client with cast (observe signs of circulatory impairment – change in skin color and temperature, diminished distal pulses, pain and swelling of the extremity; protect the cast from damage).
11. Provide care to client in traction (check the weights are hanging freely, observe skin for irritation and site of skeletal traction insertion for signs of infection; use aseptic technique when cleaning the site of insertion).
12. In case of hip fracture and hip replacement maintain the adduction of the affected extremity.
13. Provide respiratory exercises to prevent lung complications.
14. Observe for signs of thrombophlebitis, report immediately.
15. Provide appropriate skin care to prevent pressure sores.
16. Encourage fluid intake and high-protein, high-vitamin, high-calcium diet.
CLOSED FRACTURES
Instruct the patient regarding the proper methods to control pain and edema
(elevate extremity to heart level,take analgesia as prescribed etc).
Teach patient how to use assistive devices safely.
teach exercises to maintain the health of unaffected muscles and to strengthen muscles needed for transferring and for using assistive devices
(crutches,walker).
provide health teaching regarding self care ,medication information,monitoring potential complications .
need for continuing health care supervision .
OPEN FRACTURES
Administer IV antibiotics immediately upon the patients arrival in hospital
Perform wound irrigation and debridement .
Asses neurovascular status frequently
Take the patient temperature regularly and monitor signs of infection.
(The objective of the management is to prevent infection and promote healing of bone and tissue.)
1.Acute Pain Related To Fracture And Surgery.
2. Impaired Physical Mobility Secondary To Fracture
And Surgery.
3.Knowledge Deficit Regarding Treatment Regimen
And Disease Condition.
4.Risk For Fat Embolism Due To Fractutre Of Long
Bones.
5.Risk For Infection Due To Surgical Intervention And
Injury .
ASSESSMENT PLANNING IMPEMENTATION EVALUATION
CUES/EVIDENCE NURSING
DIAGNOSIS
“
Subjective
I have severe pain while
Acute Pain
Related To
Fracture And
Surgery .
moving my lower limb” as verbalized by the patient
Pain scale -
5/10 as 0 is the lowest and
10/10 is the highest objective
Facial grimace
Verbal report of pain.
GOALS AND DESIRED
OUTCOME
NURSING
ORDER/ACTION
RATIONAL FOR ACTION EVALUATION
After series of nursing interventions the client should manifest a decrease in pain scale from
5/10 to 0/10 .
1.Asses the 1.To identify the onset After 12 Hrs Of Nursing patients pain scale ,intensity and duration of Interventions The Goals Were and perception.
2.Monitor vital signs and pain scale .
pain.
2.To obtain base line vital
Met As Evidenced By-
Decrease in Pain signs .
(Vital signs changes during pain and for future comparison after
scale from 5/10 to 0/10
No pain and discomfort intervention.
3.Maintain
3.Relieves pain and
Verbalize relief of pain.
immobilization of prevents bone affected part using cast,and skin traction.
displacement and Positive response
.
extension of tissue injury during evaluation.
Display relaxed manner,
4.
Elevate and 4.Promotes venous support injured return, decreases edema, and may reduce pain.
extremity .
able to participate in activities, and sleep and rest appropriately.
5.Teach
Pain Control divertional
5.To destract clients activities attention from pain.
6.Administer analgesia as prescribed .
6.To relieve the pain.
ASSESMENT
CUES/EVIDENCE NURSING
DIAGNOSIS
PLANNING
GOALS AND DESIRED
OUTCOME
SUBJECTIVE
‘’ I cannot move my leg properly and I have pain during motion ‘’ as verbaluized by the patient.
OBJECTIVE
Limited range of motion.
Inability to perform action as instructed.
with cast on left leg .
decreased
IMPAIRED
PHYSICAL
MOBILITY
,ACUTE PAIN
SECONDARY
TO FRACTURE
AND SURGERY
Patient will be able to
Perform his physical activity and free of complications as evidenced by ….
Participates in activities of daily living
Performs physical activities independently
Intact skin and abcence of thrombophlebitis
Normal bowel pattern.
IMPLEMENTATION
NURSING
ORDER/ACTION
RATIONAL FOR
ACTION
EVALUATION
EVALUATION
1.Support affected part using pillows.
Provide footboard, wrist splints, trochanter.
1.To maintain AFTER 12 HOURS OF NURSING
INTERVENTIONS THE GOALS
2.Determine presence of complications related to immobility such as pneumonia ,elimination problem ,decubitus ulcer.
3.Encourage adequate intake of fluids 2-3L/day
.
position and function and reduce risk of pressure ulcers.
2.To assess presence of complications
3.Promote well being and maximize and energy production...
4.Instruct /assist patient 4.Increases blood with active and passive
ROM excercises of flow to muscles and bone to affected and unaffected improve muscle limb like tone, maintain flexion,extension abduction and adduction.
joint mobility; prevent contractures/atro phy and calcium resorption from disuse .
WERE MET AS EVIDENCED BY…
Patient performs physical activities independently or with assistive devices as needed.
Free of complications of immobility as evidenced by intact skin ,absence of thrombophlebitis ,normal bowel pattern
Pt able to fully complete passive range of motion exercises withassistance from the staff by the end of this shift. Pt did not complain of any pain associated with exercise session.
Conclusion
• A case of RTA patient with fr
acture
of femoral shaft and was unable to move his left lower extremity.
• Initially patient was on skin traction.
• Surgical treatment Intra Medullary Nailing done on 18/12/12.
• Patient is able to move on walker.
• Health education given on home care including physiotherapy .
• Patient was discharged on 30/12/2012.
• Patient was told to come for follow-up after 2 weeks.
Bibiliography
1.
Lippincott manual of nursing practices 9 th edition.
2.www.Local health.com.
3.ortho info.aas.org.
4.Gray
” s femur anatomy and physiology of human body.
5.
www.health
type .com
THANK
YOU