Fractures Principles 3
advertisement
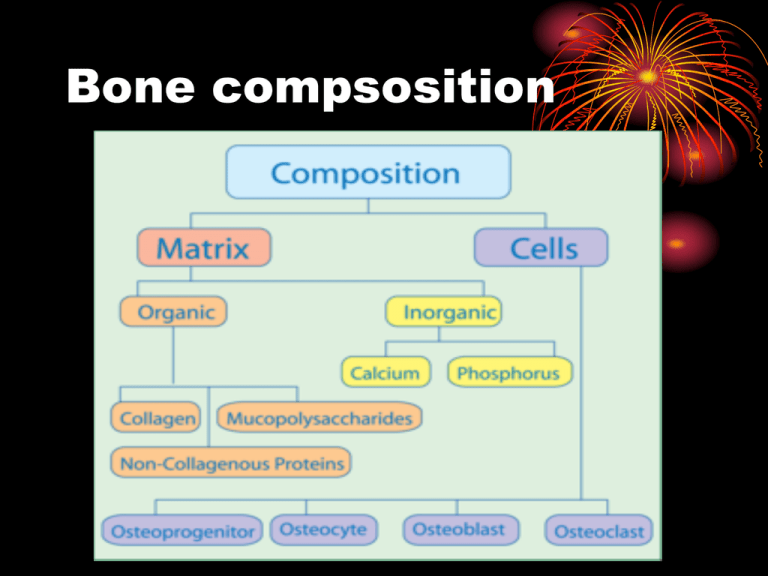
Bone compsosition Bone anatomy fracture • it’s the break in the continuity of the bone . it could be: • 1-simple(closed) • 2-compound (open) . Causes of fractures • 1- sudden truma • 2-stress’’fatigue fracture’’. • 3-pathological fracture. Types of fracture • • • • Complete fractures In-complete fractures Physeal fractures Fracture displacement Complete fractures: • • • • Transverse fracture Oblique or spiral Impacted comminuted Transverse fracture Oblique fracture Impacted fracture spiral Incomplete fractures • The bone is incompletely divided and the periosteum remains in continuity. • Exm:greenstick fracture. • Stress fracture • Compression. Fracture displacement • • • • • We describe it in terms of: Translation ‘’shift’’ Length Alignment ’’angulation’’ Rotation ‘’ twist’’ Soft tissue damage • It could be either: • Low energey fractures like closed spiral fractures,and it coz moderate soft tissue damage. • High energy fractures:like comminuted fracturs and it coz severe tissue damage,no matter whether it open or close. Fracture healing • Healing by callus • Healing Without callus Time factor • The rate of the bone depends on: • 1-type of the bone. • 2-type of fracture. • 3- blood supply • 4-general constitution. • 5- pt age. Average time for healing Callus visible union Upper limb Lower limb 2-3 weeks 2-3 weeks 4-6 weeks 8-12 weeks consolidatio 6-8 weeks n 12-16 weeks Fractures that fail to unite(non union) • Distraction and separation of the fragments. • Interposition of soft tissues between the fragments. • Excessive movement at the fracture site • Poor local blood supply. • Severe damage to soft tissues which makes them non viable. • Infx • Abnormal bone.