Pediatric Nursing
advertisement

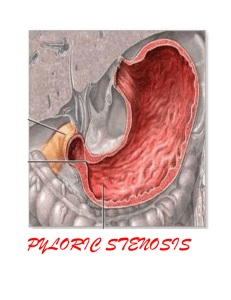
Pediatric Nursing Module 3 Caring for Children with Alterations in Nutrition/Elimination Assessment of GI System History gathering base line data infant - formula type and tolerance children - diet, appetite, preferences meal schedule any prior GI problems elimination patterns stools, characteristic, number per day, toilet habits general nutritional appearance height and weight Physical Assessment Inspection oral cavity ability to suck, swallow, chew any ulcers, sores, bleeding, thrush, dental caries,congenital anomalies (cleft lip and palate) sore throat Abdomen distention, turgor, contour, pain, girth Physical Assessment Stool number, consistency, presence of blood Vomitus color, amount, blood, projectile Urine specific gravity, frequency amount Tears Fontanels Pf closes at 2-3 months, Af closes 9-18 months Assessment - dehydration Children are more susceptible to dehydration due to greater % or portion of their body weight being water Signs and Symptoms poor skin turgor sunken fontanel decreased urine out-put (1-2ml/uo/kg/hr) decreased body weight dry mucous membranes, lips no tears Physical Assessment Auscultation Abdominal peristalsis presence/absent hypo or hyper visible - possible pyloric stenosis Adjunct Assessment Weight Temperature Labs stool culture, ova & parasite, guiac, roto virus electrolytes - Na, K, Cl, HCO3 CBC - wbc’s I&O X-ray barium swallow, barium enema What questions do you have for the parent, for the child? Signs and Symptoms of Dehydration Neurological Cardiac Respiratory Gastrointestinal Genitourinary Musculoskeletal Integumentary Disorders of Motility Gastroenteritis Acute Diarrhea bacterial vs viral isolation - good handwashing bloody stools, mucous, cramping change in the number and consistency of stool, increase in the water margin, usually green in color Gastroenteritis Acute vomiting Differentiate between vomiting vs spitting up projectile - pyloric stenosis reflux - may lead to respiratory problems A 6 month old is admitted with dehydration. Effectiveness of therapy is evaluated by which assessment measures? Choose all that apply Analysis question, first recall assessment findings for dehydrated child assess fontanel measure and document abdominal girth document mucous membrane moisture record and analyze I & O daily wt., same scale, time, no clothes Hirschsprung’s Disease Congenital absence of the parasympathetic nerve ganglion cells in the mesenteric plexus of the distal bowel area proximal to the aganglionic portion becomes hypertrophied and greatly dilated Hirschsprung’s Disease Signs/Symptoms abdominal distention intermittent progressively increasing anorexia malnutrition obstruction with diarrhea dehydration and electrolyte imbalance Hirschsprung’s Disease Treatment temporary colostomy Pre-op clear liquids bowel prep enemas/laxatives antibiotic therapy - decrease normal bowel flora Hirschsprung’s Disease Post-op Care pain control hydration assessing stoma bowel elimination teaching Gastric Reflux Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER) backward flowing of gastric contents into the esophagus incompetent lower esophageal sphincter increase intra abdominal pressure Gastric Reflux Signs and Symptoms Infant spitting up, regurgitation, vomiting crying, irritable wt. loss, FTT Children heartburn, chest pain, abd. pain dysphasia, burping, regurgitation, cough, pneumonia Gastric Reflux Treatment small frequent thicken feedings hypoallergenic formula positioning medications H 2 antagonist pepcid, tagament, zantac surgical Nissen fundoplication Inflammatory Disorders Appendicitis Inflammation of the appendix resulting from bacterial infection or obstruction Rupture = peritonitis abscess Appendicitis Signs and Symptoms G.I. n/v/a and d/c, rigid abdomen Pain peri-umbilical - localizing RLQ re-bound tenderness progressive Other fever, stooped posture, lethargy Treatment appendectomy Structural Defects Craniofacial Abnormalities Cleft orLip & Palate May occur separately together Unilateral or bilateral Associated problems feeding difficulties URTI otitis media speech dental formation self-image Cleft Lip Interference with bonding Disfigurement Feeding Techniques more upright to avoid aspiration frequent burping lamb’s nipple asepto syringe with tubing if infant unable to create closure and suction Cleft Lip Surgical repair 2-4 months old Post-op care prevent strain on suture line keep infant off their stomach keep suture line clean Q-tip, NS, antibiotic oint. Cleft Palate Feeding same as cleft lip solids as soon as possible thicken liquids aspiration may be a problem frequent URTI and ear problems Cleft Palate Surgical Repair usually 9 - 18 months perform closure prior to speech after weaned to cup Post-op Care keep on abdomen till fully awake semi-liquid, puree diet no sucking elbow restraints keep suture line clean after feeding with water Cleft Palate Long term care speech socialization dental problems psychosocial You are caring for a newborn with a cleft lip and palate. You are aware the infant and family have multiple needs. Which is your priority nursing diagnosis? HR for impaired parent/infant attachment R/T newborn structural defect Ineffective feeding pattern R/T newborn structural defect HR for aspiration R/T newborn structural defect HR for imbalanced nutrition less than body requirements R/T abnormal feeding patterns and structural defect. Obstructive Disorders Intussusception Telescoping or a portion of the small intestine or colon into a more distal segment Signs/Symptoms vomiting pain - paroxysmal colicky abdominal “current jelly” stools - brown, bloody, mucous mixed Intussusception Treatment barium enema to reduce it or surgery Post-op gastric decompression IV therapy Obstructive Disorders Pyloric Stenosis Narrowing of the pyloric valve hypertrophic muscle Signs/Symptoms projectile vomiting left to right peristalsis olive sized mass palpated in upper right quadrant cries with hunger readily accepts 2nd feeding after vomiting Pyloric Stenosis Adjunct Problems dehydration electrolyte imbalance alkalosis malnutrition Diagnosis confirmed with barium x-ray Pyloric Stenosis Surgery Pyloromyotomy Post-op Feeding post-pyloromyotomy feeding schedule sterile water, small amount, gradually increasing in substance and quantity Nursing Care - Nutrition and Fluid Balance Needs Nursing Care and Concerns Fluid Volume and Electrolyte Imbalance daily wt. I & O assess for s/s of dehydration maintain IV therapy oral care if NPO monitor labs - electrolytes Nursing Care When introducing fluids small frequent feedings clear liquids pedialyte may dilute formula monitor for vomiting diarrhea abdominal distention Nursing Care/Concerns Nutrition check for vomiting assess tolerance of feedings weight and graph thickened feedings feed slowly check suck small amounts calorie count upright - infant seat Nursing Care/Concerns High Risk for Infection Cleft Lip/Palate URTI or OM diarrhea spread of infection pyloric stenosis body may be debilitated appendicitis peritonitis Nursing Care/Concerns Local infection - superficial redness, heat, swelling tenderness, pain Systemic infection - internal abdominal pain, increasing abdominal girth guarding temperature Nursing Care/Concerns Knowledge Deficit assessing parents understanding of child’s needs and the problem assess parent’s ability to learn teach simply, clearly, allowing time for questions and return demonstration support group referrals Case Study Jesus 5-year old boy, weights 40.3Kg wakes up at 2am with a “stomach ache”, he has a fever of 100.2F and vomiting. Parents administer Tylenol 120mg which he vomits 5 minutes later. In the morning he is still sick, so parent take him to the ER. Vital signs are Ax Temp 100.4, HR 125, RR 35, B/P 119/79. RLQ guarding, crying. IV started then MS 2mg IVP given. Abdominal US is ordered, CBC shows WBC’s are 17,500. Discuss your impressions of the situation. Questions The US confirms appendicitis. Discuss the following orders. NPO B/R D5 1/2 with 10 KCL at 70ml/hr Gentamycin 45mg IV on call to OR MS 1-2mg IVP q2hrs prn pain K-pad to abdomen Prepare for OR - lap appendectomy Questions Just prior to OR, Jesus experiences a relief from his pain. What is happening now? What is your nursing action? What are your nursing priorities in the PACU? What are the pros and cons of letting parents into the PACU? Post-op orders are as follows: routine post op vitals foley catheter to straight drainage D5 1/2 NS with 20KCL 75ml/hr Gentamycin 45mg IVP q8hr Unasyn 900mg IV q 6hr MS PCA Tylenol 240mg q4rhs per N/G tube prn T>100.4 NGT to continuous drainage NPO except for meds IS 10 times each hour while awake