The Cardiovascular
System
How your Heart and
Blood Vessels Work
Learning Points
• Overview of the heart and the circulatory system
• Coronary artery disease (CAD) and peripheral arterial
disease (PAD)
• Atrial Fib and Heart Failure
• Treatment Options
The Heart
is a muscle the size of your fist located between the
breastbone and the spine just to the left of the midline
inside your rib cage
A women’s heart is smaller in size than a man’s
The Heart
•
Our bodies need oxygen to survive
•
Blood carries oxygen to the whole body
•
The heart pumps the blood (oxygen) through the
arteries to the body tissues
The Heart
• Has four chambers
– two upper chambers
called Atria
– two lower chambers
called Ventricles
• The left ventricular wall is
thicker to be able to pump
with more force
The Heart
• The grade of the left ventricle
indicates the amount of
damage to the heart muscle:
– Grade 1 - normal
– Grade 2 - some damage
– Grade 3 - more damage
– Grade 4 - weakened heart
There are four valves:
– Tricuspid
– Pulmonic
– Mitral - Bicuspid
– Aortic
• valves are strong
and flexible
• allow blood to flow
in one direction
• may be injured or
diseased requiring
repair or
replacement
Circulation of Blood to the Heart Muscle
• Through the Coronary
Arteries
– right coronary artery
– left coronary artery
• circumflex
• left anterior
descending artery
Collateral Circulation
• Collateral circulation
– develops in later age
– arteries grow to make a
natural bypass towards
an area of reduced
blood flow
Heart’s Electrical Conduction
• The Sinoatrial node or
pacemaker beats
60-100 times per minute
• Atrioventricular node can
beat 40-60 times per
minute as a backup
• Bundle of His and
Ventricles can beat 20-40
times per minute as a
further backup
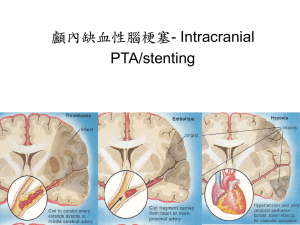
Artery disease = Atherosclerosis
• Process can start before birth
• Gradual buildup of plaque in the arteries
• Narrows the inside diameter of the arteries
• Causes the artery walls to become less elastic
Where can blockages occur?
• Any artery in the body
• Occurs more often in areas where arteries branch
• Most common in arteries to the:
– head - carotid artery disease
– heart - coronary artery disease
– legs - peripheral artery disease
– organs - eg. kidneys, male sex organs
Angina
-reduced blood flow to the heart muscle
• Temporary lack of oxygen to
the heart muscle
– is caused by a narrowing
in one or more of the
coronary arteries
• Treated with Nitrospray and
rest
Angina Symptoms
Men and Women:
• chest pain
• pain into throat and jaw
• pain down one or both arms
• shortness of breath
More common in women:
• fatigue
• shortness of breath
• pain in back between shoulder
blades
• nausea and vomiting
Claudication
-reduced blood flow to the muscles in the lower
extremities
• Temporary lack of oxygen to
one or both of your legs
– is caused by a narrowing
in one or more of the
arteries
• Treated with rest
Reduced blood flow to the brain: signs and
symptoms TIA and Stroke
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Headache
Blurred vision
Slurred speech
Dizziness
Difficulty swallowing
Weakness on one side
Difficulty with balance
How does a Heart Attack occur?
• A sudden severe blockage in a coronary
artery
– caused by plaque rupture and blood
clotting
• Coronary artery spasm
– An involuntary closing of the walls of the
artery. Usually occurs for a short period of
time but can cause severe blockage
• Coronary artery spasm and blood clot
occurring together
Heart Attack Occurs
Other Medical Conditions
• Atrial Fibrillation
• Heart Failure
Atrial Fibrillation
• A rapid and irregular heart beat
• Most common causes are
– Damage to the heart’s
structure
– Diseases affecting the
heart’s valves or pumping
system
– Long term high blood
pressure
– Undetermined cause
Atrial Fibrillation
• Signs and symptoms
– Fast, irregular heart beat
– Weak, lightheaded, confused
– Shortness of breath, chest pain
• Treatment
– Medication – slow down the heart rate
– Pacemaker – to control the heart rate
– Surgical – ablation/maze procedure to change the electrical
pathway
– Blood thinner medication - to prevent blood clots
Heart failure
• The heart is not strong enough to pump enough blood
through the body to meet the demands
• Causes – most common
– Heart attack
– Long term high blood pressure
– Heart valve problems
Heart failure
• Symptoms
–
–
–
–
–
–
Shortness of breath
Difficulty sleeping laying flat
Cough
Fluid retention causing swelling
Sudden weight gain
Fatigue, confusion, impaired memory
Heart failure
• Treatment goal is to manage the problem
– Medications
– Exercise
– Heart devices eg. Pacemaker, ICD
– Surgery - transplant
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnostic Testing – for the heart
• Resting ECG - looking at the heart’s electrical system
from 12 different views
• Holter Monitor/Loop recorders - longer term ECG
monitoring
• Exercise stress test - checking ECG changes while
increasing the work of the heart
• Echocardiogram - heart ultrasound
• Stress Thallium - nuclear dye test with or without a
stress test
• Angiogram - dye test of the heart’s arteries
Diagnostic testing – for the legs and head
• Doppler studies
• Angiograms
Treatments
Interventions
• Angioplasty
• Stent
Stent – Coronary Artery
• A wire mesh tube used to
prop open an artery after
angioplasty
• The stent is placed over the
angioplasty balloon catheter
• When the balloon is inflated
the stent expands
Drug Eluting Stent
• The stent slowly releases
a drug to reduce the
chance of a clot forming
• Used at doctors’
discretion
Angioplasty and stent
Surgical Procedures
Surgical Procedures
•
•
•
•
Pacemakers
Implantable Defibrillators
Endarterectomy
Artery Bypass Grafting (coronary,
carotid, leg arteries)
• Valve Replacement or repair
• Heart Transplantation
Pacemaker
• Stimulates the heart to beat
regularly
• The generator is the size of a
silver dollar and is implanted
just beneath the skin.
• The leads are threaded into
position through veins leading
back to the heart.
Pacemaker
• Battery life is up to 10 years
depending on the usage
• Has the ability to slow down or
speed up the heart rate
• In some models, the heart rate can
be increased with activity
Indications:
• heart rate too slow
• heart rate too fast
Implantable defibrillators (ICD)
• A pacemaker with the ability
to deliver an electrical shock
to correct a life threatening
heart rhythm
• Indications:
• life threatening irregular heart
rhythm
• heart failure
Endarterectomy
• Surgical removal of plaque from the inner lining of an
artery
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)
• Provides a new supply of blood
beyond the site(s) of the blockage
• Indications
– unstable angina that does not
respond to medical treatment
– stable angina with severe left-main
or significant three-vessel coronary
artery disease
Leg Artery Bypass
• Vein from leg or arm,
or synthetic graft is
used to bypass a
blockage in legs
• For severe blockage
when there is a risk
of losing your limb
Valve Replacement and Repair
• Valves must flex, stretch, and hold
back pressure to function normally
• Aortic and Mitral valves are the most
commonly repaired or replaced valves
• 2 types of valves used
– tissue valves from pigs; do not
need to take blood thinners
– mechanical valves; need to take
blood thinners for life
Heart Transplantation
• People who require heart
transplants suffer from severe
heart failure
• 2 major causes of heart
failure are coronary artery
disease (CAD) and
cardiomyopathy
Any Questions?