Ankle Injuries PowerPoint
advertisement

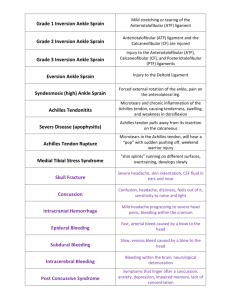
Common Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Sprain Definition: A sprain is a stretch or tearing of one or more ligaments of the ankle. Sprains are generally graded on a scale of I to III depending on their severity. Grade I: slight stretching of ligaments, may have some pain, no significant swelling or discoloration. Grade II: moderate stretching of ligaments, some swelling and discoloration, orthopedic tests will reveal a “soft” endpoint. Grade III: fibers of the ligament are completely torn, usually severe and immediate swelling, orthopedic tests will reveal no endpoint Inversion Sprain Most common mechanism for ankle sprains. Involves one or more of the lateral ligaments of the ankle Eversion Sprain Not that common due to strength of the deltoid (medial) ligament and bony structure. Severe sprains often are accompanied by fractures of the fibula. Sprain Treatment: The immediate treatment for any degree of sprain is rest, ice, compression and elevation. NSAID’s may be taken for pain and swelling. Doctor referral if fracture is suspected. Achilles Bursitis Definition: A bursa is a fluid-filled membrane that lubricates between areas of friction(bone-to-tendon or bone-to-ligament). Bursitis is occurs when the bursa becomes inflamed. Achilles Bursitis S/Sx: Point tenderness over attachment of Achilles to the heel. Swelling may be present. Usually has a gradual onset Achilles Bursitis Achilles Bursitis Treatment: Heat before activity Ice after activity NSAID’s Gentle stretching of Achilles tendon Lingering cases should be referred to a doctor. Achilles Tendonitis Def: Inflammation of the achilles tendon MOI: may be from a single incident but more often from an accumulation of smaller stresses Achilles Tendonitis S/Sx: Usually gradual onset of S/Sx Early on, pain occurs only during activity and slowly progresses to pain all of the time Point tenderness over tendon Swelling may be present Achilles Tendonitis Achilles Tendonitis Treatment: Rest, ice and NSAID’s Gentle stretching of tendon Heat before activity/Ice after activity Taping and/or heel lift Ultrasound Possible doctor referral Heel Contusion Bruise to the heel MOI: stop and go activities or jumping movements S/Sx: Severe pain on bottom of heel, pain with weight-bearing Tx: RICE, taping, donut pad, ultrasound, whirlpool Turf Toe Def: Sprain of the 1st MP joint MOI: kicking object, stubbing toe, dropping heavy object on it, fields with turf. Occurs as foot is planted and the foot and ankle is dorsiflexed. As the shoe grasps the playing surface, body weight and forward momentum force the 1st MP joint into hyperextension. Turf Toe Turf Toe S/Sx: pain during push-off phase of gait, active joint motion or manual resistance. Pain when attempting quick stops . Point tenderness over MP joint, limited ROM Tx: RICE, NSAIDs, ultrasound, tape Medial Tibial Syndrome Def: Shin splints: a general term applied to a variety of conditions that seasonally plague many athletes MOI: factors that may lead to an increase incidence of shin splints are: Biomechanical factors Change in intensity, duration, or frequency of workouts Improper or worn footwear Change in surface Improper warm-up and cool-down Change in type of workout Shin Splints S/Sx: Grade I: pain after activity GradeII: pain before and after activity not affecting performance Grade III: pain before, during and after activityand affecting performance Grade IV: pain so sever that performance is impossible Shin Splints Tx: varies by individual Constant heat (whirlpools and US) with taping NSAIDs Ice massage before or after Stretching of anterior and posterior structures Fractures Definitions: Fractures of the foot and ankle can occur in any number of places. The fibula is a non-weightbearing and can be fractured by a direct blow. Fractures of the tibia are often accompanied by a fracture of the fibula. Fractures S/Sx: Fractures of the fibula may not display any gross deformities. There will be point tenderness and a positive percussion test. The person may be able walk. Tib/Fib fractures will have a gross deformity. The athlete will not be able to bear weight. Fractures Treatment: For a suspected fibular fracture, the athlete should be immobilized and referred to a doctor. For a Tib/Fib fracture, try to calm the athlete down and monitor for signs of shock. Check for pulse and sensation distal to the injury site. Splint and send immediately to a hospital (or call 9-1-1) Tib/Fib fracture at moment of impact