8-4
advertisement

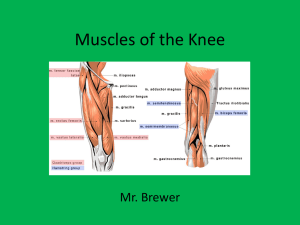
Sports Medicine Camp The Thigh and Hip Muscles Anatomy, Injuries and Assessment Quadriceps Muscles • • • • Vastus Medialis Vastus Intermedius Vastus Lateralis Rectus Femoris Ely’s Test or Prone Knee Bend • Rectus Femoris tightness – Athlete prone – Passive knee flexion – Positive test indicated by hip flexion Quadriceps MMT • Manual Muscle Test – Athlete seated – Examiner apply resistance at lower leg Rectus Femoris Strain • Mechanism of Injury – Sudden stretch – Sudden contraction • Signs and Symptoms – – – – – Pain Point tenderness Spasm Loss of function Deformity • Treatment – – – – – RICE NSAIDS Modalities Stretching Strengthening Thigh Contusion Hamstrings Muscles • Lateral side – Biceps Femoris Long Head – Biceps Femoris Short head • Medial side – Semitendinosus – Semimembranosus Hamstrings MMT • Medial hamstrings – – – – Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Internally rotate tibia (foot points in) • Lateral Hamstring – Biceps Femoris – Externally rotate tibia – (foot points out) Hamstring Strains • Mechanism of Injury – Unknown – 1st Theory • Hamstrings contract same time as quadriceps • Deficiency in complementary action of opposing muscles – 2nd Theory • Quick change of function from – Role as knee stabilizer – To – Hip extensor – Possible reasons • • • • • • • Muscle fatigue Faulty posture Leg length discrepancy Tight hamstrings Improper form Imbalance of strength between hamstrings Hamstring strength ratio to quads normal 60 - 70 % Hamstring Strains • 1st Degree injury – Muscle soreness during movement • Due to muscle spasm rather then tearing of tissue • Fewer then 20% fibers torn – Point tenderness – Stiffness after cool down • 2nd Degree injury – – – – – Partial tear Fewer then 70% fibers torn Sudden snap or tear of muscle Severe pain Loss of function Hamstring Strains • 3rd Degree injury – – – – – – – Rupture of tendon Tear of > 70% fibers Severe swelling Tenderness Loss of function Discoloration Palpable mass or gap Hamstring Strains – Treatment • Grade 2 & 3 – Extremely conservative • RICE – Grade 2: 24 - 48 hrs. – Grade 3: 48 - 72 hrs. • Stretching • Strengthening – Emphasize eccentric exercise – Complications • Recurrent as result of – Inelastic fibrous scar tissue Hip Flexors – Iliopsoas • Psoas Major • Psoas Minor • Iliacus – MMT Thomas Test – – – – – Normal length of hip flexors With low back flat Posterior thigh touches table Knee flexes approximately 80° The pelvis is in 10 ° posterior tilt – Abnormal length of hip flexors – With low back flat – Posterior thigh does not touch table – Knee flexes < 80° Hip Flexor Support Adductor Muscles • • • • • • • • • MMT Adduction Athlete sidelying Examiner supports top leg Give resistance above knee joint Adductor Magnus Adductor Longus Adductor Brevis Pectineus Gracilis Adductor Support 8-4 Hip Pointer • Mechanism of injury – Direct impact • Signs and Symptoms – – – – – One of the most handicapping injuries Immediate pain Muscle spasm Transitory paralysis Inability to • rotate trunk • Flex thigh – Discoloration – Swelling • Treatment – PRICE • Bed rest as needed • Crutches as needed – ROM exercises – Strength exercises – Severe cases MD referral 21-34