PPT-4
advertisement

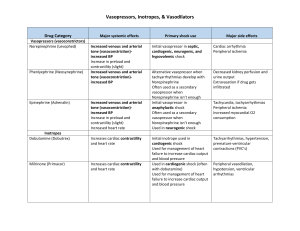
Shock Dr Mike Nicholls Emergency Medicine Consultant Auckland City Hospital 2011 Shock Definition: Inadequate oxygen delivery and utilisation by vital organs due to a problem with the circulation. Types of shock Hypovolaemic Distributive Cardiogenic Obstructive Shock…look at the observations Usually can be recognized by the observations and peripheral circulation Classic obs are Tachycardic (>90bpm), Hypotensive (<90-100mmHg), Others Shock index (pulse/systolic BP) >1 Tachypnoeic Confused Classic peripheral circulation would be delayed capillary refill and cool peripheries What can be done? Oxygen IV access x2 large bore Fluid bolus… 0.9%saline…at least 1000ml. Usually significantly more than this. When concerned re CCF, can try 500ml bolus at first (or 250ml if very concerned) Observe response Consider urinary catheter (further monitoring and obtain sample) Placement : monitoring, resus Specific treatment (depends on the cause) Hypovolaemic Hypovolaemic (blood loss) Get help : surgical emergency call ABC Blood loss : iv fluids +/ blood+/ Direct pressure surgery (arrest bleeding) Distributive Sepsis Anaphylaxis Neurogenic Sepsis Sepsis = 2 or more SIRS criteria + suspected or proven infection (1992) SIRS Temperature >38°C or <36°C Heart rate > 90 beats/min Respiratory rate > 20 breaths/min or PaCO2 <32 torr (<4.3kPa) WBC > 12.000 cells/mm3, <4.000 cells/mm3, or >10% immature (band)forms Distributive Management Distributive Sepsis : IV antibiotics, iv fluids, IV inotropes (ARISE trial) Anaphylaxis : IM adrenaline, iv fluids, steroids, antihistamines Cardiogenic Arrhythmia Primary pump problem Valve problem (acute) Cardiogenic Management Cardiogenic (iv fluid) Tachyarrythmia : DC/chemical cardioversion Bradyarrythmia : Atropine, pacing Pump problem : Inotropes PCI Obstructive PE Tension pneumothorax Pericardial tamponade Valvular obstruction Obstructive PE : heparin, fibrinolytic Tension pneumothorax : Needle decompression Pericardial effusion : Pericardiocentesis Shock : What can be done? Summary Oxygen IV access x2 large bore Fluid bolus… 0.9%saline…at least 1000ml. Usually significantly more than this. When concern re CCF, can try 500ml bolus at first (or 250ml if very concerned) Observe response Consider urinary catheter (further monitoring and obtain sample) Placement : monitoring, resus Specific treatment (depends on the cause) But… Beware…young people Elderly Pregnant Those on beta blockers Remember the observations!