Epidural Hematoma硬膜外血肿
advertisement

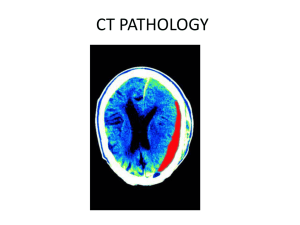
脑血管病及颅内感染 脑血管病 HEMATOMA IN CT 血肿的CT表现 Inatially, high attenuation. higher attenuation than brain but less than bone (35-80 Hu). Over several days to weeks, gradual decrease in attenuation. Hypodensity to cystic cavity. ACUTE HEMATOMA急性血肿 mild edema轻度水肿 SUBACUTE HEMATOMA 亚急性血肿 CHRONIC HEMATOMA慢性血肿 HEMATOMA IN MRI Acute (deoxyhemoglobin)急性期(脱氧血红蛋白 ) T1WI: Isointensity to mild hypointense 等到低信号 T2WI: Very high hypointense高信号 Early subacute(intracellular methemoglobin) 亚急性 早期(细胞内高铁血红蛋白) TIWI: Increasing hyper-intensity T2WI: Hypo-intensity initially, changing to isointense HEMATOMA IN MRI Late subacute (Extracellular methemoglobin) 亚急 性晚期 (细胞外高铁血红蛋白) T1WI: Hyper-intensity T1WI高信号 T2WI: Hyper-intensity centrally T2WI中 心高信号 Chronic (Hemosiderin-laden macrophages remain) 慢性期 (含铁血黄素) A thin, hypointense rim appears TIWI: Hypo-intensity decreases over time T2WI: Rim of hypo-intensity increases, central hyperintensity decrease, leaving only a low signal intensity scar ACUTE HEMOTOMA :DEOXYHEMOGLOBIN ACUTE HEMATOMA SUBACUTE HEMOTOMA CHRONIC HEMATOMA HEMOSIDERIN 慢性期(含铁血黄素) CEREBRAL INFARCTION 脑梗塞 The most common etiology of cerebral ischemia or infarction in the adult is occlusion of an artery resulting from either thrombus formation or embolism, with atherosclerosis the most common underlying cause在成人,脑缺血或脑梗塞最常见 病因是动脉闭塞,通常是血栓或动脉粥样硬化。 Carotid artery disease is especially common颈动脉疾 病尤其常见。 CEREBRAL INFARCTION ISCHEMIC INFARCTION缺血梗死 HEMORRHAGIC INFARCTION 出血性梗死形成 LACUNAR INFARCTION腔隙梗塞 Imaging appearance CT is often normal in the first few hours of infarction or ischemia, sometimes for up to 24 hours. 在梗死或 缺血的最初几个小时,CT上通常表现为正常, 有时甚至至24小时。 Subtle effacement of sulci may be an important early clue to infarction . 脑沟的细微消失可能是梗死的 重要征象。 Imaging appearance Some of the very earliest signs of MCA or internal carotid artery infarction on CT . A. Loss of the insular strip of gray matter (loss of graywhite matter distinction) B. Low attenuation in the ipsilateral caudate head if the perforating arteries are also affected C. A high attenuation MCA, representing clot within the artery Imaging appearance With time, there is increasingly well-defined low attenuation in an area of infarction because of cytotoxic and vasogenic edema. Mass effect 占位效应 Thrombotic infarctions often involve a large vascular distribution, embolic infarctions usually involve only a portion of a major arterial territory. The typical vascular distribution, often wedgeshaped and extending to the cortex. Imaging appearance MRI is more sensitive than CT for early changes of infarction, but in the first few hours after vascular occlusion, MRI also may appear normal. DWI, PWI may provide earlier evidence of infarction.对梗死的早期变化MRI较CT敏感, 但是在血管闭塞最初的几个小时,MRI也可 是正常的。DWI,PWI能提供更早的梗死证 据。 T1WI --- low signal intensity低信号强度 T2WI --- high signal intensity高信号强度 FLAIR --- high signal intensity高信号强度 Loss of the insular strip of gray matter Subtle effacement of sulci脑沟的微小消失 ACUTE INFARCTION LOW DESITY and MASS EFFECT低密度和占位效应 SUBACUTE INFARCTION LOW DENSUTY AND GYRIFORM ENHANCEMENT CHRONIC INFARCTION LOW DENSUTY and ATROPHY ACUTE INFARCTION LONG T1、 LONG T2 and MASS EFFECT T1WI T2WI Flow-void effect 流空效应 CHRONIC INFARCTION GYRIFORM ENHANCEMEMT HEMORRHAGIC INFARCTION 出血性梗死形成 LACUNAR INFACTION腔隙性梗死 hyperacute infarction 梗死的超急性期 Acute infarction shows decreased diffusion, chronic infarction showing increased diffusion. Clinical DWI can identify acute ischemic lesions that are not apparent on T2Weighted MR images. DWI能分辨出无 法在T2上显示的 急性缺血部分 INTRACRANIAL INFECTION 颅内感染 The key diagnostic evidence in suspected meningitis comes from cerebrospinal fluid analysis and culture, imaging has an adjunctive role only.脑膜炎的主要诊断依据是脑脊液分析 和培养,图像仅仅是从属地位。 Imaging may detect processes such as abscess and encephalitis, may localized focal conditions, and may help demonstrate the progress or resolution of infection图像可以显示脓肿和脑炎 的征象,可帮助确定炎症的进展或消退。 INTRACRANIAL INFECTION Bacterial meningitis is common and is associated with serious morbidity. 细菌性脑膜炎是常见的,有较高的死亡率。 Inflammatory exudates may obscure the subarachnoid cisterns on noncontrasted CT, whereas meningeal enhancement may be observed on CT or MRI following intravenous contrast material administration. (meninges thickening)在非对比的CT上炎性渗 出物可以使蛛网膜下腔模糊,而给予静脉造影剂后脑膜增 强就可以在CT或MRI上观察到(脑膜变厚) Lack of visible contrast enhancement does not exclude meningitis.缺少可见的对比增强不能排除脑膜炎。 INTRACRANIAL INFECTION Imaging is important for evaluating complications of meningitis.影像学评估脑膜炎的并发症是重要的 Communicating hydrocephalus交通性脑积水 Vasculitis or vasospasm血管炎或血管痉挛 Ischemia or infarction缺血或梗死 Subdural fluid collection硬膜下积液 Spread of infection (e.g. ventriculitis)感染扩散(脑室炎) ABSCESS 脑脓肿 Abscess of the brain usually begins as cerebritis. Cerebritis is initially detected as an area of low attenuation edema on CT or of high signal intensity on T2WI and low signal intensity on T1WI MRI. With time cerebritis progresses to abscess. 脑脓肿通常起始于脑炎。脑炎被最早发现是在CT 上是低密度的水肿区或在MRI上T2高信号影,T1 低信号影。随时间推移,脑炎可发展为脑脓肿。 ABSCESS Abscess wall is usually fairly thin and uniform, high density on CT, low signal intensity on MRI脓肿壁在 CT上通常较薄,厚薄不甚不一致,呈高密度,在 MRI上则呈低信号。 Surrounding edema周围水肿 Central fluid attenuation or signal intensity 中心液化区呈水样信号强度 Well-defined ring-like pattern of enhancement 边界清楚的环状强化 ABSCESS Abscess wall is usually fairly thin and uniform, high density on CT. ABSCESS Abscess wall is usually fairly thin and uniform low signal intensity on MRI The differential diagnosis between cerebral abscess and cystic tumor 脑脓肿和囊性瘤的鉴别诊断 Bulk phase容积相 Abscess脓肿 Hydration layer水 Multiform glioblastoma 多形恶性胶质细胞瘤 TUBERCULOUS MENINGITIS 结核性脑膜炎 TUBERCULOUS MENINGITIS 结核性脑膜炎 meninges thickening 脑膜增厚并强化 Cranial Trauma Skull颅骨 Penetrating injury穿透性损伤 Closed head injury闭合性头部损伤 Hemorrhage出血 Mass effect占位效应 Shift of intracranial structure颅内结构的移位 Secondary effects: 继发效应 infarction, hydrocephalus梗死,脑水肿 1. 脑挫裂伤 Gunshot枪弹伤 2. Intracranial hemorrhage颅内出血 •Extra-axial hematoma Subdural hematoma硬膜下血肿 Epidural hematoma硬膜外血肿 subarachnoid hemorrhage蛛网膜下腔血肿 •Intraventricular hemorrhage脑室内血肿 •Intra-axial hematoma Hematoma血肿 Acute hemorrhage is usually dense (bright) on CT. 急性出血通常在CT上是高密度(亮的) On MRI, the signal of hematoma is depended. 而在MRI上,血肿信号是不确定的 3. Epidural Hematoma 硬膜外血肿 Usually result from arterial bleeding, often from laceration of the middle meningeal artery by a squamosal temporal bone fracture . However, venous or mixed sources also may cause epidural hematoma. 通常来自动脉出血,常见的是颞骨鳞部骨折导 致的脑膜中动脉破裂。但是静脉或者混合来源 的也可以导致硬膜外血肿。 Epidural Hematoma硬膜外血肿 Extra-axial Do not cross sutures不越过颅骨缝 Usually with convex margins or a lentiform shape通常是凸面的或者是透镜状 Mass effect占位效应 Fracture骨折 lentiform shape凸透镜状 EPIDURAL HEMATOMA硬膜外血肿 Pneumatosis积气症 EPIDURAL HEMATOMAS 4. Subdural Hematoma 硬膜下血肿 Usually result from venous bleeding 通常来自静脉出血 The most common location is over the cerebral convexities 最常见的位置是脑的凸面 Subdural Hematoma硬膜下血肿 Extra-axial May cross sutures可以越过颅骨缝 Usually extending widely across the convexity and appear crescentic (new moon, luniform)通常越 过凸面,显示为新月形 Mass effect占位效应 Skull fracture (sometimes)颅骨骨折(有时) extending widely across the convexity横跨脑的凸面 SUBDURAL HEMATOMA SUBDURAL HEMATOMA SUBADURAL HEMATOMA 先天发育畸形 DISPLASIA OF CORPUS CALLOSUM 胼胝体发育不良 May be an isolated anomaly or part of a more extensive malformation complex. May be partial or complete agenesis.分为部分性或完全性 The interhemispheric lipomas are often bulky in the absence of the corpus callosum. DISPLASIA OF CORPUS CALLOSUM Lateral ventricles have a more parallel configuration, with crescent-shaped frontal horns. Occipital white matter is undeveloped . Dilatation of the atria and occipital horns. The third ventricle is usually dilated with upward herniation to the interhemispheric fissureAbsence of corpus callosun. DISPLASIA OF CORPUS COLLUSUM Lateral ventricles have a more parallel configuration, with crescent-shaped frontal horns侧脑室平行,新月形前角 DISPLASIA OF CORPUS COLLUSUM Absence of corpus callosun 课后复习题: 1、脑梗塞的影像学特点有哪些? 2、脑出血的影像学特点有哪些? 3、颅内感染的影像学特征。