Cosmetic Surgery - CriticalCareMedicine
advertisement

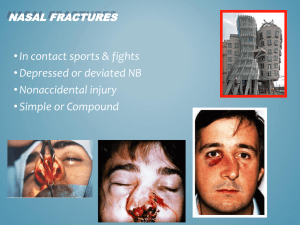
Cosmetic Surgery Complications in the ER: When Vanity Turns to Calamity Jamil Ahmad, MD, FRCSC The Plastic Surgery Clinic, Mississauga, Canada Hand Program, University Health Network, Toronto, Canada Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada CRITER 2014 Disclosures • Book royalties from CRC Press Cosmetic Surgery • Demand continues increase • Surgical and nonsurgical procedures What is an aesthetic surgery emergency? An Approach to ER Cosmetic Surgery Emergencies • Uncommon • Most patients with issues are seen in clinic However… there are some rare and devastating complications Liposuction • Significant fluid shifts • Lidocaine and epinephrine added to infiltration solution Liposuction • Complexity is underestimated Liposuction • • • • DVT/PE Lidocaine/bupivacaine toxicity Fat embolism Intraabdominal injury Venous Thromboembolism • DVT or PE • Any procedure • Body contouring VTE Treatment • Prevention • • • • Individual Procedural Duration Decreased mobility DVT/PE DVT PE • • • • • • • • • • • Leg swelling Leg pain Warmth Discolouration Leg fatigue • D-dimers • Duplex U/S Pleuritic chest pain Shortness of breath Coughing Tachycardia/palpitations Anxiety Sweating • D-dimers • ECG • CTA Wells Scoring System Remember… If you have a high index of suspicion, start treatment immediately Lidocaine/Bupivacaine Toxicity • Lidocaine in infiltration solution • Max dose differs compared with local anesthetic injection dose • Peak lidocaine serum concentration 6-12 hours after infiltration • Bupivacaine for postop analgesia Signs and Symptoms of Lidocaine Toxicity CNS Respiratory and CV • • • • • • • • • • • • Respiratory depression and arrest • Cardiovascular depression and collapse Perioral tingling Metallic taste Lightheadedness Dizziness Visual disturbances Tinnitus Disorientation Drowsiness Convulsions Loss of consciousness Coma Treatment • Evacuation of local anesthetic • Supportive • Intralipid 20% 1.5mg/kg IV bolus, 0.25mg/kg IV infusion for 60 mins Fat Embolism • • • • Liposuction Fat injection Extremely rare Potentially life threatening Signs and Symptoms of Fat Embolism Respiratory Neurological • Dyspnea • Tachypnea • ARDS • Precede respiratory symptoms by 6-12 hours • Disorientation • Coma • Cerebral edema Signs and Symptoms of Fat Embolism Petechia Ophthalmological • 2-3 days after injury • Head, neck, anterior chest, subconjuntiva, axilla • Macular edema • Retinal hemorrhages Investigations • • • • Nonspecific ABG Chest x-ray CT/MRI brain Treatment • Supportive Intraabdominal Injury • Cannula • Fascial sutures Intraabdominal Injury • Delay in diagnosis • Soft tissue infection • Acute abdomen • Hemodynamic instability Breast Augmentation • Hematoma • Implant infection • Pneumothorax Hematoma • Expanding • Vascular compromise • Pain Pneumothorax • 1 in 3 surgeons have had at least 1 patient • Subcutaneous emphysema is common • Gas in pleural cavity is abnormal Mastopexy/Breast Reduction • Hematoma • Nipple-areolar complex necrosis Treatment • Remove sutures • Evacuate any hematoma • Nitropaste TID Rhinoplasty • Epistaxis • CSF Rhinorrhea/ Intracranial injury • Toxic shock syndrome • • • • • • • • • • Epistaxis Head elevation Oxymetazoline nasal spray Pressure Anterior nasal packing Removal of internal splints Irrigation Silver nitrate Posterior nasal packing Exploration in OR Angioembolization CSF Rhinorrhea/Intracranial Injury • • • • • • Septal surgery Osteotomies CSF rhinorrhea Neurological changes CT head Neurosurgical consultation Toxic Shock Syndrome • Nasal packing/nasal splints • Breast implants • Staph aureus or Group A Strep Signs and Symptoms of Toxic Shock Syndrome Symptoms Influenzalike Syndrome • Influenzalike syndrome • Confusion • Signs of soft tissue infection • • • • • • Fever Chills Myalgia Nausea Vomiting Diarrhea Signs and Symptoms of Toxic Shock Syndrome Symptoms CDC Criteria • • • • • • • • • Fever Rash Hypotension Systemic evidence of toxicity Fever Rash Desquamation Hypotension Multisystem involvement in 3 or more systems – – – – – – – GI Muscular Mucous membranes Renal Hepatic Hematological CNS Blepharoplasty • Retrobulbar hematoma • Blindness Signs and Symptoms of Retrobulbar Hematoma Symptoms Signs • Severe pain • Visual changes • Tense or expanding proptosis • Diminished extraocular movements • Retinal/optic disc pallor • Increase intraocular pressure • Loss of pupillary reflexes • Scleral hematoma – Decreased visual acuity – Amaurosis fugax – Scintillating scotomas Treatment • Remove sutures • 95% O2/5% CO2 • 20% mannitol 1.5-2g/kg IV, 12.5g over 3 mins, remainder over 30 mins • Acetazolamide 500mg/IV • Methylprednisolone 100mg IV • Betaxolol 1 drop • Lateral canthotomy Soft Tissue Fillers • 2nd most common cosmetic procedure • Injectables for filling, volume • Hyaluronic acid most common • Everyone is doing it Intravascular Injection • Inadvertent intravascular injection • Vascular territory • Ischemia leading to necrosis • Soft tissue fillers or fat injections • Very rare Prompt diagnosis critical Symptoms • Unremitting pain, almost immediate onset Treatment • Plastic Surgery/Dermatologist consultation • Gentle massage Injection of hyaluronidase (10 IU/0.1 mg HA injected) • Warm area • ASA 81 mg PO qday • Nitropaste TID • Hyperbaric oxygen Blindness Blindness • Visual field defect • Ophthalmoscope exam shows emboli • Ophthalmology consultation • Poor prognosis Energy Based Procedures • Lasers • RF • IPL Energy Based Procedures Complications • Burns • Scarring Treatment • Update tetanus • Polysporin • Silver sulfadiazine cream • Referral NY Times, June 20, 2010 Dunning-Kruger Effect • Cognitive bias manifesting in unskilled individuals suffering from illusory superiority, mistakenly rating their ability much higher than is accurate The Unknown Unknowns ‘Reports that say that something hasn't happened are always interesting to me, because as we know, there are known knowns; there are things we know we know. We also know there are known unknowns; that is to say we know there are some things we do not know. But there are also unknown unknowns -- the ones we don't know we don't know. And if one looks throughout the history of our country and other free countries, it is the latter category that tend to be the difficult ones.’ Donald Rumsfeld, 2002 Summary • You’re going to see these patients • Communication (and documentation) is key • Recognition of major complications