High Risk Intrapartum Nursing
advertisement

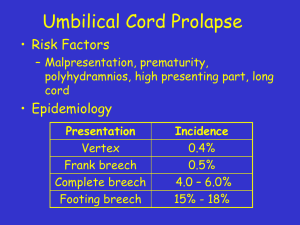
Developed by D. Ann Currie RN, MSN Preterm Labor Premature Rupture of Membranes Dystocia Labor Dysfunctions Precipitous Labor and Birth Fetal MalPositions Fetal Malpresentations Shoulder Dystocia Prolapsed Umbilical Cord Cephalopelvic Disproportion Placenta Problems Lacerations Define as a labor that occurs between 20-37 weeks of pregnancy Prematurity is the number one cause of neonatal mortality in USA. Preterm births occurs in 11-12% of births Many factors may place a woman at risk for preterm labor: such as antepartum hemorrhage trauma infections lower socioeconomic status Multiple gestation See text for other causes Clinical Manifestations of PTL: Abdominal Pain Back Pain Pelvic Pain Menstrual –like Cramps Increased Vaginal Discharge Pelvic Pressure Urinary Frequency Diarrhea Bedrest Pelvic Rest Hydration Medications: Tocolytics: Beta agonists- terbutaline Magnesium Sulfate Calcium Channel BlockersNifedipine (Procardia EL) Indomethacin (Indocin) Others: Antibiotics Fetal Demise Lethal Fetal Anomaly Severe Preeclampsia/ eclampsia Hemorrhage/Abruptio placenta Chorioamnionitis Severe Fetal Growth Restriction Fetal Maturity Acute Nonreassuring Fetal Heart Pattern Teach all pregnancy clients the clinical manifestations of PTL and to report to their health care provider if they occur. Teach self care measures to prevent PTL Teach and assist in treatment of PTL Prevent complications of TreatmentProlong bedrest Tocolytic medications PROM is defined as rupture of membranes one hour prior to labor starting. Premature Premature Rupture of Membrane is rupture of membranes prior to 37 weeks. (PPROM) Complications associated with PPROM: Preterm labor Infections Oliohydramnios Abruptio Placenta Fetal Problems-IUGR, Pulmonary Hypoplasia, and other Defined as an abnormal labor pattern that may occur because of abnormalities in the power, the passenger, or the passage. It may encompass many things in labor. Primary Labor dysfunction: Hypertonic Labor Pattern is ineffectual uterine contractions of poor quality occurring in the latent phase of labor. UC are painful but do not dilate or efface the cervix. It may cause: Increased discomfort Fatigue Stress Dehydration Infection Nonreassuring Fetal Heart Pattern Management: Rest Hydration Sedation - Sedatives such as : Seconal Dalmane Morphine Sulfate This is poor uterine contractionsirregular or low amplitude. If not caused by CPD Management: Oxytocin (Pitocin) Augmentation It is when the entire process of labor and birth occurs within 3 hours. Precipitous Labor is when cervical dilation is 5cm or more per hour for a primigravida and 10 cm per hour for a multipara. Precipitous birth is a sudden birth It may be unattended or nurse attended birth. Complications: Abruptio placenta Lacerations Fetal Risks: MAS, Brachial Palsy, Intracranial Trauma Management: Closely monitor Scheduled induction in control environment with physician available Occiput posterior position (OP) is the most common mal position. The client experiences intense BACK PAIN while in labor. Complications: Pain 3rd or 4th degree lacerations or extension of episiotomy Arrest of decent C/S Position- Side –lying Hand-and-knee position Pelvic Rocking Counter Pressure in small of back Physician may have to assist in turn baby with forceps or vacuum extraction Breech Brow Face Shoulder Complex Breech Presentation is the most common malpresentation About 4% of all Births Frank Breech is the most common type of Breech. It is characterized by flexed hips and extended knees. Footling Breech is characterized by one or both feet presenting. Complete Breech Head Entrapment Prolapsed Cord MAS Fetal Asphyxia and Hypoxia Increased Risk for perinatal morbidity and morality. Brow Presentations are the least common of all presentations. In a Brow presentation the forehead is the presenting part. Results in a prolonged labor or secondary arrest of labor. C/S is best for delivery Complications: Extension of episiotomy or lacerations Birth injuries to fetus: cerebral or neck compression Damage to the trachea and larynx. Infant Mortality A Mentoanterior position can be delivered vaginally. A Mentoposerior position can not be delivered vaginally. Complications of a face presentation: Prolonged labor Infection C/S Facial Trauma Transverse Lie Vaginal Birth is impossible Cesarean Birth Possibility of Prolapsed Cord if Membranes Rupture An Obstetric Emergency Occurs with : Macrosomic fetuses. Obese woman or excessive weight gain during pregnancy. Woman of short statue. Management: McRoberts maneuver Client should bring back legs/ thighs against abdomen The nurse will apply suprapubic anterior pressure to release anterior shoulder. When the umbilical cord precedes the fetal presenting part. The cord may fall or be washed down through the cervix into the vagina or Trapped between the presenting part and the maternal pelvis Occult cord prolapse may lay beside or just ahead of the fetal head Ant time the presenting part is not well engaged or firmly against the cervix, a prolapsed cord can occur. This is an emergency because the cord can be compressed causing hypoxia and possible fetal death. Prevent cord compression by manually preventing presenting part compressing the cord Position- Knee-Chest position ( gynopectorus position) or Tendelburg Immediate Cesarean Section is needed Remember to cover client when going through hall. Abruptio Placenta Placenta Previa Placenta and Umbilical Cord Variations Placenta Adherence : Placenta Accreta Placenta Increta Placenta Percreta Placenta Accreta: is when the chorionic villi attaches directly to the myometrium. This is the most common form of placenta adherence. Placenta Increta is when the placenta invades the myometrium. Placenta Percreta is when the placenta penetrates the myometrium. Complication is maternal hemorrhage. Depending on the amount and depth of involvement will determine treatment First Degree Laceration is limited to the fourchette, perineal skin, and vaginal mucous membrane. Second Degree Laceration involves the perineal skin, vaginal mucous membrane, underlying fascia, and the muscles of the perineal body. Third Degree Laceration extends through the perineal skin, vagina mucous membranes , and perineal body and involves the anal sphincter and may extend up the anterior wall of the rectum. Fourth Degree Laceration extends through the rectal mucosa to the lumen of the rectum. Care: Get order for ice pack Pain medications Stool Softener Pericare Sitzbath Remember nothing in rectumNo Suppostories No Enemas No Rectal Exams