osa talk
advertisement

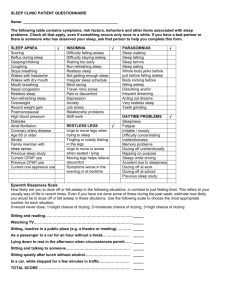
OSAHS Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Hypopnoea Syndrome Liam Doherty Consultant Respiratory Physician, Bon Secours Hospital, Cork Definition OSAHS is characterized by recurrent episodes of partial or complete upper airway obstruction during sleep Who cares? Kaplan-Meier survival curve for cardiovascular death in CPAP treated and untreated patients. Aaa 100 % surviving 95 90 85 Untreated group N=61 p=0.009 CPAP group 80 N=107 75 0 25 50 75 100 time (months) Doherty et al - CHEST 2005; Who? Who else? Children Cranio-facial abnormalities –Micrognathia, macroglossia Neuro-muscular diesases Syndromes –Downs, Prada-Willi, Treacher-Collins, Pierre-Rubin Miscellaneous –Pregnancy, Renal failure, hypothyroid, CVA How common? The Occurrence of Sleep-Disordered Breathing among Middle-Aged Adults Terry Young, Mari Palta, Jerome Dempsey, James Skatrud, Steven Weber, and Safwan Badr 1993;328:1230-1235 n=602 symptoms Classical symptoms of OSAHS Excessive daytime sleepiness Heavy snoring Witnessed apnoeas/nocturnal choking Other symptoms Dyspepsia Nocturia, Enuresis Nightmares Insomnia Excess sweating Assessing sleepiness Epworth Stanford Sleepines Score (ESS) Sleepiness Scale Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT) Maintenance of Wakefulness Test (MWT) Oxford Sleep Resistance test (OSLER) Epworth Sleepiness Scale Use the following scale to choose the most appropriate number for each situation: 0 = would never doze or sleep 1 = slight chance of dozing or sleeping 2 = moderate chance of dozing or sleeping 3 = high chance of dozing or sleeping Situation-Chance of Dozing or Sleeping 1. Sitting and reading 2. Watching TV 3. Sitting inactive in a public place 4. Being a passenger in a motor vehicle for an hour or more 5. Lying down in the afternoon 6. Sitting and talking to someone 7. Sitting quietly after lunch (no alcohol) 8. Stopped for a few minutes in traffic while driving Diagnostic tests Polysomnography Limited (PSG) sleep studies e.g. embletta Overnight oximetry PSG :- Montage EEG C4/A1 or C3/A2 EOG Chin and anterior tibialis EMG ECG Blood Pressure (optional) Airflow Saturations Sonogram Respitrace – rib – abdomen – Sum Diagnosis of OSA Apnoea:- cessation of airflow > 10sec Hypopnea:- > 30% reduction in airflow accompanied by > 4% drop in O2 saturations and/or an arousal. Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Diagnosis of OSA AHI >5 AHI 15-30 AHI >30 mild moderate severe This must only be interpreted with symptoms i.e. Epworth Score, and cardiovascular risk factors e.g. Hypertension, IHD, CVA, arrhythmias Treatment Conservative – Lose weight – Reduce alcohol – Proper sleep hygiene – Sleep on side Nasal CPAP therapy Oral appliances – Tongue-retainers – Anterior mandibular displacement Surgery – Septoplasty – Tonsillectomy – Polypectomy – Pharyngoplasty – UPPP (uvulo-palato-pharyngo-plasty) – Tracheostomy Take home messages Very common disorder (2-4% population) Substantial morbidity and ?mortality Diagnosis by sleep studies Very easy to treat On successful treatment, huge improvements in quality of life “I want to die peacefully in my sleep like my Grandfather, not screaming in terror like the other passengers in his car” Anonymous