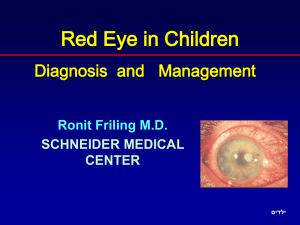
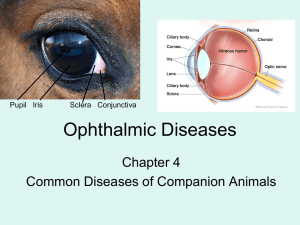
The Red Eye and Ocular Trauma Presentation
advertisement
The Red Eye and Ocular Trauma Stories from Internship Dr Nicholas Cheng Cases – Case 1 • You are on your first ED shift in Horsham. It’s Saturday morning and you’re the only doctor in ED, you’ve dealt with a few footy injuries, broken arms, ruptured spleen and now for a simple red eye. But then you realise you’ve skipped that week of med school when they showed you how to use the slit lamp… Uh oh. • Phew, a letter from the GP accompanies the patient. • “Dear doctor at Horsham ED, this young Aboriginal woman presents with 8 days of unilateral red eye with purulent discharge. I’ve started her on some topical antibiotics but it has not improved. She now has a rash and some swelling around her eye, I’m worried she has periorbital cellulitis.” Papillae vs Follicles Follicles Papillae What type of conjunctivitis? Appearance? Viral Chlamydial Greyish ‘Grains of rice’ - Opalescent ovoid elevations Vessels pass over the top rather than within follicles Allergic Bacterial ‘Velvety’ - Cone-shaped elevations with central vascular channel Composition? Foci of hyperplastic lymphoid tissue Hyperpalstic epithelium with vascular tuft Where? Most prominent in fornices Most prominent in palpebral and limbal conjunctiva Chlamydial Conjunctivitis • Symptoms: Chronic conjunctivitis – Subacute • Signs: Mucopurulent discharge, Large follices predom in inferior fornix • Ix: PCR • Rx: Azithromycin 1g single dose, reportable disease Trachoma • Chronic conjunctivitis, • Third most common cause of blindness worldwide - Leading cause of preventable blindness • Cxs: ▫ Cicatricial change with entropion, trichiasis, dry eye and secondary corneal ulceration and scarring • Rx: WHO SAFE – Surgery, Abx, Face washing, Enviro improvement Conjunctivitis Bacterial Viral Common causes Hx Staph, Strep, Hib Adenovirus HSV Gritty/FB sensation Ex Purulent discharge Papillae Recent URTI Usually unilateral then bilateral Watery discharge Follicles Pre-auricular lymphadenopathy Rx • Bathe crusts off eyelids • Topical Abx (Chlorsig 0.5% drops, 1% ointment) Duration 4-5 days with Rx 10-14 days without Rx Allergic Itch! Hx of Atopy Mucoid discharge Papillae Symptomatic – lubrication, Avoid precipitants cool compresses Cool compresses Antihistamine eye drops (Olopatidine 0.2% Patanol) Self-limiting 7-10 days Periorbital Cellulitis • Anatomy: Infection ANTERIOR to orbital septum • Path: Periorbital trauma, dermal infection • Sxs: Normal VA, unilat tender, red, swollen eyelids, low grade fever • Rx: Augmentin 875/125mg BD for 7 days, Warm compresses Orbital Cellulitis • Anatomy: Infection POSTERIOR to orbital septum • Path: Sinus infection, trauma, extension of periorbital cellulitis, haematogenous • Sx: Decreased VA, diplopia, fever, headache • Ex: Proptosis, red swollen eyelids, ophthalmoplegia ▫ Optic nerve involvement? RAPD, disc swelling • Ix: CT Orbit • Rx: IV Abx (fluclox 2g IV QID+ ceftriaxone 2g IV Daily) Case 2 • You survived Horsham ED. Now you’re onto Colorectal surgery at RMH, surely no eyes involved there. • Then goes the dreaded pager. Just a handover from the night intern to say one of your patients had a fall overnight but is fine except for a little bit of a red eye and some bruising under the eye. Subconjunctival haemorrhage Orbital Fractures Orbital Fractures • Signs: Ophthalmoplegia, Diplopia, Initially exophthalmos then enophthalmos, associated hyphaema • Infraorbital nerve involvement – altered cheek, upper lip, upper gum sensation • Anatomy: Which wall of orbit usually fractures? • Rx: Do not blow nose, Abx (cephalexin), consider surgical repair if entrapment/diploplia MCQs • Which of these bones is not part of the medial wall of the orbit? 1. Zygomatic 2. Ethmoid 3. Lacrimal 4. Maxillary 5. Sphenoid Case 3 • You’re in RMH ED this time. You’re starting to feel pretty confident with this whole slit lamp thing. You picked up another patient with a red eye, should be a breeze. Sxs: UNILATERAL ocular pain, Photophobia! Mildly decreased VA Iritis • Signs: Think outside in ▫ Conjunctiva – Ciliary injection ▫ Cornea – Keratitic precipitates ▫ Anterior Chamber – Cells, flare, hypopyon ▫ Pupil – Irregular, miotic, posterior synechiae • Path: Idiopathic, HLA B27, Vasculitides, Infection, Sarcoid • Rx: ▫ Mydriatics – atropine 1% BD for 1-2 weeks ▫ Topical steroids – Pred acetate 1% ▫ Analgesia MCQs • Which of these can be used as mydriatics? ▫ Tropicamide 0.5% Parasymp Antagonist – 2-6hours ▫ Phenylephrine Sympathetic Agonist ▫ Cocaine 10% Sympathetic Agonist ▫ Cyclopentolate Parapsymp Antagonist – 24hours ▫ Atropine Parapsymp Antagonist – 7-14days Case 4 • You come home from work, luckily no red eyes at work today. Your grandfather is waiting for you at home with a facial rash and a red eye. Sxs: Prodromal phase of tiredness, fever, headache – Painful rash Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus • Signs: UNILATERAL dermatomal rash, Hutchinson’s Sign = If side of nose is involved then eye will be involved in 75% (Which nerve?) • Small dendritic lesions tapered ends without terminal bulbs = Pseudodendrite • Punctate Epithelial Erosions Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus • Cxs: Conjunctivitis, iritis, episcleritis/scleritis, keratitis, postherpetic neuralgia • Rx: Aciclovir PO 800mg 5X/day for 3-7 days • Symptomatic – Cold compresses MCQs Which of these cause unilateral red eye?. 1. HSV keratitis 2. Retinal detachment 3. Anterior Ischaemic Optic Neuropathy 4. Optic neuritis 5. Acute angle closure glaucoma Framework for the Red Eye Infective Inflammatory 1. Conjunctivitis 1. Iritis 2. Keratitis 2. Scleritis / 3. Endophthalmitis Episcleritis Traumatic Misc 1. Corneal abrasion 1. Acute angle / foreign body closure 2. Blunt / glaucoma penetrating injury 3. Subconjunctival haemorrhage Framework for the Red Eye Lids / Orbit / Lacrimal Conjunctiva / Sclera Cornea Lids Conjunctiva 1. 2. 3. 1. Chalazion Stye / Hordeolum Blepharitis 2. 3. Lacrimal 1. Dacryocystitits / Dacryoadenitis Subconjunctival haemorrhage Conjunctivitis Pterygium = benign growth of conjunctiva Sclera Orbit 1. Periorbital / Orbital cellulitis 1. Episcleritis / Scleritis 1. 2. 3. 4. Keratitis/Ulcer Foreign body Abrasion Dry Eyes Ant Chamber Inflamm 1. Uveitis Trauma 1. Hyphema = Blood in ant chamber Infection 1. 2. Hypopyon = Pus in ant chamber Endophthalmitis Misc 1. Acute angle closure glaucoma BEWARE the Unilateral Red Eye Bilateral Red Eye 1. Conjunctivitis 2. Dry eye 3. Contact lens irritation 4. Allergy UNILATERAL Red Eye 1. Keratitis / Corneal ulcer 2. Iritis 3. Trauma 4. Foreign body 5. ACG Hx – Key Questions • Unilateral vs Bilateral • Discharge ▫ Purulent? ▫ Watery? • Pain/Discomfort? ▫ Photophobia? ▫ Grittiness? • Vision affected? • POphHx + PMHx ▫ Allergy/Atopy? ▫ HLA B27 Associated diseases? ▫ Contact lens wearer Ex - Key • • • • Visual Acuity Pupils Eye Movements Visual Fields • Fluoroscein, Eyelid inversion Sxs: Pain +++, lacrimation, FB sensation, decreased VA, Contact lens wear Keratitis • Path: Bacterial - Staph, Strep, Hib, Nesseria, Pseudomonas, Viral – HSV, HZO • Signs: Stains with fluoroscein • Ix: Corneal scrape • Rx: DO NOT GIVE topical steroids, Broad spectrum Abx (fluoroquinolone, gent, vanc, cefazolin) HSV - aciclovir 3% 5X/day for 14days Sxs: Headache, nausea, vomiting, Pain +++, Blurred vision, haloes Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma • Signs: VA 6/60 – Think outside in ▫ Cornea – cloudy ▫ Anterior chamber – shallow, aqueous flare and cells ▫ Pupil - mid-dilated non-reacting ▫ High IOP • Rx: Acetozolamide 500mg IV or PO, topical timolol 0.5%, pilocarpine 1% • Definitive Rx: YAG laser iridotomy Demographics: Females 75% Sxs: Sudden onset redness (hours), mild pain but with no radiation, hotness, discomfort, recurrent, may flit from one eye to the other Episcleritis • Path: Idiopathic, Infectious, rosacea, atopy 80% simple, 20% nodular • Signs: Sectoral or diffuse, peaks within 12hours and fades over 10-21 days • Rx: Topical steroids (FML 0.1%), lubricants, if recurrent – oral NSAIDs Demographics: Females, Fifth decade Sxs: Ocular redness followed few days later by aching pain spreading to face + temple, wakes pt at night, responds poorly to analgesics, decreased vision Scleritis • Signs: Diffuse redness + erythema, tender to touch, inflammation of sclera and episcleral vessels, failure to blanch with topical 10% phenylephrine • Associations: Underlying systemic disease in >50% HLA B27 (AS, Psoriatic, IBD, RA), Vasculitides (SLE, PAN, Wegener’s), Sjogrens, Infective (TB, Syphilis), Sarcoidosis • Rx: Simple scleritis – Oral NSAIDs, then systemic steroids (pred 1mg/kg for 1 week) Necrotising scleritis – High dose IV steroids, Cytotoxic agents (AZA, MTX, Cyclophos, Immunomodulators (ciclosporin, tacrolimus) Trauma 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Corneal abrasion Foreign body Blunt / Penetrating injury Burns Lid / Orbital injury Sxs: Pain ++, Photophobia, Foreign body sensation Corneal Abrasion • Signs: Fluoroscein staining, Evert upper eyelid! • Rx: Topical chlorsig, eye pad • Golden Eye Rule: Should heal within 24 hours if cause is removed Blunt Injury 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Corneal abrasion Subconjunctival haemorrhage Hyphaema Vitreous haemorrhage Orbital #s Globe rupture Hyphaema • Rx: ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Admit to hospital – 5 days bed rest, elevate head Stop Aspirin or NSAIDs Eye shield Mydriatic – Atropine to stop iris movement • Measure IOP, Should resolve in 10-21 days Corneal Foreign Body • Rx: Topical anaesthetic, Cotton bud, 25G needle • After – Chlorsig ointment + eye pad • Do NOT attempt if: central, infected Sharp trauma • Cornea 0.5mm thick • Sxs: High speed mechanism of injury, hammering, welding • Signs: Irregular pupil • Ix: High velocity metal fragments ▫ Order CT / X-ray • Rx ▫ Refer – NBM, hard eye shield, no drops, antiemetics, analgesia, systemic Abx + tetanus, ▫ Surgical repair Burns • Alkali > Acid • Signs: Decreased VA, Cloudy cornea, Epithelial defect • Rx: ▫ Irrigation, Evert eyelids, Remove particles with cotton bud ▫ Topical Abx ointment ▫ Oral analgesia ▫ Symptomatic lubrication ▫ Later: Topical steroids MCQs • Snellen Chart: ▫ Is used for distance vision ▫ Is in Times New Roman font ▫ 6/12 means should be carried out at 12 metres ▫ Contains backwards letters for dyslexia • Young blonde girl with 6/36 vision, photophobia, nystagmus. Most likely Dx is? ▫ Oculocutaneous albinism ▫ Posterior fossa glioma ▫ Meningitis ▫ Middle ear infection ▫ Aniridia • What are causes of sudden visual loss in a white eye. ▫ Anterior uveitis ▫ Retinal detachment ▫ Optic neuritis