Current and Future Perspectives on
Acute Coronary Syndromes
Paul W. Armstrong MD
AMI Quebec
Montreal
October 1, 2010
Pivotal Role of Time
Timing of Symptom Onset
Time to 1st Medical Contact
Time to Reperfusion
Time as Modulator of Rx Effect
Time as Modulator of Rx Choice
Time Interaction & Risk Assessment
Strategic Alignment:
Paramedical Program,
IT & ECG,
Molecular Chemistry
Coronary Intervention
Treatment Delayed is Treatment Denied
2.4hrs
Symptom
Recognition
Call to
Medical System
PreHospital
ED
CCU
Cath Lab
Delay in Initiation of Pharmacologic
Reperfusion
Armstrong Collen Antman Circulation 2003
Reperfusion Options for STEMI Pts
Step One: Assess Time and Risk
Time Since
Symptoms
Risk of
STEMI
Risk of
Lysis
Time
Required to
Initiate
Invasive
Strategy
% Salvageable Ischemic Myocardium ▲----
100.0
35.0
80.0
30.0
60.0
25.0
40.0
20.0
20.0
15.0
0.0
% Rate Aborted MI
Absolute 35-day mortality benefit per 1000
Lytic-treated patients
Reperfusion Relationships: Time & Myocardial
Salvage, Lives Saved & Frequency Aborted MI
10.0
<1.0
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
Duration of occlusion/ Treatment delay (h)
Armstrong ,Westerhout, Welsh, Circulation 2009
Efficacy vs Effectiveness …..
Isn’t All About Time?
Time
From Sx onset
9
Self presentation
to hospital
To PCI
STEMI NEXUS
Reperfusion
Choice
911 EMS
3
Strategy
Armstrong ,Westerhout,Welsh, Circulation 2009
NSTE ACS: Too Great a Theraputic Burden?
ASA
Anti thrombin(s)
Clopidogrel, Prasugrel
2B /3A
Beta Blocker
ACE inhibitor
Statin
Anti inflammatory
Mechanical Intervention
BMS vs DES
Hospital Mortality
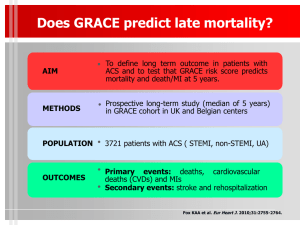
GRACE Risk Model
Variables
www.statcoder.com/grace.htm
www.umassmed.edu/outcomes/grace
Age (continuous)
Killip class
Blood pressure
ST deviation
Cardiac arrest
Creatinine
Elevated CK-MB / Tn
Heart rate
C-index = 0.84, validated in
clinical trial + registry populations
—Granger et al Archives Int Med 2003
TIMACS
Primary Outcome* Stratified by Baseline GRACE Risk Score
Non ST elev’n ACS n=3031
HR 0.65(0.48-0.89)
(1/3)
*Death, MI, Stroke @ 6mo
Early =14h : Delayed= 50h
Mehta S et al. N Engl J Med 2009
Opportunities in pre-hospital cardiovascular care
ST elevation AMI
Seamless pre-hospital
diagnosis, triage and treatment
Risk
assessment and
management
High – risk
ACS (NSTEMI)
Pre-hospital triage
Antiplatelets
Anticoagulants
Bystander CPR and AED
Rapid ACLS response
Novel EBM therapies
Cardiac
Arrest
Welsh & Armstrong Heart 2005
Perspectives on Acute Coronary
Syndromes
a
Baseline risk and its evolution
Lesson of subsets and disease heterogeneity
Time and its potential for deception
Dose: Renal function, age, body weight, sex
Bleeding is bad and choice of vascular access site a
key modulator
Guidelines are roadmaps: detours may be necessary
Beware of too rapid uptake of high profile meeting
presentations
One strategy rarely meets all clinical needs
Patients are partners: helping them make an
informed choice is an art