Document
advertisement

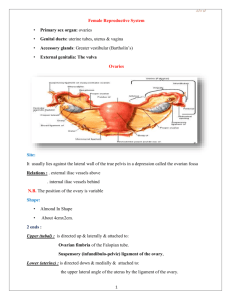
Reference TEXT BOOK Obstetrics & Gynecology (fifth edition) Author: Tamara L. Callahan, Aaron B .Caughey Williams Obstetrics Berek & Novak's Gynecology Source: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW) Anatomy of the Female Reproductive System Ai-Xia Liu Women’s Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University Outline External genitalia Internal genitalia Adjacent organs Bony pelvis Pelvic floor External Genital Organs(vulva) Mons pubis Labia majora Labia minora Clitoris Vestibule of the vagina External urethral orifice Vestibule glands paraurethral glands (Skene’s glands) Bartholin's gland vagina opening hymen External genitalia of adult female (parous) Internal Genital Organs Internal Genital Organs Vagina: extend from the uterus to the vestibule The wall is composed of a mucosal and a muscular layer Function: sexual intercourse organ, the passage way of labor and menstrual blood Fornix: divided into 4 regions Posterior fornix Fornix Uterus A pear shaped, thick walled, muscular organ Situated between bladder and rectum 7-8 cm long, 4-5 cm wide, 2-3 cm thick isthmus Uterus Divided into 2 main portions Body/Cervix Ratio: adult, 2:1, infant, 1:2 isthmus a transitional zone between body and cervix Special obstetrical significance (lower uterine segment) Internal orifice(os) anatomical internal os: narrowest position of the cavity histological internal os the columnar epithelium changes into endometrium isthmus uterus body (superior 2/3s) Fundus: the widest place of the corpus Lined with endometrium cervix (inferior 1/3) Supravaginal portion Vaginal portion External cervical os Squamocolumnar junction The cervical canal is covered by columnar epithelium The surface of vaginal portion is covered by squamous epithelium External cervical os fundus cavity isthmus corpus cervix fornix External os Anatomical os. Histologic os. Supra-vaginal Vaginal part vagina Sagittal view Coronary view uterus Position and Axis Direction anteversion: tipped forward anteflexion: the fundus is pointing forwards. The isthmus is bend. retroversion tipped backwards retroflexion: the fundus is pointing backwards. Anterior of uterus is convex. The wall of the uterus perimetrium (serous): peritoneal covering myometrium (muscular): the out layer, the inner layer the endometrium(mucous): soft and spongy 1 2 The myometrium of the uterus:1. the out layer, 2. the inner layer Ligaments 4 pairs of ligaments Round ligament Uterosacral ligament Cardinal ligament (transverse ligament of cervix) Broad ligament ligaments 1. round ligament - attaches anterior-inferiorly to uterotubal junctions, pass in the broad ligaments, end in labia majora. They help to keep uterus in the position of anteversion. Broad lig. Round lig. Cardinal lig. Ligments of uterus Ligaments 2. Broad ligament – arise from the side of the uterus to the lateral pelvic wall, provide minimal support. Between two leaves of ligaments there lies round ligaments,fallopian tube, ovarian ligament, mesosalpinx, infundibulum ligament, blood vessles and nerves 3. Cardinal ligaments - extend from cervix and lateral parts of vaginal fornix to lateral walls of pelvis. Chief means of support and suspends the uterus from the lateral walls of the pelvis minor Broad lig. Round lig. Cardinal lig. Ligments of uterus Ligaments 4.Uterosacral ligaments – arise from the sacral fascia, and insert into the posteroinferior portion of the uterus at about the level of the isthmus. They provide important support for the uterus. Fallopian tube serves to convey the ova to the uterus, running in the superior border of the broad ligments (mesosalpinx). divided into 4 parts: interstitial portion: embodied within the muscular wall of uterus isthmus: narrowest portion ampulla: wide and tortuous infundibulum: fringed by numerous diverging processes (open to cavity). Layers of the tube wall serous subserous muscular mucous: ciliated columnar epithelium Left and right tube uterine ostium in the hysteroscopy Ovary: Oval shaped, 2.5-5 cm long, 1.5-3 cm wide, 0.7-1.5 cm thick Covered by cuboid or low columnar epithelium and white fibrial tissue, no peritoneum corvered Consists of cortex and medulla cortex: contains oocytes in various stages of maturity medulla: made up of blood vessels, nerves, lymphatic vessels, and supporting tissue. ligaments superior (tubal) end of ovary is connected to lateral wall of pelvis by suspensory ligament of the ovary (infundibulum ligament) contains ovarian vessels and nerves ligament of ovary - connects inferior (uterine) end of ovary to lateral angle of uterus Mesovarium: attach to the posteroanterior layer of the broad ligament, connected with suspensory ligament Hilum: vessels , nerves and lympatics enter the ovary Ligaments of ovary Douglas pouch uterovesical pouch Neighbor organs ureter Uterine artery Water flows under a bridge 4 4 1 3 3 7 2 5 5 2 6 Figure: internal organs in female pelvis. 1. uterus, 2. ovaries, 3. fallopian tubes, 4. round ligaments, 5. utersacral ligaments, 6. rectouterine pouch (pouch of Douglas) , 7.broad ligaments. Blood supply for female genitalia Arterial system 1. Ovarian artery: the chief source of the blood for ovaries. 2. Uterine artery: corpus branch cervical-vaginal branch 3. Vaginal artery: main source of the blood for the middle part of vagina 4. Internal pudendal artery: supply for superficial perineum, labia majora, labia minora, lower part of the vagina, clitoris The lymphatic drainage of pelvis Internal iliac lymph node Surround internal iliac vessels Receive afferents from pelvic viscera, perineum, buttock and back of thigh External iliac lymph nodes Lie along external iliac artery Receive afferents from lower limb and some parts of pelvic viscera Sacral lymph node Common iliac lymph node Lie along common iliac artery Receive afferents from all the above nodes Efferents pass to lumbar lymph node Lymphatic drainage: External genital organ lymph group: 1. superficial inguinal lymph nodes. 2. deep inguinal lymph nodes Pelvic lymph group: 1. iliac lymph group. 2. presacral lymph group. 3. lumbar lymph group. The nerve of external genitalia Pudendal nerve Obstetric local anesthesia Divided into 3 branches beside tuberosity Inferior hemorrhoid nerve Dorsal nerve Perineal nerve The nerve of internal genitalia Sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves from lumbar and sacral spinal cord Sympathetic nerve are derived from Plexus Sacral plexus Ovarian plexus THANK FOR YOUR ATTENTION