Unit 2 - Joints
advertisement

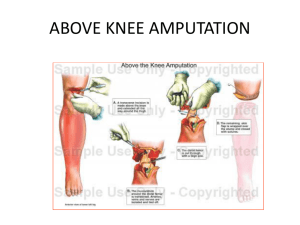
PSE4U FIBROUS JOINT ◦ Bound tightly together by connective tissue and allow no movement ◦ Ex. Joints between skull bones (sutures) CARTILAGINOUS JOINT ◦ Body of one bone connects to the other by means of cartilage ◦ Slight movement ◦ Ex. Intervetebral discs between vertebrae. SYNOVIAL JOINT ◦ Bony surfaces are separated by lubricating fluid (synovial fluid) and cartilage. ◦ Joined by ligaments (enclose ends of bones to form a capsule) ◦ Ex. Knee joint JOINT CAVITY: filled with synovial fluid (acts as a lubricant for joint) JOINT CAPSULE BURSA: small flattened fluid sac found at friction points between tendons, ligaments and bones ARTICULATING CARTILAGE: found at the end of a bone that comes into contact with another bone Fibrous Capsule: stops synovial fluid from leaking out. Is located on the outside of the joint. Synovial Membrane: allows certain nutrients to pass through. Located right below the fibrous capsule. Purpose: protection, creates smooth contact, acts as a shock absorber INTRINSIC LIGAMENTS Thick bands of fibrous connective tissue that help to thicken and reinforce the joint capsule EXTRINSIC LIGAMENTS Separate from joint capsule and help to reinforce the joint by attaching the bones together. BALL & SOCKET ‘ball’ of one bone fits into ‘socket’ of another * Movement around 3 axes* GLIDING Connects flat or slightly curved bones PIVOT A rounded point of one bone fits into a groove of another * Allows rotation in one plane* SADDLE Allows movements in 2 planes F &E, ABD & ADD but not rotation ELLIPSOID Allows movement in 2 planes HINGE Convex portion of bone fitting into concave portion of bone * Movement in 1 plane* Tendons: attach bone to muscle ◦ Composed of collagen ◦ Can stretch further than ligaments ◦ Dynamic stabilizers Ligaments: attached bone to bone ◦ Tough connective tissue ◦ Can stretch but have less movement than tendons ◦ Static stabilizers of joints ◦ Can strengthen through training = stronger joint Strains, sprains, tears and pulls: Sprains and tears – associated with ligaments Strains and pulls - associated with tendons 1st, 2nd and 3rd degree Tendinitis: Inflammation of a tendon caused by irritation due to prolonged or abnormal use Dislocations: Bone displaced from its original location Damage to join capsule and ligament occurs. SYMPTOMS – joint looks deformed, joint is painful touch or move, joint is not useable. Separations: Occurs when bones held together by fibrous ligaments tear and separate from each other Cartilage: Usually known as `torn cartilage` Arthroscopy – surgical procedure to diagnose injury Shin Splints Painful condition occurring on medial/lateral side of tibia cause by tearing of interosseus membrane or the periosteum SHARP S – swelling H – heat A – Altered (will not function properly) R- red P - painful PIER P – pressure I – ice E – Elevation R – restriction Articulation of femur and tibia Modified hinge joint: flexion and extension, however, some medial and lateral rotation can occur (technically modified ellipsoid joint – movement in 2 planes) 2 menisci (meniscus singular) ◦ sit on tibial condyles and sit on either side of intercondyle eminence 6 ligaments ◦ CRUCIATE LIGAMENTS: cross each together over the intercondylar eminence Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) – stops anterior movement Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) – stops posterior movement ◦ Ligaments that hold fibrous tissue together Medial collateral ligament (MCL) – stops medial movement Lateral collateral ligament (LCL) – stops lateral movement ◦ Other ligaments Posterior meniscofemoral ligament – strengthens posterior aspect of joint Oblique popliteal ligament – strengthens posterior aspect of joint Patellar ligament – hold patella in place Synovial ball-and-socket joint : unstable Joint – this unstableness gives the shoulder joint its versatility and movement Joint made up of scapula and humerus and indirectly the clavicle Athletes who are involved in sports where actions like throwing, swimming and lifting occur are susceptible to shoulder injuries 4 Ligaments Coracoclavicular ligament – attaches the coracoid process and clavicle Acromioclavicular ligament – attaches the acromion process and clavicle together Glenoid humeral ligament – attaches the scapula and humerus Coracoacromial ligament – attaches the acromion process and coracoid process Biceps tendinitis – overuse of biceps brachii Shoulder separation – tearing of acromioclavicular ligament Shoulder dislocation – occurs when the humerus ‘pops’ out of the glenoid cavity. Rotator cuff tears – rotator cuff: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor and subscapularis Supraspinatus, infraspinatus and teres minor share the common insertion on the greater tubercle. When part of the tendon is torn it affects all muscles.