Anatomy of the Female
Reproductive System
Renmin Hospital of Wuhan university
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Luo Ruoyu
External genitalia, Vulva
mons pubis
labium majus
• The round ligament terminate at its anterior third;contain sebaceous
glands,sweat glands and hair follicles
• Be richly supplied with venous plexus and vessels which may produce
hematoma
labium minus
• Contain numerous nerve endings
clitoris
• Erection function
• Be richly supplied with nerves,which produce sexual excitement
vaginal vestibule
• major vestibular gland
secretes mucus during sexual activity,becomes
cysto or abscess when the duct is blocked
• hymen
varying size and shape,the hymen is usually
ruptured at the first sexual experience
congenital imperforate hymen
• urethral orifice
paraurethral gland,early be infected
External genitalia, Vulva
internal genitalia
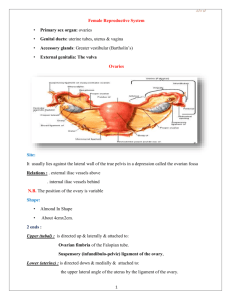
vagina
uterus
fallopian tube, oviduct
uterine adnexa
ovary
internal genitalia
internal genitalia
internal genitalia
internal genitalia
vagina
function
• sex
• the way of menstruation
• soft birth canal
position and shape
• canal,shorter anterior and longer posterior,enough distensibility
• fornix are formed at the top of vagina due to the projection of the
uterine cervix,the posterior one is the deepest, and often be used as
drainage point
structure
• mucous coat muscular layer fibrous coat
mucosa: squamous epithelium, having no glands
uterus
function
• pregnancy
• form menstruation
• soft birth canal
position and shape
situated in the pelvis between the bladder in
and the rectum behind
inverted-pear-shaped,7cm long,5cm wide,3cm
volume 5mL
front
thick,
parts:fundus、body and cervix,its walls are about
1cm
thick ,when pregnancy,the uterus becomes larger,even reach
below the xiphoid process
Isthmus
(1m)
Histological internal os
Anatomical internal os
uterus
fundus
cavity
isthmus
body
anatomical internal os
histological internal os
cervical canal
vagina fornix
external os
vagina
coronal section
supravaginal portion
portion vaginalis
sagittal section
Different parts of uterus
structure
• endometrium:functional layer and basal layer
• body:3 layers muscle fibres
• cervix:fibrous connective tissues+smooth
muscle fibres
ligament
round ligament
broad ligament
cardinal ligament
utero-sacral ligament
fallopian tube, oviduct
function
fertilization place
convey to zygote
nutrition zygote
position and shape
paired structions,measuring about 8~14cm long
slender muscular tube,one opening communicating with
the lateral angle of the uterus,the lateral part is free
structure
parts:interstitial portion、isthmic portion、ampulla、
fimbria
ovary
function
reproduction:germ cell maturation,storage and release
endocrine:steroidogenesis
position and shape
oval in shape,volume 4×3×1cm3
structures
germinal epithelium
medulla
cortex
ovary
primordial follicles
preantral follicle
germinal epithelium
antral follicle
vasa
mature follicle
corpus albicans
corpus luteum
histological structures of the ovary
medulla
ovum
vasa、lymphatics and nerves
vasa
uterine arteries:supply uterus and surrounding
notice the relationship between ureter
ovarian veins:pelvic venous congestion syndrome
lymphatics
nerves
vulva:motor nerve and sensory nerve
internal genitalia:sympathetic nerve and
parasympathetic nerve
vasa、lymphatics and nerves
uterus
oviduct
ureter
cervix
ovarian vein
ovarian artery
uterine artery
uterine vein
uterine arteriovenous and ovarian artery and vein
vasa、lymphatics and nerves
vasa、lymphatics and nerves
pelvis
function
• support trunk
• protect viscera
• bony birth canal
parts
• bones
os sacrum
promontory
os coccyx
os coxae(2)
os ilium
os ischium
os publis
• joints
public symphysis
sacro-iliac joint
sacro-coccygeal joint
• ligament
sacrotuberous ligament
sacrospinous ligament
pelvis
pelvis
pelvis
pelvis
pelvis
pelvis boundaries
superior border of public symphysis-lliopublic
edge-
superior border of promontory,
divided the pelvis into
• false pelvis (large pelvis):assess the pelvis
preliminarily
• true pelvis (small pelvis):bony birth canal
true pelvis
inlet
outlet
cavity
types
of pelvis
• gynecoid type
transverse of inlet > anteroposterior
intertuberal diameter > 10cm
• platypeloid type
transverse < anteroposterior
• anthropoid type
anteroposterior > transverse
• android type
funnel-shaped,angle of public arch < 900
pelvic floor
contain multiple layers of muscle and fascia
3 layers:
• superficial layer:superficial muscles and fascia
• middle layer:superior and inferior fascia and
muscles between them
• inner layer:pelvic diaphragm,levator ani muscle
perineum :soft tissue between vaginal orifice
and anus
near organs
urethra :short but straight,about 4~5cm,easy be infected
bladder :may prolepses in old female,easy be hurt during
operation
ureter :notice the relationship with uterine arteries
rectum :may prolepses in old female
appendix :distinguish with adnexal disease