Female
Reproductive
System Anatomy
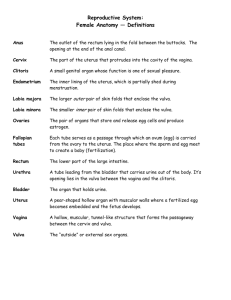
The female reproductive system consists of
organs (internal and external) in the female body
that are involved in producing offspring.
▪ The vulva refers to those parts that are outwardly visible
The vulva includes a series of muscles/blood vessels/bone/skin
folds:
Mons pubis
Labia majora
Labia minora
Clitoris
Urethral opening
Vaginal opening
Hymen
Perineum
The triangular mound of fatty tissue that
covers the pubic bone.
Serves as a protective cushion for the internal
reproductive organs.
During adolescence sex hormones trigger the
growth of pubic hair on the mons pubis.
The labia majora enclose and protect the
other external reproductive organs.
Heavy folds of skin that surround the opening
of the vagina.
Two smaller folds of skin located within the
labia majora.
The clitoris and the openings of the urethra
and the vagina are located within the labia
minora.
Small, highly sensitive structure located
above the opening of the urethra.
Richly supplied with blood vessels and nerve
endings.
Key to sexual pleasure for most women.
Urethral opening is located directly below
clitoris
The hymen is a thin membrane that stretches
across the opening of the vagina.
The hymen has small openings in it.
Some females do not have a hymen.
Other females often break or tear the hymen
when they ride bicycles or horses or exercise
strenuously.
The urethra is a tube that conveys urine from
the urinary bladder to the outside of the
body.
The muscle and tissue located between the
vaginal opening and anal canal.
It supports and surrounds the lower parts of
the urinary and digestive tracts.
The opening of the large intestine that carries
waste to the outside.
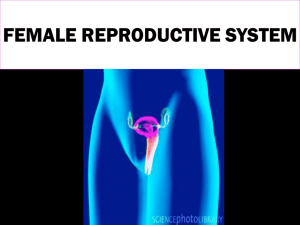
The internal organs consists of the:
Vagina
Cervix
Uterus
Fallopian Tubes
Ovaries
The vagina connects the cervix to the
external genitals.
It is located between the bladder and rectum.
It functions as:
▪ a receptacle for the penis during love-making/sexual
intercourse
▪ a outlet for blood during menstruation
▪ a passageway for the baby to pass through at birth.
According to The Guiness Book of World
Records, a Russian peasant woman who lived
in the 18th Century holds the record for the
most children born to one mother. She had
sixty-nine children within forty years. She
produced sixteen pairs of twins, seven sets of
triplets, and four sets of quadruplets!
The cervix is the lowest part of the uterus that
connects to the vagina.
The cervical opening to the vagina is small.
This acts as a safety precaution against
foreign bodies entering the uterus.
During childbirth, the cervix dilates to
accommodate the passage of the fetus.
This dilation is a sign that labor has begun.
The uterus or "womb" is a hollow, muscular
organ in which a fertilized egg, called the
"zygote," becomes embedded and in which
the egg is nourished and allowed to develop
until birth.
It lies in the pelvic cavity behind the bladder
and in front of the bowel.
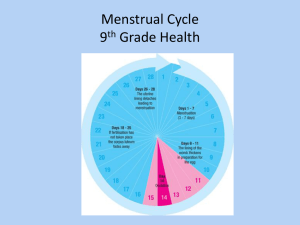
The uterus is lined with tissues which change
during the menstrual cycle.
When the hormones withdraw after the
menstrual cycle, the blood supply is cut off
and the tissues and unfertilized egg are shed
as waste.
The endometrium is the membrane that lines
the uterus.
It is a glandular mucous membrane, and is
formed during the menstrual cycle, then
expelled from the body during each
menstruation.
The endometrium is what a fertilized egg
attaches to upon fertilization, so it is not shed if
a fertilized egg is implanted.
The endometrium also supplies blood for the
fetus and allows it to receive oxygen.
Serve as a pathway for the ovum to the
uterus.
The site of fertilization by the male sperm.
Often referred to as the oviducts or uterine
tubes.
Fertilized egg takes approximately 6 to 10
days to travel through the fallopian tube to
implant in the uterine lining.
A female has two Fallopian tubes – one
connected to each ovary.
During the menstrual cycle, a mature ovum
moves through a Fallopian tube to the uterus.
If fertilization occurs, it usually occurs in a
Fallopian tube.
An ovum that is not fertilized either
disintegrates in the uterus or leaves the body
in the menstrual flow.
The ovaries are a pair of oval or almond-shaped glands
which lie on either side of the uterus and just below the
opening to the fallopian tubes.
In addition to producing eggs or "ova," the ovaries
produce female sex hormones called estrogen and
progesterone (changes lining of the uterus).
The ovaries produce a female hormone, called estrogen,
and store female sex cells or "ova."
A female is born with between 200,000 and 400,000
immature ova in her ovaries.
About 375 of these ova will mature and be released in a
female’s lifetime.
During puberty, the ova begin to develop.
Each developing ova is enclosed in a small,
hollow ball called a follicle.
Each month during the menstrual cycle, an
ovum matures and is released from its follicle.
The follicles in the ovaries produce the female
sex hormones, progesterone and estrogen
These hormones prepare the uterus for
implantation of the fertilized egg
The mammary glands are accessory organs of
the female reproductive system that are
specialized to secrete milk following
pregnancy.
They are located in the subcutaneous tissue
of the front thorax within the elevations
which are called breasts.
A mammary gland is composed of fifteen to
twenty irregularly shaped lobes, each of
which includes alveolar glands, and a duct
(lactiferous duct) that leads to the nipple and
opens to the outside.
A "nipple" is located near the tip of each
breast.
The nipple is surrounded by a circular area of
pigmented skin called the "areola."
What is another name for the egg produced by
the female reproductive system?
What is the function of the vagina?
How is an egg transported from outside the
ovary to the uterus?
What structures does the vulva include?
What is the size and function of the ovaries?
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xFpVy9OCI4o&feature=r
elated
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WGJsrGmWeKE
http://www.nucleusanimationlibrary.com/animationpreview?ccat=Ob%2Fgyn&clang=English&animationid=6731
2 (ovulation)
http://www.nucleusanimationlibrary.com/animationpreview?ccat=Ob%2Fgyn&clang=English&animationid=682
82 (breast)
http://www.nucleusanimationlibrary.com/animationpreview?ccat=Ob%2Fgyn&clang=English&animationid=7543
3 (labor)