Digestive System
Anatomy & Physiology
Digestive
Processes
Digestive
Organs
Mesentary
Peritonitis
Oral Anatomy Lateral View
Cadaver Midsaggital Section
of Oral Structures
Oral Anatomy
Anterior View
Tongue Anatomy
Taste Bud Anatomy
Salivary Glands
Cadaver ___ Gland
Tooth Anatomy
Tooth Eruption
Impacted Molar
Gingiva
Universal Tooth
Numbering System
Tooth Faces
• Lingual (Nearest Tongue)
• Facial (Farthest from tongue)
• Mesial (Closest to the incisors)
• Distal (Farthest from the
incisors
• Occlusal (Grinding surface
Splanchnic
Circulation
25% of
Cardiac
Output
Endoscope
Larynx
Esophageal Reflux
G.E.R.D. (GastroEsophageal
Reflux Disease)
Gastric Fundus
Gastritis due to
Helicobacter Pylori
Gastric Diverticulum
Gastric Polyps
Gastric Carcinoma
Duodenal Mucosa
Duodenal Ulcer
Proctologist
Testing for Occult Blood
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy Administration
Caecal Diverticula
Descending Colon
Tapeworms
Ulcerative Colitis
(Sigmoid Colon & Rectum)
Rectum
Anal Hemorrhoids (Piles)
Caused by Inflammation of
the Superior & Inferior
Hemorrhoid Veins
Scope Comparison
Barium Enema
Colostomy
& Stoma
Colostomy Bag
Peristalsis
27 Year Old Male
81 Year Old Male
Swallowing
Gastric Regions
Gastric Anatomy
Gastric
Cells
Gastric Cell FXN’s
• Goblet cells – produce alkaline mucus
• Mucus Neck cells – produce acidic mucus
• Parietal cells – produce HCl & Intrinsic
Factor
• Chief cells – produce pepsinogen
• Enteroendocrine cells – produce gastrin,
pepsin, cholecystokinin, & somatostatin
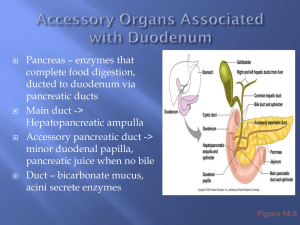
Gall Bladder & Pancreas Empty
Contents into Duodenum
Liver & Pancreas Secretions
Liver FXN’s
• Synthesizes bile (bile salts, biliruben,
& cholesterol)
• Stores glucose as glycogen
• Stores fat soluble vitamins ADEK
Gall Bladder
FXN
• Stores bile
• CCK contracts gall bladder secretion of pancreatic
juice & relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi
Pathophysiology
• Gall stones – too much cholesterol or too few bile
salts resulting in cholesterol crystal accumulation
• Obstructional jaundice – bile duct becomes
obstructed & bilirubin increases in blood
Gallstones
Bile Salt
FXN
Pancreas
• Secretes basic pancreatic juice (pH 7.5-8.0)
Pancreatic Juice (p.j.)
• Bicarbonate rich p.j. neutralizes HCl in the duodenum
(Stimulated by secretin when HCl enters the duodenum)
• Enzyme rich p.j. stimulated by CCK when fatty or protein
rich foods enter the duodenum
Note
• Hormones released in inactive form so they don’t digest the
pancreas
Accessory Organ Ducts &
Sphincter
HCO3-
Na+
Pancreatic duct
H 2O
CO2
Pancreatic
acinar
cell
H2CO3
Na+
H+
Blood capillary
Pancreatic secretion of
NaHCO3 (sodium bicarbonate)
[simplified]
Water & Mineral Digestion
Absorption of…
Vitamins –
• A,D,E,K fat soluble (diffuse into blood)
• B & C water soluble (diffuse into blood)
• B12 requires intrinsic factor for diffusion…leads to
pernicious anemia
• Electrolytes (Na+, K+, HCO3-, Cl-)
• Iron – binds to ferratin in mucosal cells & transferrin in the
blood for transport
• Calcium – PTH increases ionic calcium & vitamin D aids in
absorption
Lipid
Emulsification
Lipid
Digestion
Carbohydrate
Digestion
Na/K Symport
Protein
Digestion
Brush Border
Villi
Small Intestine
Large Intestine with
Mesentery
Cecum
Anal
Sphincter
Control
Hormonal Control of Digestion
(Produced in stomach)
•
•
•
•
Gastrin - HCl secretion & gastric emptying
Serotonin – Contracts gastric muscle
Histamine – HCl release from parietal cells
Pepsinogen – inactive form of pepsin (HCl activated)
•
Somatostatin – Inhibits:
gastric secretions
gastric emptying
pancreatic secretions
intestinal absorption
gall bladder contraction (bile release)
catabolyzes protein
Hormonal Control of Digestion
(Produced in Duodenum)
• Secretin -
pancreatic juice secretion & bile output
• Cholecystokinin - pancreatic juice output, contracts gall
bladder, & relaxes sphincter of Oddi
• Gastric inhibitory peptide – inhibits gastric secretion &
motility
• Vasoactive intestinal peptide – dilates intestinal capillaries &
inhibits HCl production
Hormonal Control of Digestion
(Produced by pancreas)
• Trypsinogen – Inactive form of trypsin (activated by
enterokinase) catabolyzes protein to peptides
• Amylase – catabolyzes polysaccharides
• Lipase – catabolyzes lipids
• Carboxypeptidase – catabolyzes protein to amino acids
• Chymotrypsin – catabolyzes protein to peptides
The absorptive state
Metabolic states
•During & for several hours after a meal
•Insulin
• glucose uptake by cells (from blood)
• glycogenesis in liver cells
• lipogenesis in fat cells
• lipolysis in fat cells
Continues until . . .
Metabolic states
The postabsorptive state
•Begins several hours after a meal
•Glucagon
• glycogenolysis
• gluconeogenesis
• lipolysis in fat cells
• lipogenesis in fat cells
Feces may indicate health issues
•Motility / timing
•Diarrhea
•Constipation
•Color / consistency
•Gray = lack of bile
•Black/tarry = bleeding (upper)
•Black = PeptoBismol
•Red = bleeding (lower)
Digestion of Alcohol