Biology of MM - International Waldenstrom`s Macroglobulinemia
advertisement

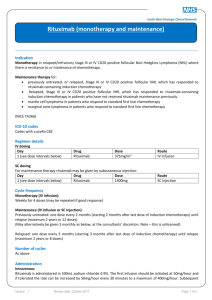
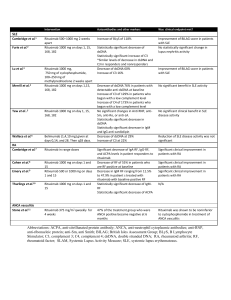
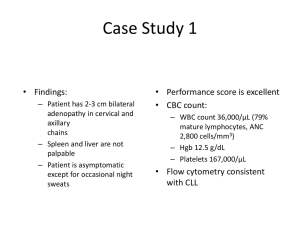
Novel treatment options for Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia Irene Ghobrial, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Dana Farber Cancer Institute Boston, MA Ghobrial et al, Lancet Oncol 2004, Treon et al, Blood 2009 MYD88 in WM Treon et al, NEJM 2012 Molecular characteristics • 30-50% of patients: deletion 6q by FISH • BLIMP (on 6q21): a tumor-suppressor gene, is the master gene regulator for B-lymphocytic cell proliferation. • 70-90% of patients have MYD88 mutation. • CXCR4 somatic mutation in 24% of samples Treon et al NEJM 2012 Consensus recommendations of the 4th International WM meeting • First Line therapy: – Combination therapy • (RCD or CPR; Cytoxan+nucleoside analogues+R; R-CHOP, R-CVP) – Rituximab single agent – Nucleoside analogues – Alkylators • Salvage therapy: – – – – – Re-use therapies Bortezomib Thalidomide+steroids Alemtuzumab AHSCT Dimopoulos, JCO 2009, Treon et al Clin Lymph and Myeloma 2009 Primary Therapy of WM with RituximabBased Options Regimen ORR CR Rituximab x 4 25-30% 0% Rituximab x 8 40-45% 0% Rituximab/cyclophosphamide i.e. CHOP-R, CVP-R, CPR, RCD 70-80% 8-10% Rituximab/nucleoside analogues i.e. FR, FCR, CDA-R 70-90% 5-10% Rituximab/thalidomide 70% 5% Rituximab/bortezomib i.e. BDR, VR 70-90% 10-25% 90% NA Rituximab/bendamustine Courtesy of Dr. Steven Treon Primary treatment of Waldenström macroglobulinemia with dexamethasone, rituximab, and cyclophosphamide. • 72 patients • cyclophosphamide 100 mg/m2 orally bid on days 1 to 5 (total dose, 1,000 mg/m2). • 83% of patients achieved a response • Including 7% complete, 67% partial, and 9% minor responses. • The median time to response was 4.1 months. • The 2-year progression-free survival rate for all patients was 67% Dimopoulos, JCO 2007 Bendamustine plus Rituximab versus CHOP plus Rituximab in the First-Line- Treatment of Patients with Waldenstrom disease: Randomized Phase III Study of the Studygroup Indolent Lymphomas (StiL) •42 pts with WM, report on 40 evaluable in interim analysis, BR=23 and CHOP-R=17. •The ORR for pts treated with B-R was similar to that associated with CHOP-R (96% vs 94%, respectively). •The median follow-up time for both groups is 26 months. •Progressive or relapsed disease: 2 in pts treated with B-R and 7 in the CHOP-R group. •Less toxicity and non-inferior response. Rummel, WM-Workshop2012 PFS: Benda-R vs CHOP-R in Frontline WM 1.0 Probability 0.9 Bendamustine-R 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 CHOP-R 0.1 0.0 0 12 24 36 48 60 72 months Rummel M, et al. Presented at: Third International Pt Physic Summit on WM; May 1-3, 2009; Boston, Massachusetts, United States. Phase II trial of bortezomib+ rituximab in upfront or R/R WM •ORR 80-90%. CR 10-15% •Minimal peripheral neuropathy V V V R R R V V V V V R V V R •A total of 6 cycles, a cycle= 28 days V R V R V V V V V V R Maintenance 1 VR treatment q3M x 2 years •No rituximab maintenance ---V Bortezomib 1.6 mg/m2 days 1, 8, 15 q 28 days x 6 cycles Ghobrial et al, JCO 2010 ---R Rituximab 375 mg/m days 1, 8, 15, 22 on cycles 1 and 4 •No dexamethasone Ghobrial et al, AJH 2011 1 cycle =28 days 2 New developments PI3K/mTOR inhibitors Proteasome inhibitors BTK inhibitors HDAC inhibitors IMIDs The PI3K/mTOR pathway Phase II trial of RAD001 in WM Maximum decrease from baseline in IgM (%) 60 40 20 0 -20 -40 -60 -80 -100 -120 15 14 + 13 + + + + + 12 + + + + + + + + + 11 + + + + + + 10 + + + 9 + + 8 0 50 1 50 2 44 3 37 4 33 5 28 6 26 7 19 Cycle Number of patients 8 18 9 15 10 12 11 11 12 10 Partial response B Stable disease Partial response A C Phase I/II Study of Everolimus, Bortezomib and/or Rituximab in Relapsed/Refractory WM Study Design Phase I study Registration • • Everolimus/rituximab Everolimus/bortezomib/rituximab Determine maximum tolerated dose (MTD) Phase II study ongoing with 3 drug combination The RVR phase I study Response CR PR MR ORR (CR+PR+MR) Stable Disease N= 23 evaluable 1 (5%) 7 (30%) 9 (39%) 17 (74%) 6 (26%) MLN128 • TORC1 and 2 inhibitor • Oral agent before after 6 months Maiso, Blood 2010 Targeting PKC in WM Phase II study 38% ORR in 42 patients relapsed/ref Ghobrial, CCR 2012 N=37 % with Phase II trial of perifosine in patients Clinical response relapsed/refractory WM CI 9 MR 35%, with another 54% showing stabilization •ORR of their 24 disease(11.8, 41 . 2 ) PR •Only SD PD 3 8 (1.7, 21. 9 ) 21 57 (39.5, 72 . 9 ) 11 (3.0, CI 25. 4 ) 11% of patients demonstrated progression. 4 N=37 % Clinical response Response by M spike MR MR PR PR 99 24 24 (11.8, 41.2) 4 11 (3.0, 25. 4 ) 20 54 (36.9,70.5) 21 4 57 11 (39.5, 72.9) (3.0, 25. 4) 4 11 (3.0, 25. 4 ) 3 SD SD PD PD Response by IgM MR PR SD Response PD (11.8,41 . 2 ) by M spike 8 (1.7, 21. 9 ) 11 30 (15.9, 47 . 0 ) 2 5 (0.7,18.2 ) 20 54 (36.9,70 .5) (11.8,41.2) 11 24 (3.0, 25. 4 ) MR PR 49 SD PD 20 4 11 (3.0, 25. 4 ) Ghobrial54 et al, CCR 2010 (36.9,70.5) CAL-101 PI3K delta (p110) Oral Well tolerated Significant Lymph node response but increase in peripheral blood lymphocytes in CLL 60% ORR in indolent lymphomas, 86% in MCL, 95% ORR in CLL in lymph nodes Roccaro et al, Blood 2011 New Proteasome inhibitors Upfront therapy with Carfilzomib/dex/rituxan (CARD study) Onyx 0912 in relapsed WM Roccaro et al, Blood 2010 Sacco et al, CCR 2011 IMIDs in WM • • • Thalidomide and rituximab: – Thalidomide 200-400 mg, rituximab weeks 2-5, 13-16 – 25 pts (20 untreated) – 70% ORR – TTP ≥38 months observed among responders. – 44% >G2 PN Lenalidomide and rituximab: – 25 mg lenalidomide 21 days, and rituximab weeks 2-5, 13-16 – 16 pts (12 untreated) – 50% response rate, TTP of 18.9 months – 88% discontinuation of therapy – Most due to anemia that occurred early with therapy – Median decrease in Hct from 32 to 27%, 4 pts required hospitalization Phase I trials of lenalidomide ongoing, phase I pomalidomide/rituximab ongoing. Treon et al, Blood 2008, CCR 2008 Phase II Study of Panobinostat in WM Best overall response CR VGPR PR MR SD PD Unevaluable N % 0 0 1 3 10 27 9 25 14 39 1 3 1 3 Total 36 PR or better 30 11 (90%CI:18, 46) 55 20 (90%CI:41,70) MR or better Ghobrial I, et al. Blood. 2010;116:3952.[Oral Presentation]. IgM response to Panobinostat Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) IgM • B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) signaling is required for tumor expansion and proliferation • Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (Btk) is an essential element of the BCR signaling pathway • Inhibitors of Btk block BCR signaling and induces apoptosis Nat Rev Imm 2:945 Ibrutinib • Breakthrough designation by the FDA for WM. • Over 80% response rate. • Very well tolerated. • Currently, no trials available. Awaiting approval and more trials or expanded access in the next few months. New Proteasome inhibitors Oprozomib in relapsed WM Roccaro et al, Blood 2010 Sacco et al, CCR 2011 Oprozomib • Oral agent. • Proteasome inhibitor without neuropathy. • Over 80% response rate so far in WM • Considering breakthrough designation in WM. • Study open in multiple sites and accruing now. Future developments • MYD88 targeting (IRAK4) • CXCR4 targeting • miRNA155 targeting (MiRNA LNA) miRNA expression in bone marrow CD19+ WM cells vs CD19+ normal counterpart Roccaro et al. Blood 2009 Association between microRNAs and clinical prognostic features P = .009 P = .004 P = .001 Roccaro et al. Blood 2009 Summary Significant advances in WM specifically MYD88 miRNA155 as a prognostic maker and therapeutic target New agents including mTOR inhibitors, BTK inhibitors, PI3K inhibitors, HDAC inhibitors, new proteasome inhibitors Can we personalize therapy in WM? Should we treat earlier to prevent complications/clonal heterogeneity and resistance FDA approval for agents in WM Acknowledgement • Ken Anderson, MD, Steven Treon, MD, Paul Richardson, MD, Nikhil Munshi, MD, Jacob Laubach, MD, Claudia Paba-Prada, MD • Supported by the NIH, FDA, IWMF, LLS, Kirsch Lab for WM, Heje Fellowship, All our patients.