Document
advertisement

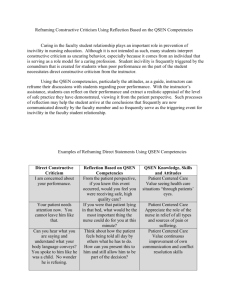
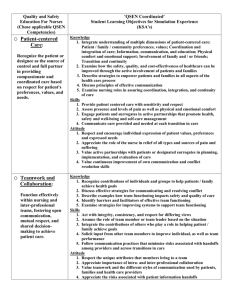
QSEN Presented by Jean Eden, Kristi Evans, Morrehea Hardman, Valerie McGouldrick, Ashton Merchant, Katelyn Peper QSEN: • Quality and • Safety • Education for • Nurses • • • • • • Includes: Patient Centered Care Teamwork and Collaboration Evidence-based Practice Quality Improvement Safety Informatics Patient Centered Care: Recognizing the patient or designee as the source of control and full partner in providing compassionate and coordinated care based on respect for patient's preference, values, and needs. In patient centered care, patient and families participate in nursing and medical decision making and in care coordination with all members of the health care team. Patient Centered Care requires nurses to seek out and apply interventions learned from the abundance of information to the individual patient receiving the care. A nurse has to have the knowledge, skills, and attitude to properly care for a patient. Knowledge Skills Attitudes Integrate Elicit patient values understanding if , preferences, and multiple expressed needs as dimensions of part of clinical Patient-Centered Care patient centered interview care Value seeing health care situations “through patient's eyes” Describe how diverse cultural, ethnic, and social backgrounds function as sources of patient, family, and community values Respect and encourage the individual expression of patient values, preferences, and expressed needs Communicate patient values, preferences, and expressed needs to other members of the health care team Sources: http://qsen.org/competencies/prelicensure-ksas/ Cherry, B. (2014). Contemporary Nursing (6th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Example: A 28 year old female was admitted to the hospital. During her assessment with the nurse, the patient stated, “ I would like to try more holistic methods in treating my pain before taking any pain medication.” The nurse noted as such in the patient's chart. Later in the day, the patient was complaining of pain. The nurse immediately administers pain medication before asking patient if she wanted to try any holistic methods first. Is this an example of patientcentered care? Why? No, the patient specifically stated she wanted to try holistic methods before any pain medication was administered. The nurse should have asked the patient if she had tried or wanted to try some deep breathing exercises, meditation, distraction, or other nonpharmacological treatments first. The ultimate goal in patient-centered care is to involve the patient in the care for themselves. Competency of Teamwork and Collaboration Nursing personnel must be able to competently interact with physicians, pharmacists, respiratory care therapists, dieticians, physical and occupational therapists, nurse practitioners, clinical nurse specialists, physician assistants, social workers and care managers, licensed practical nurses and unlicensed assistants. Effective teamwork and positive interdisciplinary collaboration among and between healthcare providers are seen as important contributors to improved patient outcomes (http://scholarworks.gvsu.edu, 2012). Knowledge Skills Attitudes Describe impact of Clarify roles and own accountabilities communication under conditions of style on others. potential overlap in Patient-Centered Care team member functioning. Respect the centrality of the patient/family as core members of any health care team. Recognize contributions of other individuals and groups in helping patient/family achieve health goals. Appreciate the risks associated with handoffs among providers and across transitions in care. Solicit input from other team members to improve individual, as well as team, performance. Sources: http://qsen.org/competencies/prelicensure-ksas/ The QSEN project contributes to this competency by offering a database of educational strategies that have been submitted to the project on the merits of being helpful to healthcare educators on the baccalaureate program and associate degree level as well as for continuing education and staff development. Evidence-Based Practice Definition: Integrate best current evidence with clinical expertise and patient/family preferences and values for delivery of optimal health care. Knowledge Skills Attitudes Differentiate Participate in clinical opinion structuring the from research and work environment evidence to facilitate Patient-Centered Care summaries. integration of new evidence into standards of practice. Value the concept of EBP as integral to determining best clinical practice Explain the role of evidence in determining best clinical practice Appreciate the importance of regularly reading relevant professional journals Question rationale for routine approaches to care that result in lessthan-desired outcomes or adverse events Sources: http://qsen.org/competencies/prelicensure-ksas/ http://www.asatonline.org/treatm ent/articles/evidencebasedpractice Evidence-based practice means that clinicians use evaluation and treatment procedures for particular disorders and populations. Evidencebased practice also takes into account current understanding of the patho-physiology of the disorder(s) being treated, clinical expertise, and the client’s preferences for treatment. -- Jeri A. Logemann Quality improvement: Nurses are in a greater demand for increasing the quality improvement according to a new study by the Center of Studying Health System Change (HSC). There are tools used to help with the competencies being completed and improved in the hospital setting. These tools would include flowcharts, cause-effect diagrams, control charts and run chart. These tools help to analyze events and understand the different variations of why the negative events occurred and their root cause. Hospitals need supportive leadership, a philosophy of quality as everyone’s responsibility, individual accountability, and effective feedback that would offer greater promise for successful improvement activities. Quality improvement Nurses are in a greater demand for increasing the quality improvement according to a new study by the Center of Studying Health System Change (HSC). Knowledge Skills Attitudes Describe Practice aligning approaches for the aims, measures changing processes and changes of care. involved in Patient-Centered Care improving care. Appreciate the value of what individuals and teams can to do to improve care. Explain the importance of variation and measurement in assessing quality of care. Appreciate how unwanted variation affects care. Use tools (such as control charts and run charts) that are helpful for understanding variation. Sources: Qsen.org/competencies/2013 www.hschange.com/CONTENT/972 /2006 There are tools used to help with the competencies being completed and improved in the hospital setting. These tools would include flowcharts, cause-effect diagrams, control charts and run chart. These tools help to analyze events and understand the different variations of why the negative events occurred and their root cause. Hospitals need supportive leadership, a philosophy of quality as everyone’s responsibility, individual accountability, and effective feedback that would offer greater promise for successful improvement activities. Safety: Definition: Minimizes risk of harm to patients and providers through both system effectiveness and individual performance. • In 2000 there was an alarming report by the institute of medicine (IOM) titled To Err Is Human: Building a safer Health System, authors extrapolated and summarized data from two major studies and concluded that up to 98,000 patients are killed each year from medical errors, confirming that poor quality of care is a major problem in the United States. Contributing factors: • Overuse of expensive invasive technology • Underuse of inexpensive care services • Error-prone implantation of care that could harm patients and waste money : Knowledge Skills Discuss potential Use national and actual impact patient safety of national patient resources for own safety resources, Care professional Patient-Centered initiatives and development and regulations to focus attention on safety in care settings Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care Attitudes Value relationship between national safety campaigns and implementation in local practices and practice settings Communicate Value own role in observations or preventing errors concerns related to hazards and errors to patients, families and the health care team Sources: Qsen.org/competencies/2013 www.hschange.com/CONTENT/972 /2006 • 2012 National Patient Safety Goals • Improve the accuracy of patient identification. • Improve the effectiveness of communication among caregivers • Improve the safety of using medications. • Reduce the risk of health-care association • Reduce the risk of patient harm resulting in from falls. • Prevent health-care associated pressure ulcers • The organization identifies safety risks inherent in its patient population • Universal protocol for preventing wrong site, wrong procedure, wrong person surgery. : Informatics: the use of information and technology to communicate, manage knowledge, mitigate error, and support decision making. “Current nursing students may present with more advanced knowledge of informatics, be it a social networking skill, word processing skill, surfing the internet and so on than faculty or staff.” --Cherry. Page 401. Knowledge Skills Attitudes Identify essential Navigate the information that electronic health must be available in record aPatient-Centered common Care database to support patient care. Value technologies that support clinical decision making, error prevention, and care coordination Describe examples of how technology and information management are related to the quality and safety of patient care Value nurses’ involvement in design, selection, implementation, and evaluation of information technologies to support patient care Respond appropriately to clinical decisionmaking supports and alerts Cherry Page 402 Table 22-6 Go to jeannieeden.com to see this PowerPoint presentation and another time. Works Cited Cherry, B. (2014). Contemporary nursing: issues, trends, & management (6th ed.). St. Louis, Mo.: Elsevier. Qsen.org/competencies/2013 www.hschange.com/CONTENT/972/2006 http://qsen.org/competencies/pre-licensure-ksas/ http://scholarworks.gvsu.edu, 2012