QSEN Presentation June 2008
advertisement

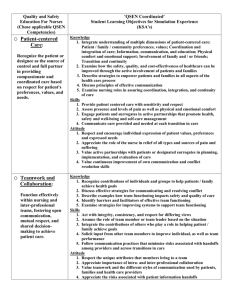
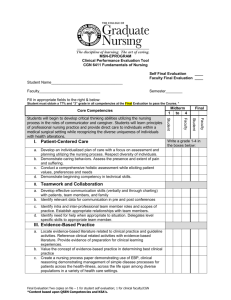
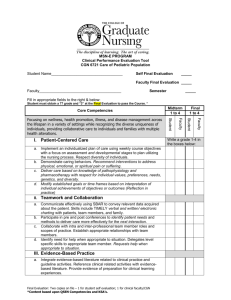
Implementation of Quality & Safety Competencies in ADN Curriculum St. John’s College of Nursing of Southwest Baptist University Springfield, Missouri June 2008 Pilot Team: Teresa Russell, Rebecca Miller & Tonyha Sumners QSEN Projects: Faculty QSEN Fact Sheet QSEN Reference Manual in Faculty Lounge QSEN Pilot Team Report @ monthly faculty meetings Incorporated QSEN into annual faculty course reports (Systematic Evaluation) Established alliance with practice partner QI VP First Touch TM Faculty accepted QSEN competencies as threads in new curriculum Faculty retreat on Simulation (May 2008) QSEN Projects: Students QSEN Fact Sheet QSEN Terminology prior to survey SBAR First Touch TM Clinical Evaluation Tool (new curriculum) Development of Process Audit Tool Interdisciplinary experiences senior level students Primary Practice Partner: St. John’s Health System One of the Nation's Top 3 Integrated Health Systems St. John’s is a Springfield, MO - based integrated health system, serving the residents of southwest Missouri and northern Arkansas since 1891. More than 10,000 co-workers, 460 physicians and 1,100 volunteers work together to fulfill St. Johns' mission of improving the health and quality of the communities we serve, with a particular concern for those who are economically poor. Introduction to Quality & Safety Fundamentals of Nursing Students Goal: Incorporate components of QSEN KSA’s into workplace orientation through collaboration with primary practice partner. Background Faculty education regarding QSEN activities and KSA’s Assessment of current compliance with KSA’s Discussion with practice partner (VP Quality and Nursing Administration) regarding current monitoring activities reflective of Quality and Safety initiatives Review of proposal for curriculum revision Approaches QSEN concepts and KSA’s introduced within first 2 weeks of the Fundamentals of Nursing course. Process and observation audits integrated into patient care unit orientation. References QSEN articles and web site Healthcare agency nursing process audits tools Healthcare agency quality department audit tools Literature search for tools Contents of Audit Tool Introduction to: Patient Care Environment: Focus- Safety, Teamwork, & Collaboration Medical Record: Focus-Quality & Informatics Patient Care Focus-Patient Centered Care & Evidence Based Practice Patient Care Environment: FocusSafety, Teamwork & Collaboration Examples: Conversations by staff in rooms, hallways, and other areas are conducted quietly and professionally Examples of Crucial Conversations heard Examples of conversations between disciplines Hallways are free of equipment and/or objects that might impede patient/visitor movement All patient care equipment/supplies are located to provide for patient privacy and safety Medical Record: Focus-Quality & Informatics Examples: Pain is assessed on admission Vital Signs are taken per hospital policy I & O is documented every shift Restraint flow sheet is completed per hospital policy Patient Care Focus-Patient Centered Care & Evidence Based Practice Examples: IV in place less than 96 hours IV location promotes comfort and safety for patient IV device used is appropriate for patient’s therapy IV dressing is dry and intact Hand washing foam/gel is available in patient’s room and outside door Patient Care Focus-Patient Centered Care & Evidence Based Practice Examples: Staff going in and out of patient’s room are using proper hand hygiene Call lights are answered within 1-2 minutes Patients and visitors are greeted and assisted in ways that exemplify the components of First Touch First Touch TM Patient-centered care Practice Partner/Press Ganey Results Patient Satisfaction averaged at the 50th percentile Website: http://www.first-touch.org/ Implementation with faculty/students The Basics of First Touch TM How we view others The first introduction Establishing presence Touch Retouch Handoffs First Touch Education Fundamentals of Nursing Students A survey tool containing Likert scale and qualitative comment items was developed to measure student understanding of major concepts of First Touch The tool was administered immediately following initial education and again immediately following students’ Fundamentals of Nursing clinical practicum Survey Results Initial findings: Understanding of major concepts Qualitative comments were primarily paraphrased from presentation information Post-clinical findings: Loss of understanding of 1 major conceptRetouch Qualitative comments reflected purpose and intent of First Touch TM Program Student Comments Post-Clinical How We View Others: “By relaying a positive message to the next care provider it sets a positive tone for care for the next shift” “It allowed me to provide unbiased care” “The next person taking care of my patient wasn’t dreading going into the room” The Implementation of Quality & Safety Competencies in ADN Curriculum at St. John’s College of Nursing of Southwest Baptist University has been influenced by participation in the Quality & Safety Education for Nurses funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Pilot Schools Collaborative Vote St. John’s College of Nursing For Most Effective Clinical Partnership Award + = RN