QSEN Project: Quality & Safety Education for Nurses Presentation
advertisement

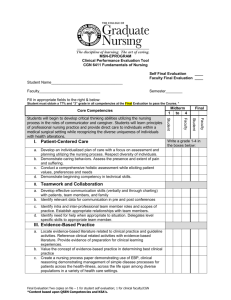
Quality and Safety Education for Nurses The QSEN Project Health Professions Education: A Bridge to Quality (IOM, 2003) All health professionals should be educated to deliver patient-centered care as members of an interdisciplinary team, emphasizing evidence-based practice, quality improvement approaches, and informatics. QSEN Grant project funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. Primary Investigator: Linda Cronenwett, Professor and Dean at the School of Nursing, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. 6 co-investigators from across the nation Purpose Address the challenges of preparing prelicensure nurses with competencies necessary to become active workforce participants in national quality and safety goals and initiatives. Research Base The QSEN faculty members adopted the Institute of Medicine’s competencies for nursing Developed definitions and statements of knowledge, attitudes, and skills that should be included in pre-licensure nursing education. Identified competencies include: Patient Centered Care Teamwork & Collaboration Evidence-based Practice Quality Improvement Safety Informatics QSEN Competencies Patient-centered Care Recognize the patient or designee as the source of control and full partner in providing compassionate and coordinated care based on respect for patient’s preferences, values, and needs Teamwork & Collaboration Function effectively within nursing and inter-professional teams, fostering open communication, mutual respect, and shared decision-making to achieve quality patient care QSEN Competencies Evidence-based Practice Integrate best current evidence with clinical expertise and patient/family preferences and values for delivery of optimal health care Quality Improvement Use data to monitor the outcomes of care processes and use improvement methods to design and test changes to continuously improve the quality and safety of health care systems QSEN Competencies Safety Minimize risk of harm to patients and providers through both system effectiveness and individual performance Informatics Use information and technology to communicate, manage knowledge, mitigate error, and support decision making St John’s College of Nursing Responded to a national call for proposals for participation in the QSEN Pilot School Learning Collaborative Our College was chosen as 1 of 2 Associate Degree Programs nationwide to be included in the project Overall, 15 proposals were selected for funding from a pool of 53 applicants. St John’s Pilot Team Tonyha Sumners, Associate Professor Rebecca Miller, ASN Program Director Teresa Russell, Associate Professor Pilot School Learning Collaborative Goals Produce curricular maps for learning activities related to quality and safety competencies in nursing prelicensure programs. Generate and evaluate teaching strategies associated with the targeted knowledge, skills and attitudes of each quality and safety competency. Describe the faculty development approaches and resources that lead to desired curricular change. Our Goals Educate faculty regarding QSEN competencies Introduce QSEN competencies to students within the 1st two weeks of the nursing program Build learning activities that highlight competencies throughout the curriculum Faculty Education Resource book placed in faculty lounge QSEN highlight at each faculty meeting Seminar for faculty Systematic Evaluation now references QSEN teaching strategies used in each course Students Introduction to QSEN competencies Process Audit tool First TouchTM education Evidence-based Practice Information Simulation Teamwork & Collaboration Ethics Grand Rounds Medication Safety Committee Resource Quality and Safety Education for Nurses