Brain Regions & Protection: Presentation
advertisement
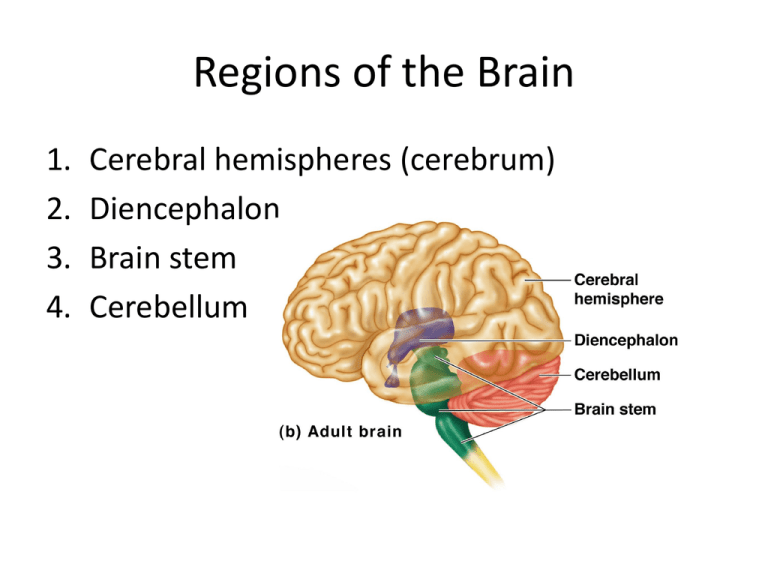
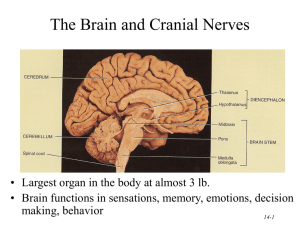
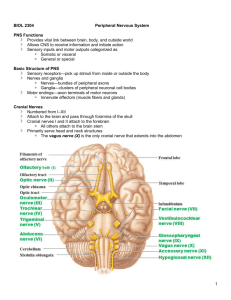
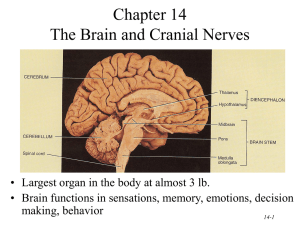
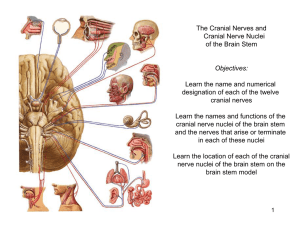
Regions of the Brain 1. 2. 3. 4. Cerebral hemispheres (cerebrum) Diencephalon Brain stem Cerebellum 1. Cerebrum Surface lobes of the cerebrum Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Occipital lobe Temporal lobe Figure 7.13a 1. Cerebrum Figure 7.13c 2. Cerebrum Figure 7.13a 3. Brain Stem • Attaches to the spinal cord • Parts of the brain stem – Midbrain – Pons – Medulla oblongata 4. Cerebrum • Cerebral Hemispheres (Cerebrum) – The surface is made of ridges (gyri) and grooves (sulci) – A gyri is an elevated ridge of cerebral tissue. – Inward folds of cerebral tissue are called fissures or sulci. Layers of the cerebrum Gray matter—outer layer in the cerebral cortex composed mostly of neuron cell bodies White matter—fiber tracts deep to the gray matter Corpus callosum connects hemispheres Basal nuclei—islands of gray matter buried within the white matter Gray matter is composed of cell bodies of neurons. White matter is composed of fiber tracts . Nuclei deep within the cerebral white matter are collectively called basal nuclei (ganglia). 4. TERMS • A bundle or fibers that provides for communication between different parts of the CNS is called a process. Like corpus callosum • A bundle of fibers that carries impulses between the periphery and CNS areas is called a nerve. 5. Diencephalon Intermediate mass Figure 7.16 6. Brain Structures • Medulla oblongata- most important autonomic center of the brain & contains autonomic centers regulating heart rate, respiration, and other visceral activities. • Corpora quadrigemina- located in the midbrain; contains reflex centers for vison and hearing. • Cerebellum- coordinates complex muscular movements. • Corpus callosum- large fiber tract connecting cerebral hemispheres. • Pituitary gland & pineal body- part of the endocrine system • Cerebral aqueduct- canal that connects the third and fourth ventricles • Thalamus- contains the intermediate mass Protection of the Central Nervous System • • • • • Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral column Meninges Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Blood-brain barrier Trauma to base of brain • Base of brain houses the brain stem, which houses most of the vital autonomic centers. Controls heart rate, respiration, blood pressure. Protection of the Central Nervous System Figure 7.17a 8. Meninges • Dura mater-outermost layer; tough fibrous connective tissue, – falx cerebri, a subdivision of dura mater that separates the right and left cerebral hemispheres – A dural fold that attaches the cerebrum to the crista galli of the skull • Arachnoid layer – Middle layer – Web-like; delicate with cottony fibers • Pia mater-innermost vascular layer covering the brain; follows every convolution – Clings to the surface of the brain Meninges Figure 7.17b 8. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) • Similar to blood plasma composition • choroid plexus- structure that forms the cerebrospinal fluid • Forms a watery cushion to protect the brain • Circulated in arachnoid space, ventricles, and central canal of the spinal cord • Arachnoid villi drains cerebrospinal fluid into venous blood in the dural venous sinuses 10. Ventricles and Location of the Cerebrospinal Fluid Choroid plexus Figure 7.18a–b 10. Ventricles and Location of the Cerebrospinal Fluid 1. Lateral ventricles 7. Dural sinuses 6 . 5. 2. 3 . 4 . Lateral ventricle third ventricle cerebral aqueduct of midbrain fourth ventricle - central canal subarachnoid space arachnoid villi dural sinuses Figure 7.18c Blood-Brain Barrier • Includes the least permeable capillaries of the body • Excludes many potentially harmful substances • Useless as a barrier against some substances – Fats and fat soluble molecules – Respiratory gases – Alcohol – Nicotine – Anesthesia Traumatic Brain Injuries • Concussion – Slight brain injury – No permanent brain damage • Contusion – Nervous tissue destruction occurs – Nervous tissue does not regenerate • Cerebral edema – Swelling from the inflammatory response – May compress and kill brain tissue Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) • Commonly called a stroke • The result of a ruptured blood vessel supplying a region of the brain • Brain tissue supplied with oxygen from that blood source dies • Loss of some functions or death may result Alzheimer’s Disease • Progressive degenerative brain disease • Mostly seen in the elderly, but may begin in middle age • Structural changes in the brain include abnormal protein deposits and twisted fibers within neurons • Victims experience memory loss, irritability, confusion, and ultimately, hallucinations and death Cranial Nerves • PNS: Cranial Nerves • I Olfactory nerve—sensory for smell • II Optic nerve—sensory for vision • III Oculomotor nerve—motor fibers to eye muscles • IV Trochlear—motor fiber to eye muscles PNS: Cranial Nerves • V Trigeminal nerve—sensory for the face; motor fibers to chewing muscles • VI Abducens nerve—motor fibers to eye muscles • VII Facial nerve—sensory for taste; motor fibers to the face • VIII Vestibulocochlear nerve—sensory for balance and hearing PNS: Cranial Nerves • IX Glossopharyngeal nerve—sensory for taste; motor fibers to the pharynx • X Vagus nerves—sensory and motor fibers for pharynx, larynx, and viscera • XI Accessory nerve—motor fibers to neck and upper back • XII Hypoglossal nerve—motor fibers to tongue PNS: The Cranial Nerves Table 7.1 (1 of 4) PNS: The Cranial Nerves Table 7.1 (2 of 4) PNS: The Cranial Nerves Table 7.1 (3 of 4) PNS: The Cranial Nerves Table 7.1 (4 of 4)