Document
advertisement

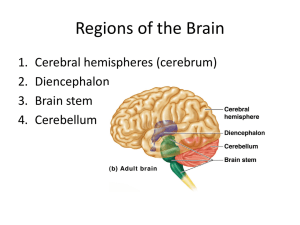
The Cranial Nerves and Cranial Nerve Nuclei of the Brain Stem Objectives: Learn the name and numerical designation of each of the twelve cranial nerves Learn the names and functions of the cranial nerve nuclei of the brain stem and the nerves that arise or terminate in each of these nuclei Learn the location of each of the cranial nerve nuclei of the brain stem on the brain stem model 1 12 pairs of Cranial Nerves arise from the forebrain and the brain stem. I II I II III Olfactory Telencephalon Optic Diencephalon IV VI V VII VIII IX XII XI Cranial Nerves III through XII arise from the Brain Stem: Midbrain III Oculomotor IV Trochlear Pons V Trigeminal VI Abducens VII Facial Medulla VIII Vestibulocochlear IX Glossopharyngeal X Vagus XII Hypoglossal X Cranial Nerve XI Spinal Accessory Nerve arises from the Spinal Cord 2 A c Drawing A shows the ventral surface of a model of a dissected human brain. The cerebral cortex with its underlying white matter and the cerebellum have been removed. In the forebrain the caudate (c) and putamen (p) join together in the anterior, ventral area of the basal ganglia. p Cranial nerves: B dorsal view OPTIC II c OCULOMOTOR III TROCHLEAR IV midbrain pons medulla spinal cord th TRIGEMINAL V ABDUCENS VI FACIAL VII VESTIBULOCOCHLEAR VIII GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL IX VAGUS X HYPOGLOSSAL ROOTLETS XII SPINAL ACCESSORY XI Only the trochlear nerve IV arises from the dorsal surface of the brain stem. It courses around the midbrain to join III and VI to enter the orbit. 3 Cranial Nerve Nuclei The cranial nerves innervate the head and neck, Cranial nerve fibers include the same four “general” functional components as the spinal nerves : GSE, GVE, GVA and GSA. In addition the head contains 1) “special” visceral sensory organs for olfaction and taste, 2) “special” somatic sensory organs for vision, audition, and balance, and 3) a “special” group of muscles embryologically derived from the branchial arches. Thus seven functionally-distinct columns of cells in the brain stem comprise the cranial nerve nuclei: GSE GVE SVE GVA SVA GSA SSA somatic motor preganglionic parasympathetic branchial motor visceral sensory olfaction and taste somatosensory audition and vestibular function The model shows a “dissection” of the cranial nerve nuclei in the tegmentum of the brain stem. 4 4 III MOTOR NULCEI IV GSE SOMATIC MOTOR V oculomotor III extraocular mm. trochlear IV abducens VI hypoglossal XII tongue mm. GVE VII VI PARASYMPATHETIC VII IX Edinger Westphal III (not on model) salivatory nuclei VII, IX dorsal motor nucleus of X SVE XII X BRANCHIOMOTOR motor nuc. V mastication facial nuc. VII facial expression nucleus ambiguus IX, X, cXI pharynx, larynx accessory sXI trapezius, sternomastoid Nucleus ambiguus IX, X and cXI sXI 5 5 V mesencehaplic SENSORY NULCEI V principal sensory SSA AUDITION AND BALANCE vestibular VIII cochlear VIII GSA SOMATOSENSORY trigeminal V: mesencephalic proprioception principal sensory discriminative touch spinal pain & temperature SVA TASTE nucleus solitarius, rostral VII, IX, X GVA VIII vestibular VIII cochlear rost nuc solitarius VII, IX, X caud nuc solitarius IX, X V spinal PAIN, etc. nucleus solitarius caudal IX, X 6 6 Cranial Nerves and Cranial Nerve Nuclei of the Brain Stem F Question I Match each cranial nerve nucleus (A - H) with the appropriate functional designation (1 - 8). _____ 1. receives pain input from teeth A _____ 2. innervates pharyngeal mm. B _____ 3. receives input from inner ear C _____ 4. Innervates tongue mm. D G H I _____ 5. receives fine tactile input from lips E _____ 6. Innervates mm. of mastication _____ 7. preganglionic parasympathetic _____ 8. Innervates extraocular mm. 77 Cranial Nerves and Cranial Nerve Nuclei of the Brain Stem ANSWER SHEET Question I 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. E D C I B G H F 8