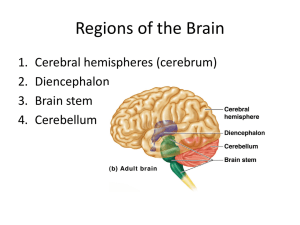
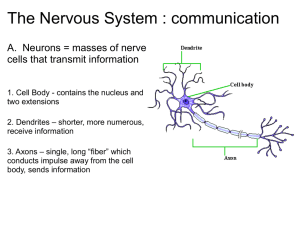
cells of the brain
advertisement
Anatomy & Physiology of the Brain (Encephalon): Preparing for ICD-10-CM/PCS © Irene Mueller EdD, RHIA May 2, 2013 Objectives Review Brain Anatomy and Physiology for ICD-10-CM/PCS Coding Overlap of Circulatory and Nervous Systems Functions of Brain Components of Brain Cells of Brain Brain Nerves ICD 10 CM Terminology ICD 10 PCS Terminology Integrated into presentation Have you completed the Pre-Test???? Overlap of Circulatory and Nervous Systems in Brain Connected through organ & bodily function control All body functions are regulated by brain through nervous system W/o messages from brain, circulatory system does not work Heart function & fluid circulation triggered by nervous system Messages sent from the brain control both blood and lymphatic parts of circulatory system Blood provides energy for brain Brain = 2% of mass, uses 20% of energy Avg weight of adult brain is about 3 pounds Examples of Overlap in brain Blood pressure and heart rate regulation Vagus nerve controls pumping of heart As heart pumps, blood moves through blood passageways around body to organs Baroreceptors pass information about blood pressure to brain so brain makes adjustments to heart rate Dependent on each other to ensure homeostasis Nervous system may have control, but circulatory system must relay information for adjustments Both systems need to function properly & work together to ensure proper body functions Circulatory System Components of Brain Cerebral Arteries AKA Intracranical Middle Cerebral Anterior /Posterior Communicating Anterior/Posterior Cerebral Cerebellar Other specified Precerebral Arteries AKA Extracranial Leading to cerebrum, but NOT in cerebrum Right vs Left for coding Basilar artery Carotid (Common, Internal) External does NOT feed brain) Vertebral Other Anterior spinal Auditory internal Circle of Willis Basilar Internal carotid Vertebral artery http://etc.usf.edu/clipart/15400/15496/bldbrnvessls_15496.htm Functions of Brain Control Center of body Maintains homeostasis (w/endocrine system) http://etc.usf.edu/clipart/8100/8171/human _brain_8171.htm Nervous System Components of Brain Nervous system = 2 parts CNS = Brain and Spinal Cord (not part of this webinar) Cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem PNS = Nerves and Ganglia Somatic – connect CNS with skeletal muscles and skin Autonomic – connect CNS with cardiac/smooth muscle and glands Cerebrum (L, brain) Largest Part of brain Cortex = Gray Matter on surface 6 layers of nerve cell bodies Millions of cells Cerebral White Matter Under cortex Myelinated axons of nerve cells Transmit in 3 directions Association = within same hemisphere Commissural = from one hemisphere to other Projection = from cerebrum to other parts of CNS Functions of Cerebrum 3 general functions Motor = Govern muscle movement Sensory = Interpret sensory input Vision = 30 % of cortex Touch = 8% Hearing = 3 % Association = Emotional and intellectual processes Cortex As brain grows, more gray matter Cortex folds on itself, creating Gyri (AKA convolutions) Gk, gyro, circle Upfolds winding over surface Fissures – Deep downfolds Sulci –sulcus /sul·cus/ (sul´kus) pl. sul´ci [L.] a groove, trench, or furrow shallow downfolds separating gyri http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/traumaticbraininjury.html Hemispheres of Cerebrum Right and Left halves of brain Divided by Longitudinal Fissure Connected by Corpus Callosum Large bundles of transverse nerve cell fibers “Rain Man” – born w/o Each hemisphere divided into 4 lobes Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, and Occipital Fifth lobe = Insula Oval region of cerebral cortex overlying extreme capsule, lateral to lenticular nucleus, buried in depth of the fissura lateralis cerebri (sylvian fissure) Separated from the adjacent frontal, parietal, and temporal opercula by circular sulcus of insula. Synonym(s): insular area, insular cortex, island of Reil Corpus Callosum L, - callous, hard AKA colossal commissure of brain A tract of nerve fibers passing from one side to other of spinal cord or brain Larger in women Can transfer data between R & L hemispheres faster than men Woman’s intuition Lobes of Cerebrum http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lobes_of_the_brain Frontal Lobe Functions Responsible for higher cognitive functions, including: Problem solving Memory Language Judgment Spontaneity Motivation Impulse Control Social and Sexual Behavior Temporal Lobe Functions Role in emotions Responsible for Smelling Tasting Perception Memory Understanding music Aggressiveness Sexual behavior Language areas of brain Language areas of Brain Broca’s area French surgeon, 1861 Frontal lobe Motor neurons Control of Speech Wernicke’s area German pathologist, 1874 Temporal lobe Motor neurons Comprehension of Language, Speech sounds http://wwwrohan.sdsu.edu/~gawron/intr o/course_core/lectures/aphas ia_cases_slides.html Uncus L. – uncus – hook From Gk onkos Hooklike anterior end of hippocampal gyrus on temporal lobe of brain Parietal Lobe Functions Role in sensations of touch, smell, and taste Processes sensory & spatial awareness Key part of eye-hand co-ordination & arm movement Wernicke’s area Matching written words to sound of spoken speech Occipital Lobe Functions Controls vision and recognition Receives visual input from retina Visual perception Color recognition Retina is part of brain Visual signals are interpreted in occipital lobes Each optic nerve has million fibers Cerebellum Sited below back of cerebrum Transverse fissure separates from cerebrum 2 hemispheres separated by vermis Both gray and white matter Connected to brain stem by cerebellar peduncles (paired fiber bundles) http://etc.usf.edu/clipart/15500/15558/bra inbase_15558.htm Functions of Cerebellum Motor area of brain Controls unconscious movements in skeletal muscles Coordination, Posture, Balance Brain Stem Located below cerebrum & in front of cerebellum Structures (from top to bottom) Thalamus Hypothalamus Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata http://birthinjury.org/brain-injury-cerebral-palsy-tour-of-brain.html Thalamus (Gk: Inner Room) Oval-Shaped, Large, Located above midbrain Relays all sensory impulses (EXCEPT smell) to cerebral cortex “Gateway” Interprets and produces conscious Pain recognition Corpus striatum Striped mass of white & grey matter located in front of thalamus in each cerebral hemisphere Consists of caudate nucleus and lenticular nucleus Hypothalamus Controls many homeostasis-related body actions Interprets viscera-based sensory impulses Controls Body temperature Regulates Biorhythms (Wake/Sleep) ANS – heartbeat, food movement, urinary bladder Regulates food intake (Hunger/Satiety) Regulates fluid intake (Thirst) Monitors/Works with endocrine system Responds to Mental states – Fear, etc. Midbrain Connects Pons and Cerebellum Short, Constricted Origination of 2 Cranial Nerves III – Oculomotor IV - Trochlear Pons (L. Bridge) Located anterior to Cerebellum, above Medulla Bridge between spinal cord & Brain Connects other parts of brain as well Origination for 4 cranial nerves V – Trigeminal VI – Abducens VII – Facial VIII – Vestibulocochlear Medulla oblongata Lowest part of brain Form upper part of Spinal Cord Main Conduction Pathways 2 pyramids - ventral aspect Motor tracts from cortex to cord Nerve fibers cross to other side Extrapyramidal = functional, not anatomical, unit comprising nuclei & fibers (excluding pyramidal tract) involved in motor activities; control/coordinate especially postural, static, supporting, & locomotor mechanisms. 2 nuclei on dorsal aspect Receive sensory impulses from spinal cord (ascending) Relay to OPPOSITE side of medulla Origination for 4 cranial nerves IX – Glossopharyngeal X – Vagus XI – Accessory XII - Hypoglossal Medulla oblongata, cont. Reflex Centers Cardiac – Regulates Heartbeat Respiratory – Rate and Depth of Breath Vasoconstrictor – Regulates Diameter of Blood Vessels Cerebellar peduncles 3 sets of paired bundles of hindbrain, connecting cerebellum to Midbrain (superior) Pons (middle) Medulla oblongata (inferior) Tapetum of brain L. tapeta - a carpet Layer of fibers of corpus callosum forming roof of part of lateral ventricle Glands in the Brain Pineal (L., Pine cone) Pituitary L. - pītuītārius pertaining to/secreting phlegm Pineal Gland Endocrine gland Source of melatonin Hormone derived from tryptophan Regulates circadian rhythm (sleep cycle) Located behind 3rd cerebral ventricle Midline of brain Pituitary Gland Master gland Central role in homeostasis, maintaining reproductive cycle, directing activity of other glands Anterior, intermediate, and posterior lobes function as 3 separate endocrine organs Distinct cell populations, secretory products, & regulatory mechanisms Anterior lobe secretes thyroid stimulating hormone, corticotropin, luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, growth hormone, and prolactin. Regulated by hypothalamus via portal vascular system Posterior lobe releases oxytocin & vasopressin from axon terminals originating in cell bodies located in hypothalamus Intermediate lobe rudimentary in humans, but produces several hormones (which are just now being studied). Limbic System of Brain Thalamus Hypothalamus Cingulate gyrus Amygdala Hippocampus Basal Ganglia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lobes_of_the_brain Limbic System Functions Regulates emotion and memory Directly connects lower & higher brain functions Influences Emotions Visceral responses to emotions Motivation and Mood Sensations of pain and pleasure Limbic System Components Cingulate gyrus , L. - Girdle (surrounding), Gk. - Circle Amygdala, Gk. – Almond (also used for tonsil) Hippocampus, Gk. – seahorse Basal Ganglia, Gk. - knot Cingulate gyrus Part of cerebrum gray matter Surrounds, directly connected to parts of inner Limbic System Serves as conduit for messages to and from inner Limbic System Amygdala Makes associations across different modes of stimulus Appears responsible for influence of emotional states on sensory inputs Smell of lilacs = visual memory of my house in Great Falls Same stimulus = Different perceptions Sound of USAF Jets not noise – memory of childhood Responsible for face recognition? Hippocampus VERY important in transition of information from short to long term memory Search Engine of brain Learning and consciously remembering everyday facts and events Also part of Temporal Lobe Damage to that lobe can result in memory loss Basal Ganglia AKA Substantia nigra, Subthalmic nucleus Important in planning & coordinating motor movements and posture Basal Ganglia linked with Cerebral Cortex via complex neural connections Major effect of Basal Ganglia = Prevention of unwanted muscular activity Basal Ganglia Disorders result in exaggerated, uncontrolled movements Ventricles (Ependyma) Network of connected cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 2 Lateral Ventricles Third Ventricle Cerebral Aqueduct AKA Aqueduct of Sylvius Fourth Ventricle http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1923254-overview Functions of Ventricles Choroid plexuses located in ventricles produce CSF, which fills ventricles & subarachnoid space Cycle of production and re-absorption (toxic wastes) Buoyancy, Protection, & Chemical stability Protection = CSF in meninges protects brain from striking cranium when head jolted Buoyancy = CSF and brain have similar density, so brain is suspended neutrally, allowing growth without sitting on bone CSF has protein, glucose, electrolytes, etc 500 ml per day, space for 130 ml in system Meninges Protect brain and spinal cord 3 membranes Dura mater = Outermost, tough, thick, fibrous Arachnoid = Middle, delicate, fibrous Pia Mater = Inner, transparent, tender Contains blood vessels Only layer that adheres to brain surface Leptomeninges – 2 innermost; CSF circulates between them Gk – Small, thin CELLS OF THE BRAIN http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/brain_basics/ninds_neuron.htm Cells of Brain 100 billion neurons (nerve cells) Sensory (afferent) – messages TO brain Motor (efferent) – messages FROM brain Trillions of Glia (Gk: Glue) (glial cells) AKA Neuroglia Connective tissue of brain 4 main types Astrocytes, ependymal cells, microglia, oligodentrocytes Common tumors of nervous system 3 classes of neurons Sensory neurons carry information from sense organs (such as eyes and ears) to brain Motor neurons control voluntary muscle activity (ex: speaking) carry messages from nerve cells in brain to muscles All other neurons are Interneurons Neurons - 3 basic parts Cell body - includes nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell organelles Dendrites Nucleus =DNA & information needed for growth, metabolism, and repair Cytoplasm = substance filling cell, including all chemicals/parts needed for cell to work properly Cell organelles = small structures (chromosomes, Golgi bodies, etc.) http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Branch from cell body, act as point of contact for receiving impulses (chemical/electrical signals) from neighboring neurons Axon Sends impulses, extends from cell body to meet/deliver impulses to another nerve cell Range in length from fraction of inch to several feet Sciatic nerve axons extend from buttock to top of foot Types of Glia cells Microglia = Brain’s immune system Schwann cells/Oligodendrocytes form insulating sleeves around neurons to keep electric signals from diffusing (Myelin) Radial glia in developing brain After helpng neurons move around Then become astrocytes Ependymal cells (ependymocytes) Cells lining central canal of spinal cord (pyramidal shape) or brain ventricles (cuboidal shape) Produce/absorb/move (cilia) CSF Myelin Insulating material wrapped around axons Complex mixture of proteins and fats Nodes of Ranvier – gaps in myelin Electrical signal jumps from node to node Increases conduction speed of electrical signals along nerve fibers to muscle Made by Glial cells Oligodendrocytes in CNS Schwann cells in PNS Transmission electron micrograph of a myelinated axon, generated at the Electron Microscopy Facility at Trinity College, Hartford, CT http://frcables.blogspot.com/ Astrocytes Have starlike rays Reach out in all directions Most abundant type of glial cells So, most abundant of all brain cells One astrocyte can wrap its rays around a million+ synapses Astrocytes fuse together Conduits for molecules moving from cell to cell Brain Waves Cells in Cerebrum generate electrical potentials Pass thru skull; Can be detected by electrodes EEG = recording/graph of brain waves http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epilepsy Beta - consciously alert, or feeling agitated, tense, afraid Frequencies from 13 to 60 pulses/second in Hertz scale Alpha - state of physical and mental relaxation, but aware of surroundings Frequencies around 7 to 13 pulses/second Theta - state of somnolence w/reduced consciousness +/- 4 to 7 pulses/second Delta - unconsciousness, deep sleep or catalepsy 0.1 to 4 cycles/second NERVES OF THE BRAIN Cranial Nerves ICD-10-CM Index I uses numerical order (first, fourth, etc), but also provides names III ICD-10-PCS uses NAMES only II V IV VI VI VIII AKA Auditory IX XII X Only First and Second Cranial Nerves originate in Cerebrum http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cranial_nerve XI Mnemonics for Cranial Nerves On Old Olympus’ Towering Top A Famous Vocal German Viewed Some Hops On Old Olympic Towering Tops A Finn And German Viewed Some Hops OLd OPie OCcasionally TRies TRIGonometry And Feels VEry GLOomy VAGUe And HYPOactive Some Say Marry Money, But My Brother Says Big Business Makes Money Some say my mother bought my brother some bad beer, my, my S= Sensory, M = Motor, B = Both Bonus Mnemonic for MS Some Lovers Try Positions That They Can't Handle!!! Scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate Neurotransmitters Chemicals that run brain 60+ affect memory, learning, relationships Thoughts, Food, Drugs affect brain chemicals Stored in sacks near synapse at end of axon Electrical charges from cell body free chemicals, propel them across synapse Special receptors at end of dendrites form to accept certain neurotransmitters Important Neurotransmitters Serotonin Epinephrine Aids in smooth transmission of Moving body when needs instant action, - fear/danger messages in brain/body Large role in regulating mood, Acetylcholine Enhances memory (chemical appetite, memory & learning responsible for many dreams) Lack of serotonin may result in low self-esteem, depression, Endorphin (neuropeptide) Body’s natural pain killer -lots of aggression endorphin can create euphoric feelings Dopamine Helps information flow to higher brain levels Key role in regulating pain/pleasure Melatonin Related to wake/sleep cycles Cortisol (neuropeptide) Released when under stress Can be dangerous at high levels – interrupts transmission of messages from neuron to neuron Documentation Requirements for Coding Laterality Specific Arteries Site Must use proximal branch for nerve that does not have separate body part value in ICD-10-PCS Ex: mandibular nerve is branch of trigeminal nerve, only the trigeminal nerve has a body part value When procedure performed on mandibular nerve, must assign trigeminal nerve for body part value Artery/Nerve Families, etc. (ICD-10-PCS Body Key) Alphabetical listing of body parts shows PCS Description to use with Table Rows when constructing a ICD-10-PCS code Anatomical Term PCS Description Caroticotympanic artery Internal Carotid Artery, R/L Carotid sinus nerve Glossopharyngeal nerve Leptomeninges Cerebral/Spinal meninges Mammillary body Hypothalamus Middle cerebral artery Intracranial artery QUESTIONS? Homework 1. Review Powerpoint before taking post-test 2. Go online to at least two of the Resource sites with Games and/or Quizzes and see what A&P about the brain you have learned/reinforced http://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/educational-resources/brain-basics/nimh-brain-basics.pdf Resources Amar AP, Weiss MH. Pituitary Gland Anatomy and Physiology. Abstract. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2003 Jan;14(1):11-23, v. Anatomy of the Brain. American Association of Neurological Surgeons. http://www.theonlinelearningcenter.com/free-medicalgames/AP001/anatomy-physiology-brain-skull.html Brain Anatomy. Game. http://www.aans.org/Patient%20Information/Conditions%20and%20Tre atments/Anatomy%20of%20the%20Brain.aspx Anatomy of the Brain and Skull. Philips Medical Games. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12690976?report=abstract http://www.purposegames.com/game/brain-anatomy-quiz Brain Anatomy and Functions. Tutorial and Quiz. Getbodysmart. http://www.getbodysmart.com/ap/nervoussystem/cns/brain/menu/menu.html Resources Cliff Notes. Anatomy & Physiology. Well-organized and includes quizzes. http://www.cliffsnotes.com/study_guide/AnatomyPhysiology.topicArticleId-277792.html Cranial Nerves: Review Info. Quizzes. Cranial Nerves: Review Info http://www.gwc.maricopa.edu/class/bio201/cn/cranial.htm Cranial Nerves Dirty Mnemonic Tutorial. Video. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LTUHTxWG6EQ Crisan, E. Ventricles of the Brain. Jun 27, 2011. Medscape Reference. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1923254-overview Resources Division of Disability and Aging Services. Vermont. Brain 101: The neurotypical brain. http://www.ddas.vermont.gov/ddas-policies/policies-tbi/policies-tbidocuments/tbi-trng-modules-workbks/training-module-1-brain-101 Gray, H. Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918. http://www.bartleby.com/107/ Human Brain Anatomy. Study and Quiz Modules. http://www.psych.ualberta.ca/~ITL/brain/ Interactive Tour of the Brain. National Brain Tumor Society. http://www.braintumor.org/patients-family-friends/about-braintumors/index8.html Intro to the Brain. ITS. San Diego State Univ. Includes Test. http://its.sdsu.edu/multimedia/mathison/index.htm Kean, M. L. The Brain. Tutorial. http://wwwrohan.sdsu.edu/~gawron/intro/course_core/lectures/aphasia_cases_s lides.html Resources Match a Brain. Game. http://www.anatomyarcade.com/games/matchingGames/MatchA Brain/matchABrain.html McGuire, N. ICD10 Session 11 Chapter 6. Codapedia. 32 Minute video. http://codapedia.com/article_548_ICD-10-Session-11-ChapterSix-Diseases-of-the-Nervous-System.cfm Neuron-Glia Interactions in Nerve Development and Disease. http://www.ngidd.eu/public/index.html NIMH. Brain Basics. http://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/educational-resources/brainbasics/brain-basics.shtml Pineal Gland. Encyclopedia Brittanica. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/460967/pineal-gland Resources Secret Life of the Brain. PBS. 3-D brain anatomy. http://www.pbs.org/wnet/brain/history/index.html Tamarkin, D. A. Glia. http://faculty.stcc.edu/AandP/AP/AP1pages/nervssys/unit10/glia.htm University of Bristol. How the Brain Works. Video, 6+ min. 2010. WebMD. Brain & Nervous System Health Center. http://www.webmd.com/brain/default.htm WebMD. Medical References Related to Brain & Nervous System. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9UukcdU258A http://www.webmd.com/brain/medical-reference-index Wernicke area. Encyclopedia Britannica. Videos, Animations. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/639879/Wernicke-area