Contents of Neurocranium II
advertisement

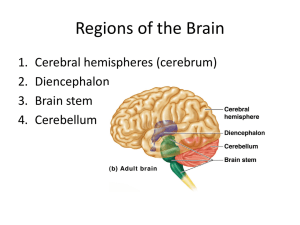
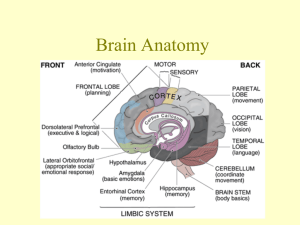
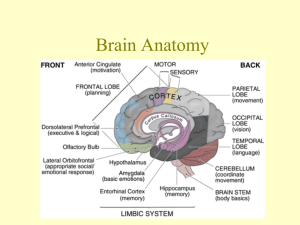
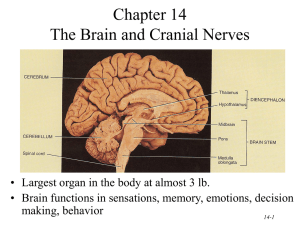
Contents of the Neurocranium, Part II The Brain, its Blood Supply and the Cranial Nerves Embryology • Central nervous system begins as neural tube • Anterior portion of neural tube differentiates into three primary divisions: – Hindbrain – Midbrain – Forebrain Embryology • Lateral walls of the forebrain expand and protrude from both sides of the neural tube • Median portion of forebrain is the diencephalon • Lateral projections form the telencephalon Embryology Two primary axes of growth in the developing brain 1. Longitudinal flexion of anterior neural tube 2. Inferior spiral rotation of the telencephalon Ventricles • Lumen of neural tube becomes the CNS ventricular system • Shape of ventricular system reflects developmental deformation of neural tube Ventricles • Lateral ventricles – – – – Anterior horn Body Posterior horn Inferior horn • Third ventricle – Interventricular foramen (of Monro) – Cerebral aqueduct • Fourth ventricle Hindbrain Cerebellum • Motor coordination • Cognitive functions – temporal coordination – planning Hindbrain Medulla Oblongata • Anatomical and physiological junction of brain and spinal cord • Initiates respiration • Regulates heart rate • Origin of cranial nerves IX, X, XI, and XII Hindbrain Pons • Bridge between cerebellum and the rest of the brain • Origin of cranial nerves V, VI, VII, and VIII Midbrain • Least differentiated primary brain division • Contains cerebral aqueduct • Origin of cranial nerves III and IV (from dorsal surface) Midbrain Corpora Quadrigemina Superior Colliculi • Visual tracking • Coordination of head turning & eye movements • Inferior Colliculi • Sound location • Focusing attention to auditory stimuli Midbrain Substantia Nigra • Darkly pigmented (neuromelanin) nucleus • Produces dopamine • Parkinson’s disease— destruction of the cells of the substantia nigra Midbrain Substantia Nigra • In 1982, 6 drug addicts in Santa Clara, CA manifested with Parkinson’s disease (oldest patient was 41 yrs. old) • Each had injected synthetic heroin—MPPP (1methyl-4-phenyl-4-propionpiperidine), an analog of meperidine (Demerol) • The poorly synthesized designer drug contained a contaminant—MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6tetrahydropyridine), which kills the cells of the substantia nigra Midbrain Cerebral Peduncles • Major fiber bundles connecting forebrain to hindbrain • Contain descending axons of upper motor neurons from cortex Diencephalon Thalamus • Potato-shaped structure • Sensory relay for all afferents except olfaction Diencephalon Thalamus • Thalami form walls of 3rd ventricle Diencephalon Hypothalamus • 4 g neural structure • Connected to pituitary gland • Regulates: – Body temperature – Hunger – Thirst – Sexual activity – Goal-seeking behavior – Endocrine functions – Affective behavior – Visceral motor system Telencephalon • Caudate nucleus • Globus pallidus • Putamen Basal Ganglia • Modulate and integrate components of motor activity (and cognitive functions) • System depends on dopamine— affected by Parkinson’s disease Telencephalon Amygdala • Lies at tail of caudate nucleus but is not functionally part of the basal ganglia • Involved in the control of rage, aggression and sexuality Telencephalon Hippocampus • Composed of three-layered cortex (archicortex) • Fornix—major output pathway • Involved in the formation of new episodic memories Telencephalon Cerebrum • Composed of six-layered neocortex and deep white matter • Center of sensory input, motor output, and higher cognitive functions Cerebrum Primary Fissures • Longitudinal cerebral fissure Cerebrum Primary Fissures • Lateral fissure • Central sulcus Cerebrum Lobes • • • • Frontal Parietal Occipital Temporal Cerebrum Lobes • Insula Cerebrum White Matter • Corpus callosum— primary connection between left and right cerebral hemispheres Cerebrum White Matter • Internal capsule—primary pathway of fibers ascending to cortex from thalamus and descending from cortex to cerebral peduncles Motor Cortex • Primary motor cortex lies along the precentral gyrus in the frontal lobe • Motor output projects to contralateral side Motor Output Pathways • Voluntary movement—conducted to lower motor neurons via the pyramidal pathway Motor Output Pathways • Balance, posture, limb coordination information conducted by numerous extrapyramidal pathways Somatosensory Cortex • Primary somatosensory cortex lies along the postcentral gyrus in the parietal lobe • Representation of body is from contralateral side Somatosensory Cortex Somatosensory cortex (like motor cortex) is mapped somatotopically and proportionate to sensitivity, not size Other Sensory Cortices • Visual cortex— occipital lobe • Auditory cortex— superior portion of temporal lobe • Rhinal (olfactory) cortex—anterior medial temporal lobe • Gustatory (taste) cortex—inferior aspect of postcentral gyrus Language Areas • Occur only in the left hemisphere of most people (96 % of right-handed individuals, 72% of lefthanded individuals) • Broca’s area—motor speech center, in frontal lobe • Wernicke’s area—language interpretation center, in temporal & parietal lobes Cranial Nerves I. II. III. IV. V. VI. VII. VIII. IX. X. XI. XII. Olfactory Optic Occulomotor Trochlear Trigeminal Abucens Facial Vestibulocochlear Glossopharyngeal Vagus Spinal Accessory Hypoglossal Cranial Nerves Exit from Neurocranium I Cribriform plate Cranial Nerves Exit from Neurocranium II Optic canal Cranial Nerves Exit from Neurocranium III, IV, VI Superior orbital fissure Cranial Nerves Exit from Neurocranium V1 Superior orbital fissue V2 Foramen rotundum V3 Foramen ovale Cranial Nerves Exit from Neurocranium VII, VIII Internal auditory meatus Cranial Nerves Exit from Neurocranium IX, X, XI Jugular foramen Cranial Nerves Exit from Neurocranium XII Hypoglossal Canal Cranial Nerves Exit from Neurocranium Blood Supply • Vertebral arteries – Provide ~30% of blood supply to brain • Internal carotid arteries – Provide ~70% of blood supply to brain Circle of Willis Vertebral aa. basilar a. posterior cerebral aa. Internal carotid a. middle cerebral aa. anterior cerebral aa. Posterior communicating arteries connect posterior cerebral aa. and internal carotid aa. Anterior communicating ARTERY (sing.) connect anterior cerebral arteries Blood Supply Blood Supply Venous Drainage • Blood from the cortex drains to surface veins that drain into the dural venous sinuses Venous Drainage • Blood from the deep brain (thalamus, basal ganglia) drains into great cerebral vein (of Galen) before entering the straight sinus • Blood from the lower brainstem drains through the foramen magnum into the vertebral venous plexus Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) • Ruptured aneurysm—failure of a localized defect in the elasticity of a vessel • Arterial thrombus—blockage of an artery • Embolism—clot from elsewhere in the body that lodges in a cerebral artery • Hypertensive apoplexy—sudden effusion of blood into cerebral tissue due to rise in blood pressure