Presentation Slides - Global Foundation for Peroxisomal Disorders
advertisement

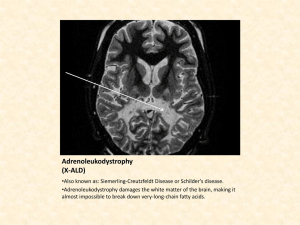
Newborn Screening for X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) and Other Peroxisomal Disorders: Measurement of 26:0 Lyso-PC by LC-MSMS Ann B. Moser 1, Walter C. Hubbard 2, and Gerald V. Raymond 3 1 Hugo W. Moser Research Institute, Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore, MD 2 Dept of Clinical Pharmacology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore , MD 3 Univ. MN, Dept. of Pediatric Neurology GFPD 7/27/13 LC-MSMS C26:0 lyso-PC Newborn Screening Test Identifies The Following Peroxisomal Disorders: X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) – genetically inherited; affects 1 in 21,000 births, more severe in males; 3 phenotypes: 1) Childhood Cerebral phenotype: 35-40% of subjects appear normal at birth and at age 4 to 8 years symptoms occur, rapidly progressive to death in childhood 2) Adrenomyeloneuropathy (AMN) phenotype starting in 20s slowly progressive spinal cord disease 3) severe Addison’s disease live to 4th - 5th decades with treatment Test also identifies: 80% of X-ALD Heterozygotes, Peroxisomal Biogenesis Disorders (PBDs) (Zellweger spectrum disorders) and Single Enzyme Defects of peroxisomal FA oxidation Primary Purpose of Newborn Screening Presymptomatic Diagnosis of Males with X-ALD in Order to: 1. Prevent overt adrenal insufficiency 2. Reduce the risk for childhood phenotype with LO diet 3. Improve prognosis of cerebral ALD by facilitating early hematopoietic stem cell and gene transplants 4. Improve success of future therapies Secondary Purpose of Newborn Screening Identification of 80% of X-ALD Heterozygotes in order to: 1. Provide family screening for male X-ALD relatives. Diagnosis of PBD/SED Patients in Order to: 1. Prevent diagnostic odyssey, provide genetic counseling supportive therapy. and early Authentic Standards H2-C-O-C-(CH2)24 -CH3 HO-C-H O + H2-C-O-P-O-CH2-CH2-N(CH3)3 O - 26:0-Lys o-PC, M W 635.5 Elevated in blood spots X-ALD * = 2H **** H2-C-O-C-(CH2)24 -CH3 HO-C-H O + H2-C-O-P-O-CH2-CH2-N(CH3)3 O 2H - 4-26:0-Lys o-PC, M W Internal Standard 639.5 MS/MS Fragmentation of 26:0 Lyso-PC 26:0-Lys o-PC, M W 635.5 H2-C-O-C-(CH2)24 -CH3 HO-C-H 103 O + H2-C-O-P-O-CH2-CH2-N(CH3)3 OH 2H 4-26:0-Lys o-PC, M W = 2H * **** H2-C-O-C-(CH2)24 -CH3 HO-C-H 103 O + H2-C-O-P-O-CH2-CH2-N(CH3)3 OH 183 M S/M S: m /z 636 > 184 m /z 636 > 104 639.5 183 M S/M S: m /z 640 > 184 m /z 640 > 104 Heel Stick from newborn Methods 1 • Neonatal heel stick blood or Postnatal venous blood on filter paper cards • Stored @ -20o C. until sampling with a 1/8” punch into test tube or 96 well plates • Add a 10ul of purified water • Add 150ul methanol containing 10.56pmoles deuterium labeled internal standard, D-4 -26:0 LysoPC. Mix gently for 1 hour at room temp. • Centrifuge and transfer supernatant to glass injection vials with 100ul inserts for LC-MSMS, Inject 5ul API4000 LC-MSMS, 10ul API3200 LC-MSMS Methods 2 Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectroscopy Electrospray ionization (ESI) LC-MS/MS MRM Analysis: Instruments: Applied Biosystems API 4000 or 3200 – MRM transitions: 1-acyl-lyso-PCs =[ M+H]+ >m/z 104, 1-alkyllyso-PCs =[ M+H]+ >m/z 104 – Reversed phase column: C8-MS, Waters XTerra, 3.5u particle, 4.6x50 mm (7min) or 1.0x50mm (2 min isocratic) analyses. – HPLC Solvents: MPA H20:CH3CN:HCOOH 54.5:45:0.5 MPB HCOOH:CH3CN:CHCl3 0.5:90:10 (2mMHCOONH4) – Flow: 0.5ml/minute for 4.6x50mm column 75% MPA to 0% at 6 min; – .18ml/minute for 1.0x50mm column 50% MPA and MPB isocratic for 2 min, for high throughput analysis. – Optimized: declustering potential (DP), collision energy (CE, collision exit potential (CXP) API 4000 LC-MSMS High throughput analysis For accurate quantitation, need to calculate C26:0-lyso-PC based on retention time as well as MW/MRM. This newborn DBS C26:0-lysoPC is within normal range. Table 1: Summary of LC-MS/MS Data Obtained From Newborn Blood Spots: 26:0-Lyso-PC Levels Expressed as Picomoles per 1/8” Blood Spot Normal newborns X-ALD/PBD newborns (retrieved from CA and MI) Mean Standard Deviation Range Number of Subjects 0.329 6.53 0.123 1.62 0.13 – 0.75 4000 4.69 – 9.71 16 Newborn Screening for ALD and PBD: Together with the Maryland State Screening Lab, we performed a prospective study to offer optional testing for ALD / PBD to parents of 5000 newborns born in 3 hospitals in the Baltimore area. We have finished analyzing the consented newborn samples with no positives. We hope to start ALD newborn screening in Maryland in November 2014. Newborn Screening for ALD and 6 lysosomal disorders, a combined highthroughput assay: Drs. Silvia Tortorelli and Dietrich Matern of the Mayo Biochemical Genetics Laboratory and Dr. Fred Lorey of the State of CA Newborn Screening Laboratory are screening 100,000 newborn blood spots from CA using a combined assay. To date they have completed the anonymous screening on 60,000 newborns and have identified positives for the ALD screening that will be confirmed by analysis of mutations in the ALD gene and other genetic and biochemical tests if negative for ALD. By mid-September 2013 the screening of 100,000 newborn blood spot samples is expected to be completed. Prior to the September 13, 2012 SACHDNC ( the Secretary’s Advisory Committee on Heritable Disorders in Newborns & Children, section 1111 of Public Health, Newborn Screening Saves Lives Act 0f 2008) meeting in Washington, DC, Drs. Charlie Peters and Amber Salzman organized and sent the documents supporting the petition to add ALD to the Recommended Uniform Screening Panel (RUSP) for all state newborn screening labs. The lobbyists who were allowed to speak at the meeting in support of ALD newborn screening were: Dr. Gerald Raymond, and Ann Moser from KKI; Spencer Barsh ,son of Amber Salzman, The Stop ALD Foundation; and Taylor Kane, daughter of Diane Kane, Run 4 ALD. Despite the eloquent speeches of the lobbyists and the compelling data showing that the newborn screening test method is valid and that ALD newborn screening would save lives of ALD boys if identified before symptoms start, the advisory committee decided to wait for the completion of Mayo Biochemical Genetics Lab screening of 100,000 newborns from CA. Importance of Lobbying for ALD newborn screening by ALD family support groups!! Lobbying in NY, NJ, CT, MD have resulted in legislative approval to add ALD newborn screening. Lobbying continues in TX , IL and MA. We Did It! Bill Requiring ALD Newborn Screening Passed in CT 7/3/13 Brian's Hope <jeankelley=brianshope.org@createsend4.com> We Did It! Our bill (Brian’s hope) requiring ALD newborn screening passed in CT. Governor Dannel Malloy signed it into law. Brian had BMT 18 years ago shortly after ALD was diagnosed due to brain disease. Brian Kelly’s 25th Birthday, July 3. 2013 Update 7/20/13 by Ann B Moser • *Mayo Medical Laboratory continues screening of 100,000 NBS from CA with 60,000 screened to date. Report on validation of 2 ALD positives will be given to SACHDNC for the September 2013 meeting. • *NY state newborn screening lab will add ALD to their newborn screening panel in January 2014. (200,000 births/yr) • *The states of CT and NJ legislatures have voted to add ALD to their newborn screening panels. • *MD will add ALD newborn screening after the state lab moves into their new building in the spring of 2014, provided funds are available. We are applying for a grant to support ALD newborn screening in MD. Acknowledgements Steven Steinberg, Anita Liu, Richard O. Jones – Kennedy Krieger Institute Fred Lorey – Genetic Disease Screening Program, California Susan R. Panny, Fizza Majid –Newborn Screening Program Maryland Dept. Mental Health/Hygiene Robert F. Vogt, Jr., Christopher Haines – CDC, Newborn Screening Branch Silvia Tortorelli, Dietrich Matern – Mayo Biomedical Genetics Laboratory Baltimore Hospitals: Johns Hopkins, Greater Baltimore Medical Center, Frederick Memorial Funding: United Leukodystrophy Foundation, European Leukodystrophy Association, Myelin Project, Run 4 ALD, Brian’s Hope, Stop ALD Foundation NIH: Newborn Screening Grant : HD057136 NIH: Instrumentation API4000 1-S10 RR16798 (WCH)