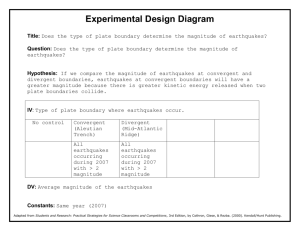
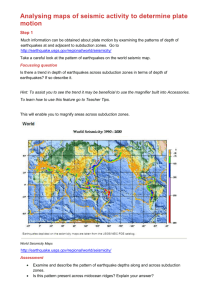
Document
advertisement

Exploring Earthquakes By Melanie Brady, Elly Glenn, and Carleigh Wellenreiter How many original “supercontinents” where there? There was only one, it is Pangaea Pangaea was a huge landmass containing all of our continents we know today 225 million years ago the continents all fit together like a puzzle, and have moved apart. There are twelve major unconnected landmasses. What are the ones that affect the USA The answer is the North American Plate, Juan De Fuca plate, and the Pacific plate. If you count Puerto Rico as the USA then the Caribbean plate is also involved. Why does California have so many earthquakes but Florida doesn't? The reason why California has more earthquakes than Florida is because California lies on the junction plate of the Pacific plate and the North American plates. Why does California have so many earthquakes but Florida doesn't? (continued) When they move past each other, it causes earthquakes. Florida is in the middle of the North American plate, that is why it doesn't move as much as California. What hazard zone is Illinois in? Illinois is mostly in the hazard zone of 2-4 part of Illinois is in the 4-8 hazard zone What is considered the most destructive earthquake in history In Shaanxi, China in 1556 830,000 killed Magnitude was 8.0 What are the three basic plate boundaries ? The three basic types of plate boundaries. The first is the convergent plate boundary, these ones move toward each other and collide at some point The second boundary is a divergent boundary, these boundaries move away from each other. The last is a transform boundary, these boundaries move past each other What is a tsunami? How fast can they travel? A tsunami is an underwater eruption or earth quake. They can travel up to 500 miles per hour The word tsunami comes from Japan, it means harbor wave. What are the two types of energy waves created by an earthquake? How do they differ? The first wave is called a Primary wave The second wave is the Secondary wave The Primary waves travel through solids, liquids, and gases. The Secondary wave can only travel through solids A primary wave works like this slinky Which of those two waves is quicker The Secondary waves are slower therefore the Primary waves are quicker How much more energy is released by a 7.2 earthquake than a 6.2 earthquake It releases 10 times more ground power but releases 32 times more energy What applications does seismology have besides measuring the magnitude and location of earthquakes By combining seismograms from many earthquakes recorded all over the world, an image of the interior at the earth can be created Where did most of the earthquakes happen last week? They where located in Chile, Haiti, and California Can scientist predict earthquake? Scientists can predict where major earthquakes are likely to occur, however, based on the movement of the plates in the Earth and the location of fault zones. They also can make general guesses about when earthquakes might occur in a certain area, by looking at the history of earthquakes in the region and detecting where pressure is building along fault lines. How do scientists know where earthquakes actually occur? Using a ratio based on Primary and Secondary waves scientists can calculate the distance between any point on the earths surface. They do this by using seismographs. Video of an earthquake