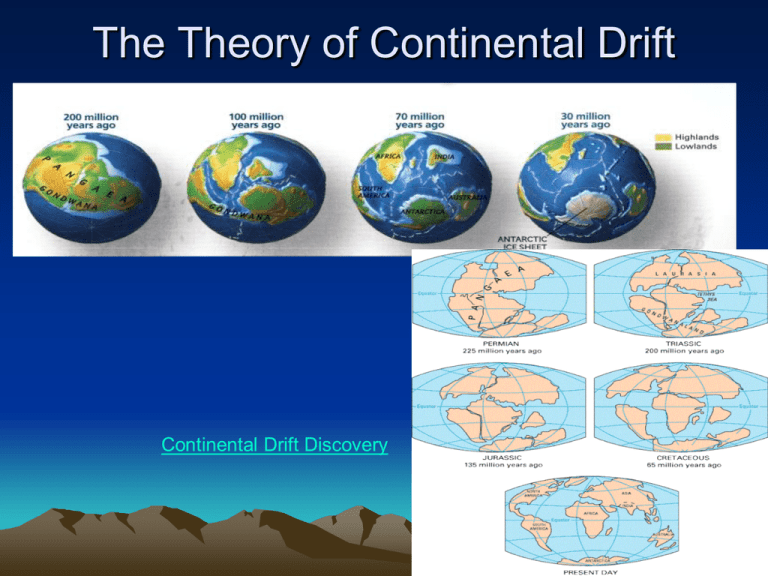
The Theory of Continental Drift
Continental Drift Discovery
Bell Ringer 2.10.14
1. Pangaea was:
a.) A time period when the dinosaurs lived
b.) A unified ocean
c.) A super-continent
2. TRUE or FALSE: Plates below us, and all
over the world beneath Earth’s crust are still
moving
Advanced: Bell Ringer 2.11.14
1. Plates move because:
a.) Heat in the earth’s core provides energy
for movement
b.) earthquakes push & move plates
c.) Tides push and move plates
2. TRUE or FALSE: Pangaea was the 1st
super continent to form on earth
The World
ALFRED WEGENER
THEORY OF CONTINENTAL
DRIFT
Found evidence for
PANGAEA and
proposed the theory of
continental drift.
Continental Drift
(p95 red book, 182 in Sciencesaurus)
• Theory that continents were
once part of a single
landmass that broke apart
and have moved to their
present locations.
• can drift apart from one
another and have done so in
the past
For more information about what the continents looked like throughout the Earth’s
History go to:
htttp://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/geology/anim1.html
Pangaea
Pangaea is the name given to the single
landmass that was present 200 million
years ago
Can you name the continents in Pangaea?
http://kids.earth.nasa.gov/archive/pangaea/Pangaea_game.html
WEGENER’S EVIDENCE
Fossil Evidence
•fossils are remains
of living things that
lived long ago.
•similar fossils have
been discovered in
matching coastlines
on different
continents.
WEGENER’S EVIDENCE
WEGENER’S EVIDENCE
• Mountains
– Some mountain ranges on different continents
seem to match.
• Ex: ranges in Canada match Norway and Sweden
• Ex: Appalachian Mtn. match UK mtn
•Mountain Evidence
•some mountain ranges on different
continents seem to match.
•mountain range in eastern Canada
seems to match one found in Norway
and Sweden.
•Rock Evidence
•The age and kind of rocks and minerals
along the edge of one continent match
rocks and minerals along the edge of
another continent.
WEGENER’S EVIDENCE
• Climatic evidence such as glaciers in
areas that are now close to the Equator
Evidence of Continental Drift
Satellites used to
measure the
movement of
continents
• Laser Geodynamics
Satellite (LAGEOS)
The Plates Move…
So what now?
Which way?
- look at this image – this is the way the
plates are moving.
• 50 million years- what they predict the world will
look like
THEORY OF PLATE
TECTONICS
• THEORY STATES THAT EARTH’S
OUTER LAYER (LITHOSPHERE) IS
DIVIDED INTO PLATES THAT ARE IN
CONSTANT SLOW MOTION MOVING
AROUND ON TOP OF THE
ASTHENOSPHERE
Theory of Plate Tectonics
• Theory that pieces of lithosphere move
around on top of the asthenosphere
Layers of the Earth
• If we could take a chunk out of the
Earth, we would see that it is made up
of different layers.
Layers of the Earth
• Earth is made up of 3 main layers
– Crust
– Mantle
– Core
– Each layer has it’s own individual composition
and physical properties.
Physical Properties and
Composition
• Composition= what it’s made of
• Physical properties= characteristic that is
unique and helps to identify the substance
(temp, size, shape, color)
• Example: Chocolate Chip Cookies
• Composition- flour, eggs, sugar, chocolate
chips, baking powder, butter
• Properties- round, rough, sweet, tan and black,
hot, lumpy,
Layers of the Earth(p90)
• CRUST
– Physical Properties:
• outermost layer
• thinnest layer (5-70km thick)
• Surface temperature
• 1% of Earth’s mass
• where we live
• touches the atmosphere
– Composition:
• consists of loose rocks
& soil
Crust
• Very
thin
2 Types of Crust
• Continental Crust:
dry land, granite
less dense
Oceanic Crust:
ocean floor,
Basalt, thinner
than cont. crust
but more dense
Layers of the Earth
• MANTLE
– Physical Properties:
• thickest layer (2900km thick)
• 1600-4000 F
• 66% of earth’s mass
• flowing
– Composition:
• Molten rock
–Magma
Layers of the Earth
• CORE
– Physical properties:
• HOT! 4000-8000 F
• Very dense
• High pressure
• 4000 miles from surface
• 33% of Earth’s mass
• About the same size as
Mars
– Composition:
• Iron and Nickel (metals)
What have you noticed about
temperature and pressure?
• As you get deeper inside the Earth,
temperature Increases
• As you get deeper inside the Earth,
pressure Increases
Layers of the Earth
• The 3 main layers
of the Earth can be
divided further by
the way they “act”
within the Earth
and by their
different physical
properties.
Lithosphere
Crust and upper Mantle
• outermost layer –
includes crust and
upper mantle
• rigid
• divided into
pieces or
tectonic plates
• Rocks and soil
Asthenosphere
Middle Mantle
• composed of solid
flowing rock
• layer on which pieces of
lithosphere move on top
(solid rock that flows)
– Think of
it like caramel
Mesosphere
Bottom Mantle
• strong, lower
part of the
mantle
• layer between
asthenosphere
and core
The Core
Outer and Inner
• The core is divided into two parts
– Outer Core:
• Liquid iron and nickel that’s spinning
– Inner Core:
• Solid iron and nickel
• Solid because of all the pressure of the rest of the
Earth surrounding it.
How do we know?
• Seismic waves
produced by
earthquakes
travel at
different
speeds through
solid rock
and liquids
Layers of the Earth
How do the plates move? P.3
A.) CONVECTION CURRENTS
• This is where Hot material from deep
within the Earth rises (add this) while
cooler material near the surface sinks
Convection currents
The
asthenosphere
consists of
solid rock that
is flowing. But
it’s not all
flowing in the
same
direction.
How do we know?
B.) Sea-floor spreading
This is where new ocean
floor is created as two
lithospheric plates
pull away from
one another.
These plate movements can
cause…
1.) volcanoes
2.) earth quakes
3.) Mountain ranges (to form)
4.) Deep ocean trenches (to form)
Seafloor spreading
So the plates move.
Now What?
•As the plates move,
they produce changes
in Earth’s surface,
including volcanoes,
earthquakes, mountain
ranges, and deepocean trenches.
Plate Boundaries
• The edges of
different pieces of
The lithosphere
meet at lines
called plate
boundaries
3 types of plate boundaries:
1.) Convergent
2.) Divergent
3.) Transform
3 Types of Plate Boundaries
Divergent
Convergent
Transform
DIVERGENT BOUNDARY
= WHEN TWO PLATES ARE MOVING
AWAY FROM EACH OTHER
MAGMA RISES AND SPILLS OUT FROM
UNDER THE PLATES, MAKING NEW
CRUST
Ex.) rift valley OR trench
3 Types of Boundaries
Divergent boundary= two plates move apart
• Magma rises and creates new crust or
seafloor
Ex:
sea-floor
spreading or a
rift
Boundary animation
Divergent Boundaries
© All Rights Reserved.
Diverging Africa
edge of the Eurasian continent/plate where it drops into a rift valley
which lies between the former and the North American tectonic plate.
CONVERGENT BOUNDARY
= when one plate is pushed under
(subducts) another plate. The plate that is
pushed under is then recycled back into the
asthenosphere.
This is when the plates converge
3 Types of Boundaries
• Convergent= when two tectonic
plates push into one another.
Convergent Boundaries
• Continental vs. Continental
• Continental vs. Oceanic
• Oceanic vs. Oceanic
Continental vs. Continental
•When two continental
crustal plates collide,
the continents buckle
upward and form
mountains.
Himalayas- Asia
Himalayas- Asia
Continental vs. Oceanic
•The oceanic plate
slides under the
continental plate.
•The continental crust
crumbles and forms
new mountains or volcanoes.
Subduction Zone
Oceanic vs. Continental
• Ex: Andes mtn in S.
America
Cascade Mtns. in N.
America- Mt. St.
Helens
• The oceanic plate slides under the
continental plate.
(Why doesn’t the continental plate slide
under the oceanic crust?)
• This causes continental crust to crumble
and forms new mountains or volcano
Oceanic vs. Oceanic
•Two oceanic plates
collide, one of the
oceanic plates slides
under the other.
•also called a
subduction zone
Oceanic vs.
Oceanic Hawaiian
Islands
Transform boundary
• When two tectonic plates slide past each
other horizontally
Produces?
Earthquakes
San
Andreas
Fault
New Madrid Fault
WEGENER’S EVIDENCE
Continents
“fit together”
like puzzle
pieces
Bell Ringer Monday, 2/17/14
Pick up a convection lab guide, and answer
pre-lab questions 1 - 3
CONVECTION LAB
1. WHAT QUESTION ARE WE TRYING TO
ANSWER TODAY?
1. WHAT QUESTION ARE WE TRYING TO
ANSWER TODAY?
How do the tectonic plates move?
2. WHAT DO WE ALREADY KNOW ABOUT
HOW THE PLATES MOVE?
CONVECTION LAB
2. WHAT DO WE ALREADY KNOW ABOUT
HOW THE PLATES MOVE?
• HEAT FROM THE EARTH’S CORE
PROVIDES THE ENERGY FOR THE
PLATES TO MOVE
• THE PLATES ARE ALWAYS MOVING
3. So, how is heat from the earth’s core
getting to where the tectonic plates are?
Convection Lab
3. So, how is heat from the earth’s core
getting to where the tectonic plates are?
It is transferred through touching
(conduction)!!!
3. HOW is the heat transferred from the
earth’s core to the plates? Through
CONDUCTION (touching) and
CONVECTION (moving)
Convection is the transfer of heat by the
circulation or movement of the heated parts
of a liquid or gas. HOT AIR RISES, COLD
• Convection is the transfer of heat by
the circulation or movement of the
heated parts of a liquid or gas. HOT
AIR RISES, COLD AIR SINKS
How do the plates move?
This is where hot
material from deep within the Earth rises
while cooler material near the surface sinks
5.) CONVECTION CURRENTS
Convection Candle Currents
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m_lqsyr
Opvc
• Slide 75: When a candle burns,
CONVECTION CURRENTS- rise above
the flame. We are not able to see them,
however, without special help like the light
from a projector. Convection is the
transfer of heat by the MOVEMENT of the
heated parts of a liquid or gas.
• Slide 76: When air is heated, its
molecules actually bump into each other,
spreading them farther apart and creating
MOVEMENT. Think about magma in the
asthenosphere: When magma is heated
by touching the hot core below it, the
magma will RISE.
Slide 77: After the magma cools, it will sink
back down again to the core, just like the
cold water from your ice cube sinks to the
bottom of your cup. The core will again heat
the magma, and the magma will again rise.
The up and down, rising and sinking motions
of the magma causes the tectonic plates to
move.
Complete your diagram:
Convection in the mantle:
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p0dWF
_3PYh4
• BGJHS Mission Statement: At BGJHS, all
students are empowered to become
respectful and responsible 21st century
learners and leaders.










