Living in an active zone
advertisement

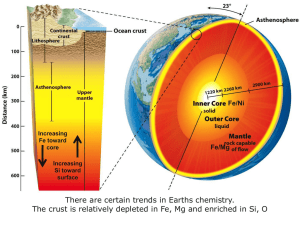
Living in an active zone Revision lesson Why are plate margins hazardous? • What are the plate margins and how do plate movement generate a variety of landforms? • What are the primary and secondary hazards associated with volcanoes and earthquake zones? • Why do people continue to live in hazardous zones? The structure of the earth….. • THINK ABOUT WHAT THIS IMAGE HAS TO DO WITH THE EARTHS STRUCTURE? • YOU HAVE ONE MINUTE TO SEE IF YOU CAN COME UP You will be selected at WITH AN ANSWER random to share your answer with the class!! • YOU MUST USE THE WORDS ; Core Mantle Crust Plates and Plate Boundaries 3 7 W Y Z 5 1 8 X 6 2 4 Test yourself – Name the plates 1 – 8 + Type of margins W-Z Destructive plate boundaries • Think about the direction that these plates move in….one of you will be selected at random to come to the front of the class to mime the motion of a destructive plate boundary! • No helping • No shouting out What can you remember? Match the letter with the number! 2 1 A Oceanic crust 3 4 B Continental crust c. Volcanic arc d. Trench What can you remember? Match the letter with the number! A Oceanic crust B Continental crust c. Volcanic arc d. Trench What happens at the destructive margin? 1. As the pressure is released we get earthquakes. 2. Where plates move together, the denser oceanic crust slips down into the mantle under the continental crust. 3. An oceanic trench is formed on the sea bed. 4. Molten magma is forced to the surface where we get volcanoes eventually building a mountain range. 5. This movement builds up a large amount of pressure between the two plates. 6. The oceanic plate melts. This is known as the zone of subduction. Activity Put these in the correct order ! Answers: Can you remember what case study we used for this? The Andes 2 6 3 5 4 1 Constructive plate boundaries • Think about the direction that these plates move in….one of you will be selected at random to come to the front of the class to mime the motion of a Constructive plate boundary! • No helping • No shouting out What can you remember? Match the letter with the number! 1 2 3 4 A. Sea floor spreading c. Magma b. Midoceanic rige d. Oceanic crust Strato and shield Volcano A 1. layers of ash and lava 2. Constructive margin Strato Shield 3. Destructive margin 4. High summit 5. Low height B 6. Steep gradient 7. Gentle slopes 8. Wide profile 9. Explosive eruptions 10. Runny lava – spreads easily Can you remember what case study we used for this? Iceland Primary or secondary hazards of a volcanic eruption? A. Primary B. Secondary 7. tsunamis 1. Lava flow 2. lahars 3. landslides 4. Pyroclastic flow 5. Ash and tephra falls 6. Volcanic gases Primary or secondary hazards of a volcanic eruption…answers A. Primary B. Secondary 7. tsunamis 1. Lava flow 2. lahars 3. landslides 4. Pyroclastic flow 5. Ash and tephra falls 6. Volcanic gases Primary or secondary hazards of an earthquake? A. Primary 1. Ground shaking 3. tsunami B. Secondary 2. landslides 4. Soil liquifaction Primary or secondary hazards of an earthquake? A. Primary 1. Ground shaking 3. tsunami B. Secondary 2. landslides 4. Soil liquifaction Why do people live in hazardous zones? You have 2 minutes to come up with as many reasons as possible to explain why people live in risky areas! GO! Fertile soil Geothermal energy No choice Unwillingness to move Tourism How can the risks associated with volcanic and earthquake zones be reduced? • How are volcanoes monitored and what does this tell us about their state? • How might the effects of volcano eruptions and earthquakes be reduced in MEDCs and LEDCs? Answers: Short term or long term responses? 1. T True or false? 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. F F TAttempt the paper ‘true or false’ quiz F F T F F T T F Super volcanoes! • Watch the video clip (in lesson folder) • What might happen in the future – Yellowstone, USA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v =1Vn6kxfD3Ek&feature=related